|
Turritopsis Rubra
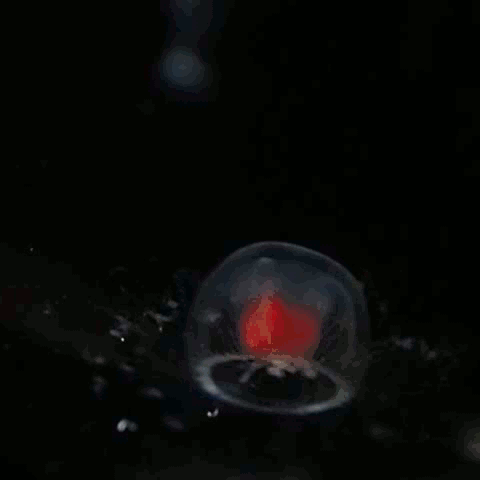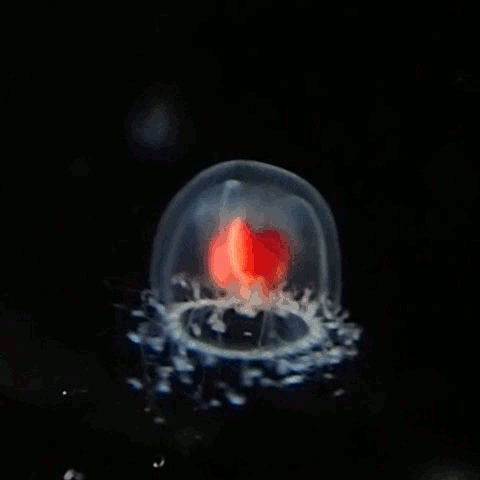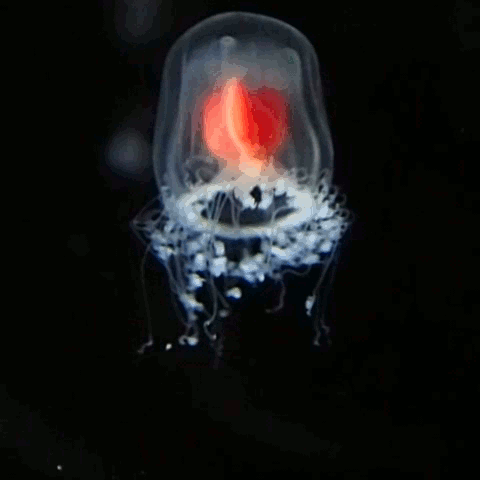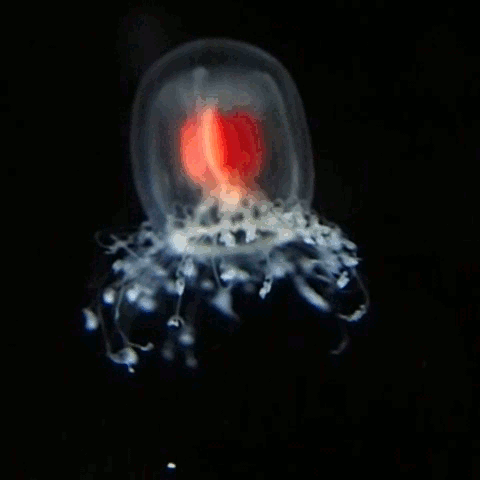
''Turritopsis rubra,'' sometimes known as the crimson jelly, is a species of hydrozoan of the family Oceaniidae. Medusae of such species are informally called jellyfish. Description Adult medusae are energetic swimmers. They are 3–7 mm in diameter, with a bell-shaped, transparent umbrella. The margin of the umbrella has a fringe of up to 120 closely-spaced, long, thin tentacles which coil up or extend out in strings to catch small planktonic animals to feed on. The tentacles have adaxial ocelli. The bright red or red-orange stomach and the gonads can be seen. They cannot sting humans as their stings are too small. @ 10:36 Life cycle As a hydrozoan, ''T. rubra'' has two distinct stages in their life, a polyp stage and a medusa stage. Polyps grow in benthic colonies and asexually reproduce to create medusae, which are free-swimming, dieocious, and reproduce sexually. Female medusae brood their larvae, sometimes up to the primary polyp stage. The larvae are small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turritopsis Rubra Swimming
''Turritopsis'' is a genus of hydrozoans in the family Oceaniidae. Species According to the ''World Register of Marine Species'', this genus includes the following species: * ''Turritopsis chevalense'' – ''species inquirenda'' * '' Turritopsis dohrnii'' also known as the " Benjamin Button jellyfish", or the "immortal jellyfish". It can reverse its life cycle and transform itself back to a polyp. * ''Turritopsis fascicularis'' * ''Turritopsis lata'' * ''Turritopsis minor'' * ''Turritopsis nutricula'' (several separate species, including the "immortal jellyfish", were formerly classified as ''T. nutricula'') * ''Turritopsis pacifica'' * ''Turritopsis pleurostoma'' – ''species inquirenda'' * ''Turritopsis polycirrha'' * ''Turritopsis rubra ''Turritopsis rubra,'' sometimes known as the crimson jelly, is a species of hydrozoan of the family Oceaniidae. Medusae of such species are informally called jellyfish. Description Adult medusae are energetic swimmers. They a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detritus
In biology, detritus () is dead particulate organic material, as distinguished from dissolved organic material. Detritus typically includes the bodies or fragments of bodies of dead organisms, and fecal material. Detritus typically hosts communities of microorganisms that colonize and decompose (i.e. remineralize) it. In terrestrial ecosystems it is present as leaf litter and other organic matter that is intermixed with soil, which is denominated "soil organic matter". The detritus of aquatic ecosystems is organic material that is suspended in the water and accumulates in depositions on the floor of the body of water; when this floor is a seabed, such a deposition is denominated " marine snow". Theory The corpses of dead plants or animals, material derived from animal tissues (e.g. molted skin), and fecal matter gradually lose their form due to physical processes and the action of decomposers, including grazers, bacteria, and fungi. Decomposition, the process by whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turritopsis Dohrnii
''Turritopsis dohrnii'', also known as the immortal jellyfish, is a species of small, biologically immortal jellyfish found worldwide in temperate to tropic waters. It is one of the few known cases of animals capable of reverting completely to a sexually immature, colonial stage after having reached sexual maturity as a solitary individual. Others include the jellyfish ''Laodicea undulata'' and species of the genus '' Aurelia''. Like most other hydrozoans, ''T. dohrnii'' begin their lives as tiny, free-swimming larvae known as planulae. As a planula settles down, it gives rise to a colony of polyps that are attached to the sea floor. All the polyps and jellyfish arising from a single planula are genetically identical clones. The polyps form into an extensively branched form, which is not commonly seen in most jellyfish. Jellyfish, also known as medusae, then bud off these polyps and continue their life in a free-swimming form, eventually becoming sexually mature. When sexually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonochorism
In biology, gonochorism is a sexual system where there are only two sexes and each individual organism is either male or female. The term gonochorism is usually applied in animal species, the vast majority of which are gonochoric. Gonochorism contrasts with simultaneous hermaphroditism but it may be hard to tell if a species is gonochoric or sequentially hermaphroditic. (e.g. Parrotfish, '' Patella ferruginea''). However, in gonochoric species individuals remain either male or female throughout their lives. Species that reproduce by thelytokous parthenogenesis and do not have males can still be classified as gonochoric. Terminology The term is derived from Greek (''gone'', generation) + (''chorizein,'' to separate). The term gonochorism originally came from German gonochorismus. Gonochorism is also referred to as unisexualism or gonochory. Evolution Gonochorism has evolved independently multiple times and is very evolutionary stable in animals. Its stability and ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turritopsis Polycirrha
''Turritopsis'' is a genus of hydrozoans in the family Oceaniidae. Species According to the '' World Register of Marine Species'', this genus includes the following species: * '' Turritopsis chevalense'' – ''species inquirenda In biological classification, a ''species inquirenda'' is a species of doubtful identity requiring further investigation. The use of the term in English-language biological literature dates back to at least the early nineteenth century. The term ...'' * '' Turritopsis dohrnii'' also known as the " Benjamin Button jellyfish", or the "immortal jellyfish". It can reverse its life cycle and transform itself back to a polyp. * '' Turritopsis fascicularis'' * '' Turritopsis lata'' * '' Turritopsis minor'' * '' Turritopsis nutricula'' (several separate species, including the "immortal jellyfish", were formerly classified as ''T. nutricula'') * '' Turritopsis pacifica'' * '' Turritopsis pleurostoma'' – ''species inquirenda'' * '' Turritopsis poly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turritopsis Nutricula
''Turritopsis nutricula'' is a small hydrozoan that once reaching adulthood, can transfer its cells back to childhood. This adaptive trait likely evolved in order to extend the life of the individual. Several different species of the genus ''Turritopsis'' were formerly classified as ''T. nutricula'', including the "immortal jellyfish" which is now classified as '' T. dohrnii''. Life cycle Hydrozoans have two distinct stages in their life, a polyp stage and a medusa stage. The polyp stage is benthic, with the cells forming colonies, while the medusa stage is a singular, planktonic organism. Generally in hydrozoa the medusa develops from the asexual budding of the polyp and the polyp results from sexual reproduction of medusae. In ''T. nutricula'', planktonic medusa have the capability to bud polyps or medusae which also have the ability to spawn new medusae. Several nominal species have been described for this genus, but most of them had been synonymized and attributed to on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turritopsis
''Turritopsis'' is a genus of hydrozoans in the family Oceaniidae. Species According to the ''World Register of Marine Species'', this genus includes the following species: * '' Turritopsis chevalense'' – ''species inquirenda'' * '' Turritopsis dohrnii'' also known as the " Benjamin Button jellyfish", or the "immortal jellyfish". It can reverse its life cycle and transform itself back to a polyp. * ''Turritopsis fascicularis'' * ''Turritopsis lata'' * ''Turritopsis minor'' * ''Turritopsis nutricula'' (several separate species, including the "immortal jellyfish", were formerly classified as ''T. nutricula'') * ''Turritopsis pacifica'' * ''Turritopsis pleurostoma'' – ''species inquirenda'' * ''Turritopsis polycirrha ''Turritopsis'' is a genus of hydrozoans in the family Oceaniidae. Species According to the '' World Register of Marine Species'', this genus includes the following species: * '' Turritopsis chevalense'' – ''species inquirenda In biologi ...'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
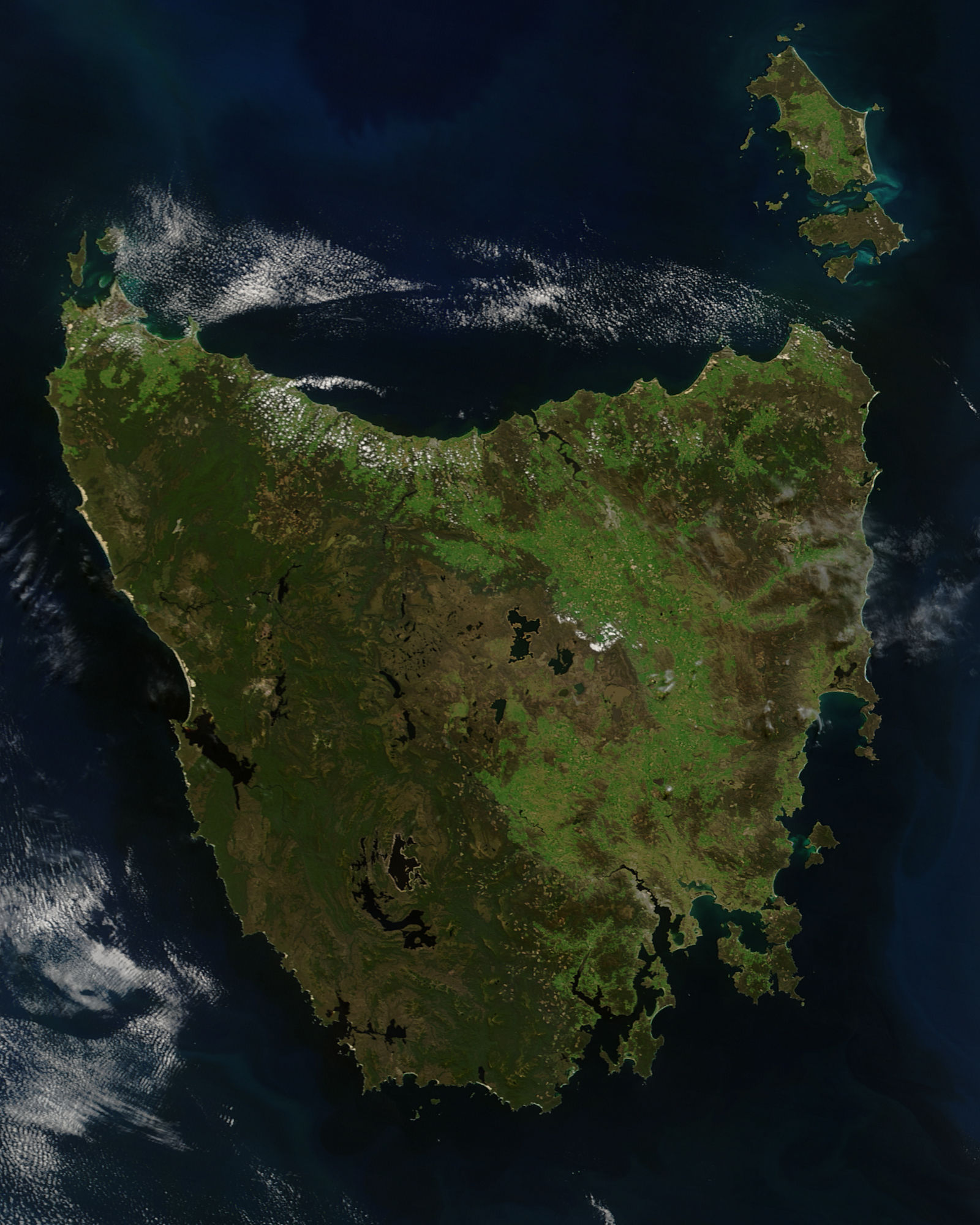
Tasmania
) , nickname = , image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of Tasmania , established_title2 = Federation , established_date2 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Abel Tasman , demonym = , capital = Hobart , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center = 29 local government areas , admin_center_type = Administration , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign ''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'. The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ... country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with deserts in the centre, tropical Forests of Australia, rainforests in the north-east, and List of mountains in Australia, mountain ranges in the south-east. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south east Asia approx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the List of island countries, sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's Capital of New Zealand, capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perisarc
Hydrozoa (hydrozoans; ) are a taxonomic class of individually very small, predatory animals, some solitary and some colonial, most of which inhabit saline water. The colonies of the colonial species can be large, and in some cases the specialized individual animals cannot survive outside the colony. A few genera within this class live in freshwater habitats. Hydrozoans are related to jellyfish and corals and belong to the phylum Cnidaria. Some examples of hydrozoans are the freshwater jelly ('' Craspedacusta sowerbyi''), freshwater polyps (''Hydra''), '' Obelia'', Portuguese man o' war (''Physalia physalis''), chondrophores (Porpitidae), " air fern" (''Sertularia argentea''), and pink-hearted hydroids ('' Tubularia''). Anatomy Most hydrozoan species include both a polypoid and a medusoid stage in their lifecycles, although a number of them have only one or the other. For example, ''Hydra'' has no medusoid stage, while '' Liriope'' lacks the polypoid stage. Polyps The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrozoa
Hydrozoa (hydrozoans; ) are a taxonomic class of individually very small, predatory animals, some solitary and some colonial, most of which inhabit saline water. The colonies of the colonial species can be large, and in some cases the specialized individual animals cannot survive outside the colony. A few genera within this class live in freshwater habitats. Hydrozoans are related to jellyfish and corals and belong to the phylum Cnidaria. Some examples of hydrozoans are the freshwater jelly ('' Craspedacusta sowerbyi''), freshwater polyps (''Hydra''), '' Obelia'', Portuguese man o' war (''Physalia physalis''), chondrophores (Porpitidae), " air fern" (''Sertularia argentea''), and pink-hearted hydroids ('' Tubularia''). Anatomy Most hydrozoan species include both a polypoid and a medusoid stage in their lifecycles, although a number of them have only one or the other. For example, ''Hydra'' has no medusoid stage, while '' Liriope'' lacks the polypoid stage. Polyps The hydro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)