|
Tupolev Tu-1
The Tupolev Tu-1 was a prototype Soviet night fighter variant of the Tupolev Tu-2 medium bomber that first flew after the end of World War II. It was cancelled when its experimental Mikulin AM-43V engines reached the end of their service life. Development Impressed by the performance of the de Havilland Mosquito the Soviets asked Tupolev to modify a Tu-2 as a high-speed day bomber with a reduced crew as the ANT-63. The second prototype of this project was ordered to be converted in February 1946 for use as a three-seat long-range interceptor capable of carrying an airborne radar set with the internal designation of ANT-63P and the official designation of Tu-1. It was given prototype Mikulin AM-43V engines driving four-bladed propellers, and fitted with new radio equipment. It reverted to the standard Tu-2S undercarriage. Two Nudelman-Suranov NS-45 guns with 50 rounds each were fitted on the underside of the nose, two Volkov-Yartsev VYa-23 or Nudelman-Suranov NS-23 cannon were f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Night Fighter
A night fighter (later known as all-weather fighter or all-weather interceptor post-Second World War) is a largely historical term for a fighter aircraft, fighter or interceptor aircraft adapted or designed for effective use at night, during periods of adverse meteorological conditions, or in otherwise poor visibility. Such designs were in direct contrast to day fighter, day fighters: fighters and interceptors designed primarily for use during the day or during good weather. The concept of the night fighter was developed and experimented with during the First World War but would not see widespread use until WWII. The term would be supplanted by “all-weather fighter/interceptor” post-WWII, with advancements in various technologies permitting the use of such aircraft in virtually all conditions. During the Second World War, night fighters were either purpose-built night fighter designs, or more commonly, heavy fighters or light bombers adapted for the mission, often employing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bill Gunston
Bill Gunston (1 March 1927 – 1 June 2013) was a British aviation and military author. He flew with Britain's Royal Air Force from 1945 to 1948, and after pilot training became a flying instructor. He spent most of his adult life doing research and writing on aircraft and aviation. He was the author of over 350 books and articles. His work included many books published by Salamander Books. Early life Born William Tudor Gunston in London on 1 March 1927,"William Tudor Gunston." '' Contemporary Authors Online.'' Detroit: Gale, 2001. ''Biography in Context''. Web. 21 February 2013. Gunston was educated at Pinner County Grammar School. In his spare time, he was Flight Sergeant in the school Air Training Corps squadron and, for several months, the London Philharmonic Orchestra's librarian. Royal Air Force Gunston joined the Royal Air Force in 1945 and went to University College, Durham on an RAF cadetship. In 1946 he moved to No 4 Flying Training School in Bulawayo, Southern Rh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid-wing Aircraft
A monoplane is a fixed-wing aircraft configuration with a single mainplane, in contrast to a biplane or other types of multiplanes, which have multiple wings. A monoplane has inherently the highest efficiency and lowest drag of any wing configuration and is the simplest to build. However, during the early years of flight, these advantages were offset by its greater weight and lower manoeuvrability, making it relatively rare until the 1930s. Since then, the monoplane has been the most common form for a fixed-wing aircraft. Characteristics Support and weight The inherent efficiency of the monoplane is best achieved in the cantilever wing, which carries all structural forces internally. However, to fly at practical speeds the wing must be made thin, which requires a heavy structure to make it strong and stiff enough. External bracing can be used to improve structural efficiency, reducing weight and cost. For a wing of a given size, the weight reduction allows it to fly slower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1940s Soviet Fighter Aircraft
Year 194 ( CXCIV) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Septimius and Septimius (or, less frequently, year 947 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 194 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Decimus Clodius Septimius Albinus Caesar became a Roman Consul. * Battle of Issus: Septimius Severus marches with his army (12 legions) to Cilicia, and defeats Pescennius Niger, Roman governor of Syria. Pescennius retreats to Antioch, and is executed by Severus' troops. * Septimius Severus besieges Byzantium (194–196); the city walls suffer extensive damage. Asia * Battle of Yan Province: Warlords Cao Cao and Lü Bu fight for control over Yan Province; the battle lasts for over 100 days. * First year of the ''Xingping'' era during the Han Dynasty i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tupolev Aircraft
Tupolev ( rus, Туполев, , ˈtupəlʲɪf), officially United Aircraft Company Tupolev - Public Joint Stock Company, is a Russian aerospace and Arms industry, defence company headquartered in Basmanny District, Moscow. UAC Tupolev is successor to the Soviet Tupolev Design Bureau (OKB-156, Soviet Union military aircraft designation systems#Soviet system after December 9.2C 1940, design office prefix ''Tu'') founded in 1922 by aerospace pioneer and engineer Andrei Tupolev, who led the company for 50 years until his death in 1972. Tupolev designed over 100 models of civilian and military aircraft and produced more than 18,000 aircraft for Russia, the Soviet Union and the Eastern Bloc since its founding, and celebrated its 100th anniversary on 22 October 2022. Tupolev is involved in numerous aerospace and defence sectors including development, manufacturing, and overhaul for both civil and military aerospace products such as aircraft and weapons systems, and also missile and nava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petlyakov Pe-3
The Petlyakov Pe-3 was the long-range heavy fighter version of the successful Petlyakov Pe-2 high-speed dive bomber used by the Soviet Union during World War II. Its design and use followed a comparable path to those taken by the German Luftwaffe with the Junkers Ju 88 and the British Royal Air Force with the De Havilland Mosquito. The Soviets realized the need for a night fighter after the first night bombing of Moscow during Operation Barbarossa. The Petlyakov Pe-2 was selected for modification as the most suitable aircraft available. It was initially used for daylight ground attack missions during the Battle of Moscow, but this proved to be costly since the aircraft was unarmored. Armor and additional guns were retrofitted to the existing aircraft to make it more effective, but the evacuation of the sole factory building the Pe-3 in October 1941 limited the number of aircraft available and many units of the Soviet Air Forces flying the Pe-3 were either disbanded or converted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junkers Ju 88
The Junkers Ju 88 is a twin-engined multirole combat aircraft designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Junkers Aircraft and Motor Works. It was used extensively during the Second World War by the ''Luftwaffe'' and became one of the most versatile combat aircraft of the conflict. The Ju 88 originated from a ''Reichsluftfahrtministerium'' (RLM) requirement issued in 1934 for a new multipurpose aircraft. Junkers was one of several firms to respond, producing two separate design studies that produced both the Ju 85 and Ju 88. The design work was headed by Junkers' chief designer Ernst Zindel. The Ju 88 was envisioned to function as a so-called '' Schnellbomber'' ("fast bomber") that would evade interception by enemy fighters of its era by flying at high speed. On 21 December 1936, the first prototype performed its maiden flight. The performance of the third prototype was highly favourable, resulting in the competing Henschel Hs 127 and Messerschmitt Bf 162 bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focke-Wulf Ta 154
The Focke-Wulf Ta 154 ''Moskito'' was a fast twin-engined night fighter aircraft designed by the Nazi Germany, German aeronautical engineer Kurt Tank and produced by the aircraft manufacturer Focke-Wulf. It was unofficially named ''Moskito'' due to its similarities with the de Havilland Mosquito (which was also largely made of wood) that were already in service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). The Ta 154 commenced development in 1942 and was worked on during much of the latter half of the Second World War. It was designed to replace variants of the Messerschmitt Bf 110 and Junkers Ju 88 and function as a specialised night fighter. As per a stipulation issued by the Ministry of Aviation (Nazi Germany), ''Reichsluftfahrtministerium'' (RLM), wood comprised over half of the material needed to build the Ta 154. A special phenolic resin adhesive called Tego film was used to bond sections together. It was originally designated ''Ta 211'' in reference to the intended Junkers Jumo 211, Jum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas A-20 Havoc
The Douglas A-20 Havoc (company designation DB-7) is an American light bomber, attack aircraft, Intruder (air combat), night intruder, night fighter, and reconnaissance aircraft of World War II. Designed to meet an Army Air Corps requirement for a bomber, it was ordered by France for their air force before the USAAC decided it would also meet their requirements. French DB-7s were the first to see combat; after the fall of France, the bomber served with the Royal Air Force under the British military aircraft designation systems#Names, service name Boston. From 1941, night fighter and Intruder (air combat), intruder versions were given the service name Havoc. In 1942 USAAF A-20s saw combat in North Africa. It served with several Allies of World War II, Allied air forces, principally the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF), the Soviet Air Forces (''VVS''), Soviet Naval Aviation (''AVMF''), and the Royal Air Force (RAF) of the United Kingdom. A total of 7,478 aircraft were built, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dornier Do 217
The Dornier Do 217 was a bomber used by the German ''Luftwaffe'' during World War II. It was a more powerful development of the Dornier Do 17, known as the ''Fliegender Bleistift'' (German: "flying pencil"). Designed in 1937-38 as a heavy bomber but not meant to be capable of the longer-range missions envisioned for the larger Heinkel He 177, the Do 217's design was refined during 1939 and production began in late 1940. It entered service in early 1941 and by the beginning of 1942 was available in significant numbers. The Dornier Do 217 had a much larger bomb load and a much greater range than the Do 17. In later variants, dive bombing and maritime strike capabilities using glide bombs were experimented with, considerable success being achieved. Early Do 217 variants were more powerful than the contemporary Heinkel He 111 and Junkers Ju 88, having a greater speed, range and bomb load. Owing to this it was called a heavy bomber rather than a medium bomber. The Do 217 served on al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dornier Do 17
The Dornier Do 17 is a twin-engined light bomber designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Dornier Flugzeugwerke. Large numbers were operated by the ''Luftwaffe'' throughout the Second World War. The Do 17 was designed during the early 1930s as a '' Schnellbomber'' ("fast bomber") that was intended to use its speed to outrun opposing fighter aircraft. It was a lightly built aircraft, possessing a twin tail, " shoulder wing" and typically powered by a pair of Bramo 323P radial engines. The first prototype made its maiden flight on 23 November 1934; it entered regular service with the ''Luftwaffe'' three years later. Sometimes referred to as the ''Fliegender Bleistift'' ("flying pencil") or the ''Eversharp'', the Do 17 was a relatively popular aircraft among its crews due to its handling, especially at low altitude, which made the type harder to hit than other German bombers of the era. During 1937, the Do 17 made its combat debut during the Spanish Civil War, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
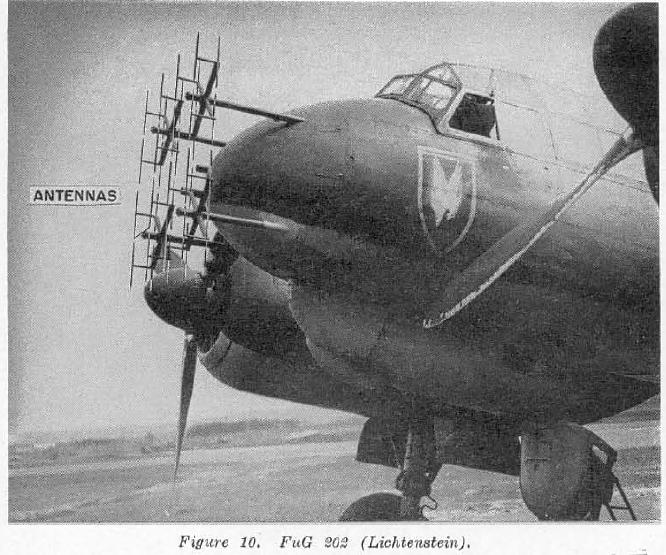
Lichtenstein Radar
The Lichtenstein radar was among the earliest airborne radars available to the Luftwaffe in World War II and the first one used exclusively for air interception. Developed by Telefunken, it was available in at least four major revisions, called FuG 202 Lichtenstein B/C, FuG 212 Lichtenstein C-1, FuG 220 Lichtenstein SN-2 and the very rarely used FuG 228 Lichtenstein SN-3. (FuG is short for ''Funk-Gerät'', radio set). The Lichtenstein series remained the only widely deployed airborne interception radar used by the Germans on their night fighters during the war — the competing FuG 216 through 218 ''Neptun'' mid- VHF band radar systems were meant as a potentially more versatile stop-gap system through 1944, until the microwave-based FuG 240 "Berlin" could be mass-produced; the ''Berlin'' system was still being tested when the war ended. FuG 202 Lichtenstein B/C Early FuG 202 Lichtenstein B/C units were not deployed until 1942. They operated at a maximum RF output power o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |