|
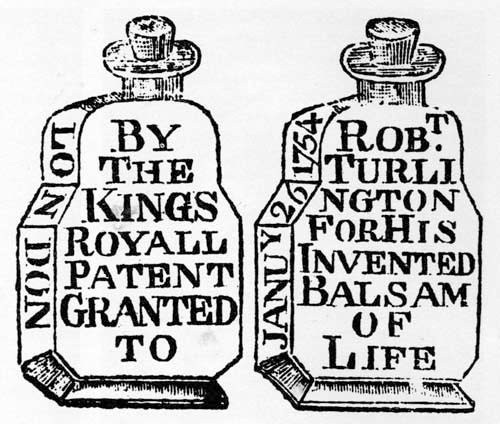
Turlington's Balsam
Turlington's Balsam of Life was a patent medicine A patent medicine (sometimes called a proprietary medicine) is a non-prescription medicine or medicinal preparation that is typically protected and advertised by a trademark and trade name, and claimed to be effective against minor disorders a ... developed by English merchant Robert Turlington. Background He succeeded in obtaining a royal patent from King George II in 1744, which gave him the right to pursue anyone attempting to pass off their own product as his, one of the earliest medicinal patents. In his royal patent application Turlington claimed that his nostrum contained 27 ingredients, and was effective in the treatment of "kidney and bladder stones, cholic, and inward weakness", a list of ailments he greatly expanded upon in a 46-page marketing brochure printed shortly afterwards. Turlington's Balsam quickly became popular in England and in the American colonies. Packaging During the 17th and 18th centuries, the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patent Medicine
A patent medicine (sometimes called a proprietary medicine) is a non-prescription medicine or medicinal preparation that is typically protected and advertised by a trademark and trade name, and claimed to be effective against minor disorders and symptoms, as opposed to a prescription drug that could be obtained only through a pharmacist, usually with a doctor's prescription, and whose composition was openly disclosed. Many over-the-counter medicines were once ethical drugs obtainable only by prescription, and thus are not patent medicines. The ingredients of patent medicines are incompletely disclosed. Antiseptics, analgesics, some sedatives, laxatives, antacids, cold and cough medicines, and various skin preparations are included in the group. The safety and effectiveness of patent medicines and their sale is controlled and regulated by the Food and Drug Administration in the United States and corresponding authorities in other countries. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letters Patent
Letters patent (plurale tantum, plural form for singular and plural) are a type of legal instrument in the form of a published written order issued by a monarch, President (government title), president or other head of state, generally granting an office, right, government-granted monopoly, monopoly, title or status to a person or corporation. Letters patent can be used for the creation of corporations, government offices, to grant city status or heraldry, coats of arms. Letters patent are issued for the appointment of representatives of the Crown, such as governors and governor-general, governors-general of Commonwealth realms, as well as appointing a Royal Commission. In the United Kingdom, they are also issued for the creation of peers of the realm. A particular form of letters patent has evolved into the modern intellectual property patent (referred to as a utility patent or design patent in United States patent law) granting exclusive rights in an invention or design. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George II Of Great Britain
George II (George Augustus; ; 30 October / 9 November 1683 – 25 October 1760) was King of Great Britain and King of Ireland, Ireland, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg (Electorate of Hanover, Hanover) and a prince-elector of the Holy Roman Empire from 11 June 1727 (Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.) until his death in 1760. Born and brought up in northern Germany, George is the most recent British monarch born outside Great Britain. The Act of Settlement 1701 and the Acts of Union 1707 positioned his grandmother Sophia of Hanover and her Protestant descendants to inherit the British throne. George married Princess Caroline of Ansbach, with whom he had eight children. After the deaths of George's grandmother and Anne, Queen of Great Britain, George's father, the Elector of Hanover, ascended the British throne as George I of Great Britain, George I in 1714. In the first years of his father's reign as king, Prince George was associated with opposition politicians until they rej ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
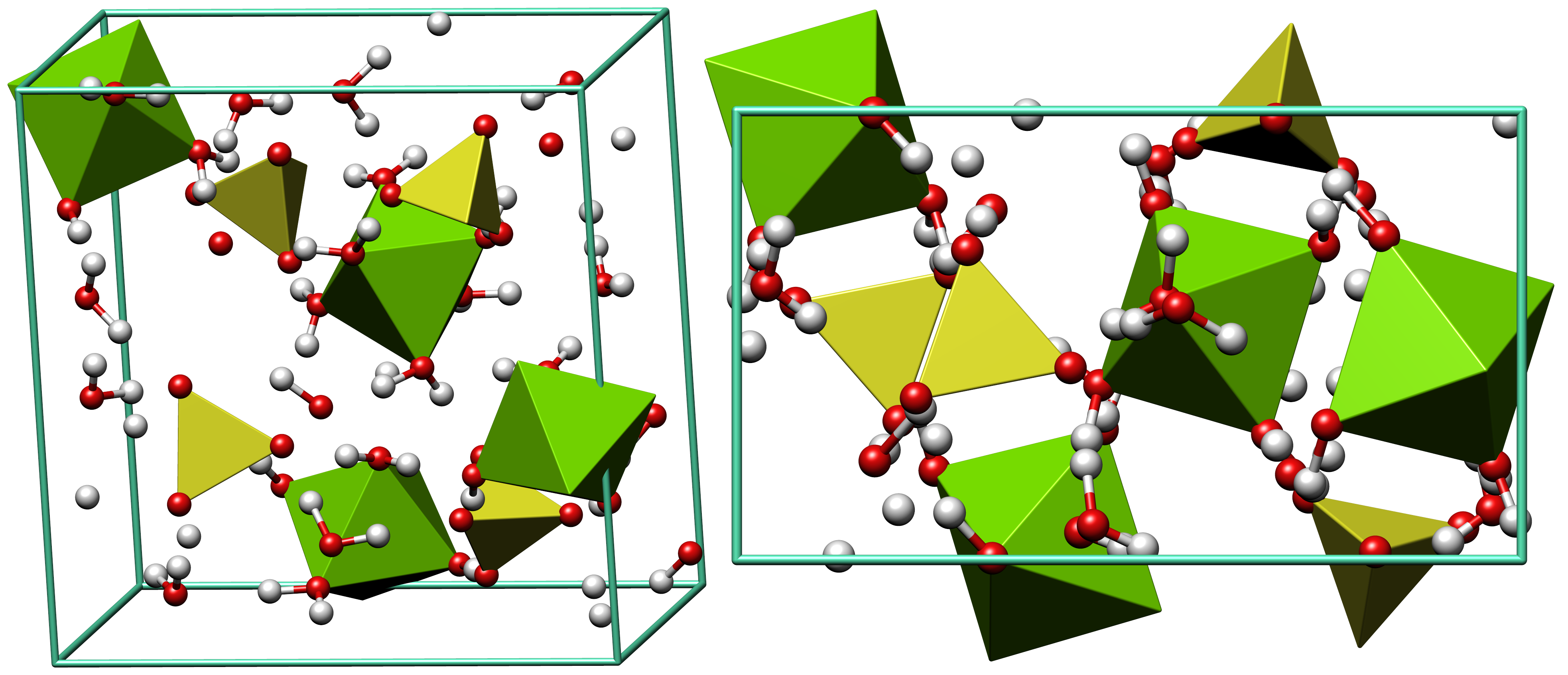
Epsom Salts
Epsomite, Epsom salt, or magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, is a hydrous magnesium sulfate mineral with formula . Physical properties Epsomite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system. The normal form is as massive encrustations, while acicular or fibrous crystals are rarely found. It is colorless to white with tints of yellow, green and pink. It is a soft mineral with variable Mohs hardness around 2.0~2.5, and it has a low specific gravity It is readily soluble in water, and absorbs water from the air. It converts to hexahydrate with the loss of one water molecule and a switch to monoclinic structure. The epsomite group includes solid solution series with morenosite (·) and goslarite (·). Etymology It was first systematically described in 1806 for an occurrence near Epsom, Surrey, England, after which it was named. It has been also referred to as "cave cotton" when in its fibrous form. Occurrence Epsomite forms as encrustations or efflorescences on limestone cave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |