|
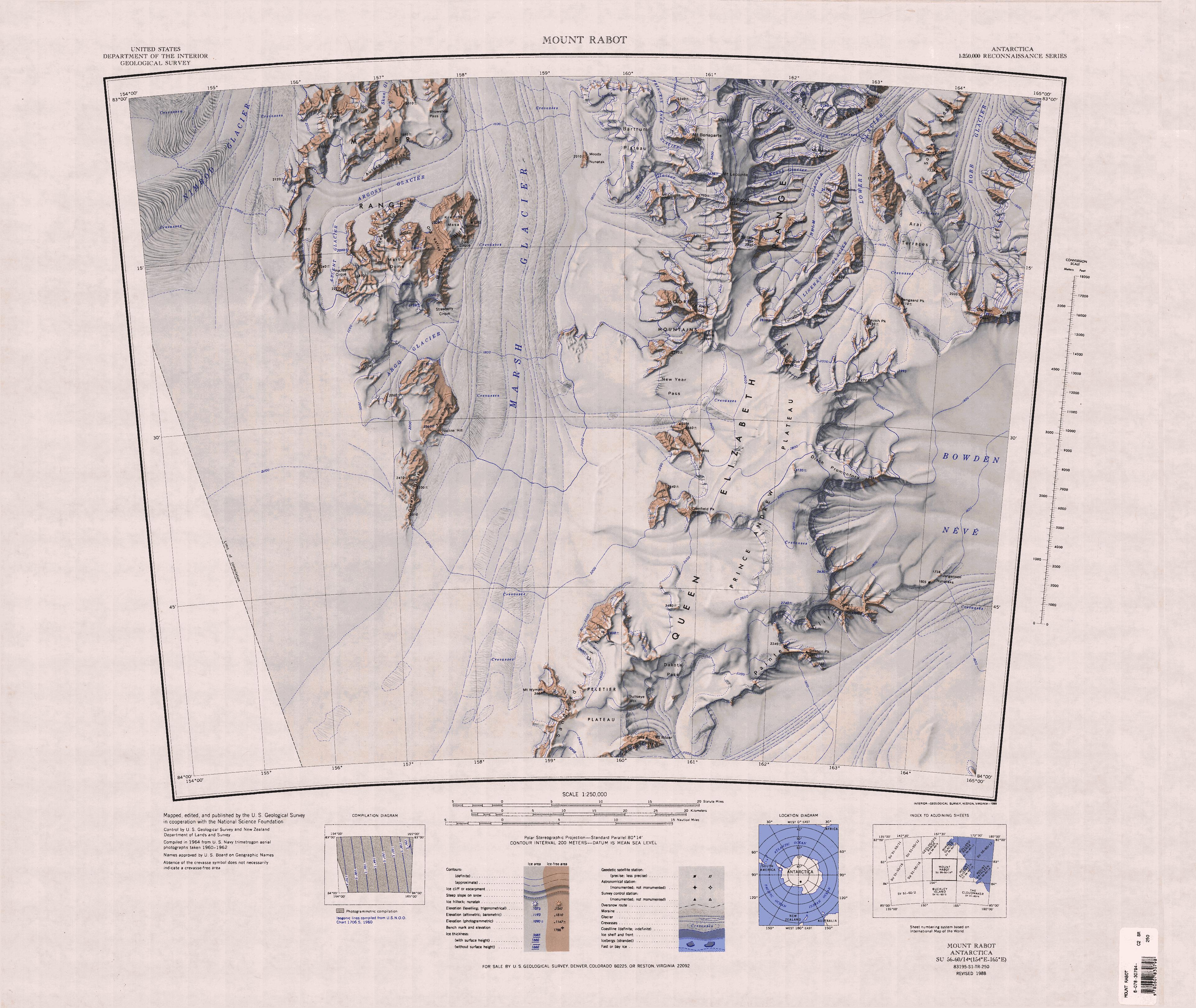
Turnabout Ridge
Prince Andrew Plateau () is an ice-covered plateau, about long and wide, lying south of Mount Rabot in the Queen Elizabeth Range of Antarctica. Exploration and name The Prince Andrew Plateau was named by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE) (1961-62) for Prince Andrew, son of Queen Elizabeth II of Great Britain. Location The Prince Andrew Plateau is in the southern Queen Elizabeth Range between the Moore Mountains and Ārai Terraces to the north and the Peletier Plateau to the south. The Marsh Glacier is to the west and the Bowden Névé to the east. Features to the east include Painted Cliffs in the southeast, which include Dawson Peak and Mount Picciotto and the Disch Promontary further north. Features to the west include Dakota Pass in the south, Cranfield Peak, Mount Weeks and New Year Pass to the south of the Moore Mountains. Features to the north include Helm Glacier, Linehan Glacier, Turnabout Ridge, January Col, Claydon Peak and Baulch P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Elizabeth Range (Antarctica)
The Queen Elizabeth Range () is a rugged mountain range that parallels the eastern side of Marsh Glacier for nearly from Nimrod Glacier in the north to Law Glacier in the south. Mount Markham, high, is the highest elevation in the range. Name The Queen Elizabeth Range was named by J.H. Miller of the New Zealand party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (CTAE; 1956–58) who, with G.W. Marsh, explored this area. It was named for Queen Elizabeth II of Great Britain, the patron of the expedition. Location The Queen Elizabeth Range is bounded to the north by the Nimrod Glacier, which separates it from the Churchill Mountains and Nash Range. To the east the Lowery Glacier and Robb Glacier separate it from the Holland Range. The Law Glacier to the south separates its from the Colbert Hills (Antarctica), Colbert Hills and Queen Alexandra Range. The Marsh Glacier separates it from the Miller Range to the west. Major glaciers *Nimrod Glacier (), a major glacier, about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helm Glacier
Lowery Glacier () is a glacier about long, a tributary of the Nimrod Glacier, which enters the west of the Ross Ice Shelf, Antarctica. Location The Lowery Glacier flows north from Prince Andrew Plateau, Antarctica, along the east side of the Queen Elizabeth Range to enter Nimrod Glacier. To the north of Softbed Ridges it converges with Robb Glacier, but the two glaciers separate when they reach Taylor Hills. It was named by the New Zealand Geological and Topographical Survey Expedition (1959–60) for J.H. Lowery who, as a member of a field party, suffered injuries when a Sno-cat broke through a crevasse bridge off Cape Selborne in November 1959. Icefalls Arai Terraces . A series of crevassed terraces and icefalls close southward of Fazekas Hills, near the head of Lowery Glacier. So named by the NZGSAE (1959-60) because the feature is a natural barrier to sledge travel which the party was unable to traverse. Arai is the Maori term for barrier. Left tributaries Tribu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition
The Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (CTAE) of 1955–1958 was a Commonwealth-sponsored expedition that successfully completed the first overland crossing of Antarctica, via the South Pole. It was the first expedition to reach the South Pole overland for 46 years, preceded only by Amundsen's expedition and Scott's expedition in 1911 and 1912. In keeping with the tradition of polar expeditions of the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration, the CTAE was a private venture, though it was supported by the governments of the United Kingdom, New Zealand, United States, Australia and South Africa, as well as many corporate and individual donations, under the patronage of Queen Elizabeth II. It was headed by British explorer Vivian Fuchs, with New Zealander Sir Edmund Hillary leading the New Zealand Ross Sea Support team. The New Zealand party included scientists participating in International Geophysical Year research while the British team were separately based at Halley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl R
Carl may refer to: *Carl, Georgia, city in USA *Carl, West Virginia, an unincorporated community *Carl (name), includes info about the name, variations of the name, and a list of people with the name *Carl², a TV series * "Carl", an episode of television series ''Aqua Teen Hunger Force'' * An informal nickname for a student or alum of Carleton College CARL may refer to: *Canadian Association of Research Libraries *Colorado Alliance of Research Libraries See also *Carle (other) *Charles *Carle, a surname *Karl (other) *Karle (other) Karle may refer to: Places * Karle (Svitavy District), a municipality and village in the Czech Republic * Karli, India, a town in Maharashtra, India ** Karla Caves, a complex of Buddhist cave shrines * Karle, Belgaum, a settlement in Belgaum ... {{disambig ja:カール zh:卡尔 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Antarctic Research Program
The United States Antarctic Program (or USAP; formerly known as the United States Antarctic Research Program or USARP and the United States Antarctic Service or USAS) is an organization of the United States government which has a presence in the Antarctica continent. Founded in 1959, the USAP manages all U.S. scientific research and related logistics in Antarctica as well as aboard ships in the Southern Ocean. United States Antarctic Program The United States established the U.S. Antarctic Research Program (USARP) in 1959—the name was later changed to the U.S. Antarctic Program—immediately following the success of the International Geophysical Year (IGY). Today, the National Science Foundation (NSF) has a Presidential Mandate to manage the United States Antarctic Program, through which it operates three year-round research stations and two research vessels, coordinates all U.S. science on the southernmost continent, and works with other federal agencies, the U.S. militar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linehan Glacier
Lowery Glacier () is a glacier about long, a tributary of the Nimrod Glacier, which enters the west of the Ross Ice Shelf, Antarctica. Location The Lowery Glacier flows north from Prince Andrew Plateau, Antarctica, along the east side of the Queen Elizabeth Range to enter Nimrod Glacier. To the north of Softbed Ridges it converges with Robb Glacier, but the two glaciers separate when they reach Taylor Hills. It was named by the New Zealand Geological and Topographical Survey Expedition (1959–60) for J.H. Lowery who, as a member of a field party, suffered injuries when a Sno-cat broke through a crevasse bridge off Cape Selborne in November 1959. Icefalls Arai Terraces . A series of crevassed terraces and icefalls close southward of Fazekas Hills, near the head of Lowery Glacier. So named by the NZGSAE (1959-60) because the feature is a natural barrier to sledge travel which the party was unable to traverse. Arai is the Maori term for barrier. Left tributaries Trib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Year Pass
The Moore Mountains () are a small but conspicuous group of mountains just north of New Year Pass in the Queen Elizabeth Range in Antarctica. Name The Moore Mountains were observed in 1957 by the New Zealand southern party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (CTAE; 1956–58) and named for R.D. Moore, Treasurer of the Ross Sea Committee. Location The Moore Mountains are in the west of the Queen Elizabeth Range. The Prince Andrew Plateau is to the southeast, the Marsh Glacier to the west and Mount Rabot to the northeast. Features, or nearby features, include Baillie Peak, Mount Angier and New Year Pass to the south. Features Baillie Peak . A peak over high, located south-southeast of Mount Angier in the Moore Mountains. The peak was observed by the Ohio State University Geological Party, 1967-68, which named it for Ralph J. Baillie, field assistant with the party. Mount Angier . A prominent peak in the Moore Mountains. Named by the New Zealand Geological Surv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Rabot
Mount Rabot () is a mountain, high, standing southeast of Mount Lecointe in the Queen Elizabeth Range in Antarctica. Name Mount Rabot was discovered and named by the British Antarctic Expedition (BrAE; 1907-09). Charles Rabot was editor of ''La Géographie'', bulletin of the Société Geographique, Paris, and was an outstanding glaciologist of that period. Location Mount Rabot is in the center of the Queen Elizabeth Range, to the east of the Marsh Glacier and west of the Helm Glacier. The Moore Mountains and Prince Andrew Plateau are to the south. Markham Plateau is to the north. Features near Mount Rabot include Solitary Peak to the south, Mount Counts and Rabot Glacier to the west, Moody Nunatak, Bartrum Plateau and Mount Bonaparte to the northwest, Mount Lecointe to the north, Fopay Peak and Mount Macbain to the northeast. Features Solitary Peak . A peak high located southeast of Mount Rabot. An important geologic section was measured on the feature by the Ohio St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dakota Pass
The Peletier Plateau () is an ice-covered plateau, about long and wide, forming the southern part of Queen Elizabeth Range. Exploration and name The Peletier Plateau was named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Rear Admiral Eugene Peletier, CEC, United States Navy, Bureau of Yards and Docks, who was of assistance to Rear Admiral George J. Dufek in the preparation of United States Navy Operation Deep Freeze II, 1956–57. Location The Peletier Plateau is in the southwest of the Queen Elizabeth Range between the head of Marsh Glacier to the west and Law Glacier to the southeast. Mount Allsup is at its southern tip, at the southwest end of the Canopy Cliffs, which face the Law Glacier. Mount Ropar is at the northeast end of the Canopy Cliffs. The Sandford Cliffs extend along the west side of the plateau, facing the Marsh Glacier. Mount Wyman stands west of them, extending into the glacier. Bullseye Mountain and Dakota Pass are to the nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowden Névé
Lennox-King Glacier is a large valley glacier, about long that flows east into the Ross Ice Shelf. Location Lennox-King Glacier drains Bowden Névé and flows northeast between the Holland Range and the Queen Alexandra Range of Antarctica to enter Richards Inlet and the Ross Ice Shelf. The Law Glacier supplies ice to the Lennox-King Glacier, leading some glaciologists to refer to it as the Law/Lennox-King Glacier system or Law-Lennox-King glacier corridor. Its mouth is south of the Robb Glacier and west of the Beardmore Glacier. Lennox-King Glacier was named by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (1959–60) for Lieutenant Commander James Lennox-King, Royal New Zealand Navy, leader at Scott Base, 1960. Mouth Richards Inlet . A large ice-filled inlet at the mouth of Lennox-King Glacier, opening to the Ross Ice Shelf just southeast of Lewis Ridge. Named by the NZGSAE (1959–60) for R. W. Richards, a member of the Ross Sea Party of the Imperial Trans-Ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |