|
Turkish Abductions
The Turkish Abductions ( ) were a series of slave raids by pirates from Algier and Salé that took place in Iceland in the summer of 1627. The adjectival label "''Turkish''" () does not refer to ethnic Turks, country of Turkey or Turkic peoples in general; at the time it was a general term for all Muslims of the Mediterranean since the majority were from or subjects of the Ottoman Empire. The pirates came from the cities of Algiers and Salé. They raided Grindavík, the East Fjords, and Vestmannaeyjar. About 50 people were killed and close to 400 captured and sold into slavery. A ransom was eventually paid, 9 to 18 years later, for the return of 50 individuals. Raids The 1627 raid was not the first one. In 1607, both Iceland and the Faroe Islands were subjected to a slave raid by the Barbary pirates, who abducted hundreds of people for the slave markets of North Africa. In 1627, the Barbary pirates came to Iceland in two groups: the first group was from Salé and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marche Aux Esclaves D Alger Gravure
Marche ( ; ), in English sometimes referred to as the Marches ( ) from the Italian name of the region (Le Marche), is one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. The region is located in the Central Italy, central area of the country, and has a population of about 1.5 million people, being the thirteenth largest region in the country by number of inhabitants. The region's capital and largest city is Ancona. The Marche region is bordered by Emilia-Romagna and the republic of San Marino to the north, Tuscany and Umbria to the west, Lazio to the southwest, Abruzzo to the south, and the Adriatic Sea to the east. Except for river valleys and the often very narrow coastal strip, the land is hilly. A railway from Bologna to Brindisi, built in the 19th century, runs along the coast of the entire territory. Inland, the mountainous nature of the region, even today, allows relatively little travel north and south, except by twisting roads over the passes. From the Middle ages t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ) (alt. the Faroes) are an archipelago in the North Atlantic Ocean and an autonomous territory of the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. Located between Iceland, Norway, and the United Kingdom, the islands have a population of 54,609 and a land area of 1,393 km². The official language is Faroese language, Faroese, which is partially mutually intelligible with Icelandic language, Icelandic. The terrain is rugged, dominated by fjords and cliffs with sparse vegetation and few trees. As a result of its proximity to the Arctic Circle, the islands experience perpetual Twilight, civil twilight during summer nights and very short winter days; nevertheless, they experience a Oceanic climate#Subpolar variety (Cfc, Cwc), subpolar oceanic climate and mild temperatures year-round due to the Gulf Stream. The capital, Tórshavn, receives the fewest recorded hours of sunshine of any city in the world at only 840 per year. Færeyinga saga, Færeyinga Saga and the writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
En Kort Beretning Om De Tyrkiske Søe-Røveres
EN or En or en may refer to: Businesses * Bouygues (stock symbol EN) * Island Rail Corridor, formerly known as the Esquimalt and Nanaimo Railway (reporting mark EN) * Euronews, a news television and internet channel Language and writing * N, 14th letter of the Roman alphabet * EN, a mark in Sumerian cuneiform script for a High priest or Priestess (meaning "lord", or "priest") *En (digraph) /‹en›/, a phoneme *En (Cyrillic), 15th letter of the Cyrillic alphabet *En (typography), a unit of typographical width ** Dash#En dash /en dash/, a dash of length 1 en * En language, a language spoken in northern Vietnam *English language (ISO language code: en) Organisations * Eastern National, a US organization providing educational products to National Park visitors * English Nature, a former UK government conservation agency * Envirolink Northwest, an environmental organization in England Religion * En (deity) in Albanian mythology Science and technology * Engineer * E''n'' (Lie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world's Major religious groups, second-largest religious population after Christians. Muslims believe that Islam is the complete and universal version of a Fitra, primordial faith that was revealed many times through earlier Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophets and messengers, including Adam in Islam, Adam, Noah in Islam, Noah, Abraham in Islam, Abraham, Moses in Islam, Moses, and Jesus in Islam, Jesus. Muslims consider the Quran to be the verbatim word of God in Islam, God and the unaltered, final revelation. Alongside the Quran, Muslims also believe in previous Islamic holy books, revelations, such as the Torah in Islam, Tawrat (the Torah), the Zabur (Psalms), and the Gospel in Islam, Injil (Gospel). They believe that Muhammad in Islam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Conversion
Religious conversion is the adoption of a set of beliefs identified with one particular religious denomination to the exclusion of others. Thus "religious conversion" would describe the abandoning of adherence to one denomination and affiliating with another. This might be from one to another denomination within the same religion, for example, from Protestant Christianity to Roman Catholicism or from Shia Islam, Shi'a Islam to Sunni Islam. In some cases, religious conversion "marks a transformation of religious identity and is symbolized by special rituals". People convert to a different religion for various reasons, including active conversion by free choice due to a change in beliefs, secondary conversion, deathbed conversion, conversion for convenience, marital conversion, and forced conversion. Religious conversion can also be driven by practical considerations. Historically, people have converted to evade taxes, to escape military service or to gain political representation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heimaey
Heimaey (), is an Icelandic island. At , it is the largest island in the Vestmannaeyjar archipelago, and the largest and most populated island off the Icelandic coast. Heimaey is off the south coast of Iceland. It is the only populated island of the Vestmannaeyjar islands, with a population of 4,414. The Vestmannaeyjar Airport and the Westman Islands Golf Club taken together cover a good portion of the island. In January 1973, lava flow from nearby Eldfell destroyed half the town and threatened to close its harbour, its main income source. An operation to cool the advancing lava with sea water saved the harbour. History First settlers In tradition, Herjólfur Bárðarson was said to be the first person to settle in Heimaey. According to the ''Landnáma'', he built his farm in Herjólfsdalur (literally: Herjólf's valley) about 900. The archaeological excavation in 1971 of ancient ruins in Herjólfsdalur revealed that there had been settlement nearly 100 years earlier. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fáskrúðsfjörður
Fáskrúðsfjörður (; previously named also Búðir ) is a village (''þorp'') in eastern Iceland. It has a population of 735 (as of 2024) and constitutes one of the villages composing the municipality of Fjarðabyggð. Geography Fáskrúðsfjörður, located on the same-named fjord, lies between Reyðarfjörður and Stöðvarfjörður. It is one of the easternmost settlements of Iceland. The other neighbouring villages which compose the municipality of Fjarðabyggð are: Eskifjörður (1,043 inh.), Mjóifjörður (35 inh.), Neskaupstaður (1,437 inh.), Reyðarfjörður (1,102 inh.) and Stöðvarfjörður (203 inh.). History and culture Fáskrúðsfjörður was home to a hospital founded to serve French fishermen working here until 1935. The former hospital building dating from 1903 has now been restored as a hotel. Even nowadays there are bilingual signs in town indicating the street names in Icelandic and in French. The French cemetery with 49 graves of fishermen from Franc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
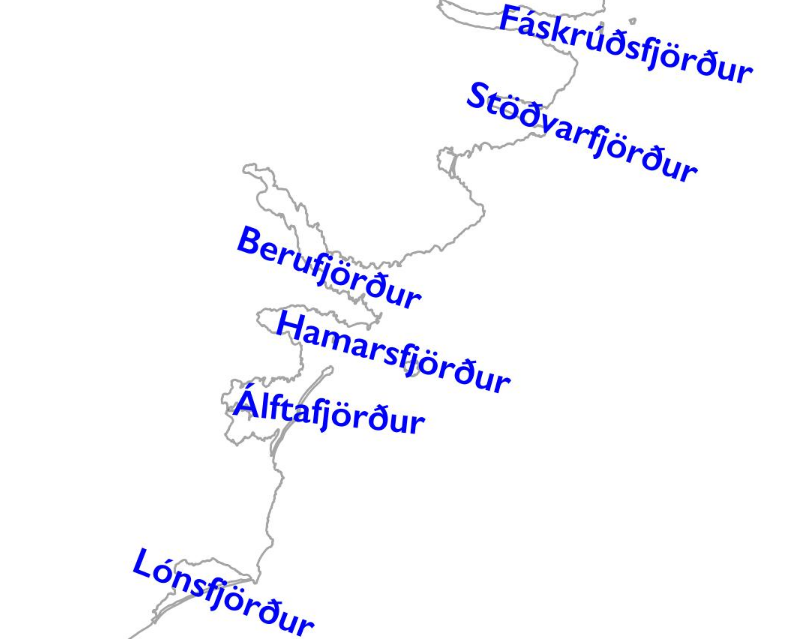
Berufjörður
Berufjörður () is a fjord in Eastern Region (Iceland), Eastern Iceland. It is about long and wide. The village Djúpivogur (pop. 456) is located on its western shores. Mt. Búlandstindur which is above sea level is located west of the fjord. Route 1 (Iceland), Route 1 passes on its shores. See also * Djúpivogur * Búlandstindur * Eastern Region (Iceland), Eastern Iceland References External links Fjords of Iceland Eastern Region (Iceland) {{Iceland-fjord-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Peninsula (Iceland)
Southern Peninsula (, ) is an administrative unit and part of Reykjanesskagi (pronounced ), or Reykjanes Peninsula, a regions of Iceland, region in southwest Iceland. It was named after Reykjanes, the southwestern tip of Reykjanesskagi. The region has a population of 30,933 (2024) and is one of the more densely populated parts of the island. The administrative centre is Keflavík, which had 7,000 residents when it merged with the nearby town of Njarðvík and Hafnir in 1995 to create Reykjanesbær, which is the largest settlement outside the Capital Region (Iceland), Greater Reykjavík area; in 2018, the region had a population of 17,805. The region is the location of Keflavík International Airport, the major point of entry for Iceland. Some fishing towns, such as Grindavík, Njarðvík and Sandgerði, are situated on the peninsula. The peninsula is marked by active volcanism under its surface and large lava fields, allowing little vegetation. There are numerous hot springs in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancer
A lancer was a type of cavalryman who fought with a lance. Lances were used for mounted warfare in Assyria as early as and subsequently by India, Egypt, China, Persia, Greece, and Rome. The weapon was widely used throughout Eurasia during the Middle Ages and the Renaissance by heavy cavalry, but fell out of general use by the late 16th century, before its revival by light cavalry in the early 19th century. Lance cavalry remained in an active role into the early 20th century and World War I. In modern times, many militaries retain units designated as lancers. However, the lance itself has been relegated to a ceremonial role. 17th-, 18th-, and 19th-century lancers The lancer ( Polish: ''ułan'', German: ''Ulan'', French: ''uhlan'') had become a common sight in the majority of European, Ottoman, and Indian cavalry forces during this time, but, with the exception of the Ottoman troops, they increasingly discarded the heavy armour to give greater freedom of movement in combat. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Iceland
The recorded history of Iceland began with the settlement by Vikings, Viking explorers and the people they enslaved from Western Europe, particularly in modern-day Norway and the British Isles, in the late ninth century. Iceland was still uninhabited long after the rest of Western Europe had been settled. Recorded settlement has conventionally been dated back to 874, although archaeological evidence indicates Gaelic monks from Ireland, known as papar from Sagas of Icelanders, sagas, may have settled Iceland earlier. The land was settled quickly, mainly by Norsemen who may have been fleeing conflict or seeking new land to farm. By 930, the chieftains had established a form of governance, the ''Althing'', making it one of the world's oldest parliaments. Towards the end of the tenth century, Christianity came to Iceland through the influence of the Norwegian king Olaf Tryggvason. During this time, Iceland remained independent, a period known as the Old Commonwealth, and Icelandic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |