|
Tunisian Army
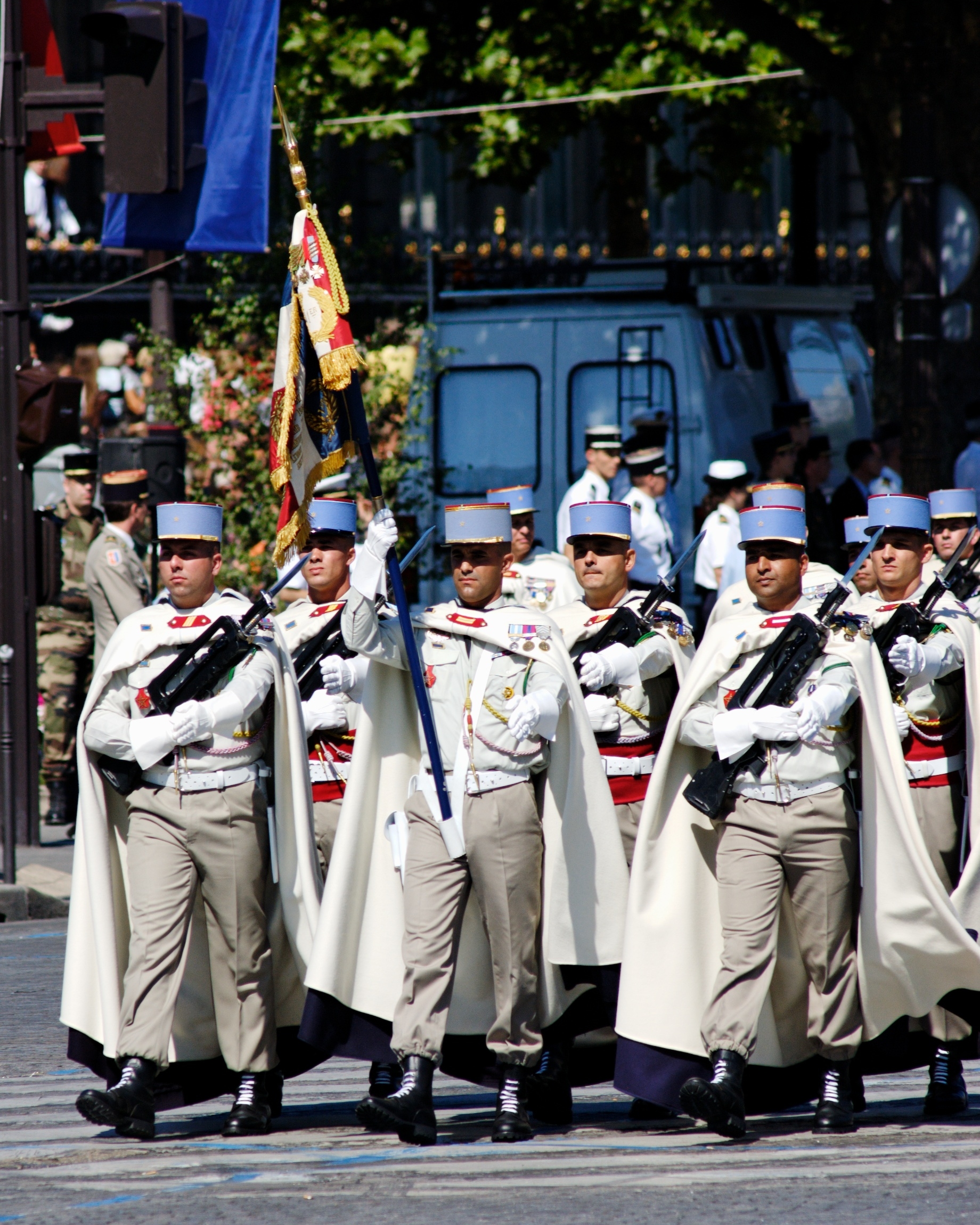
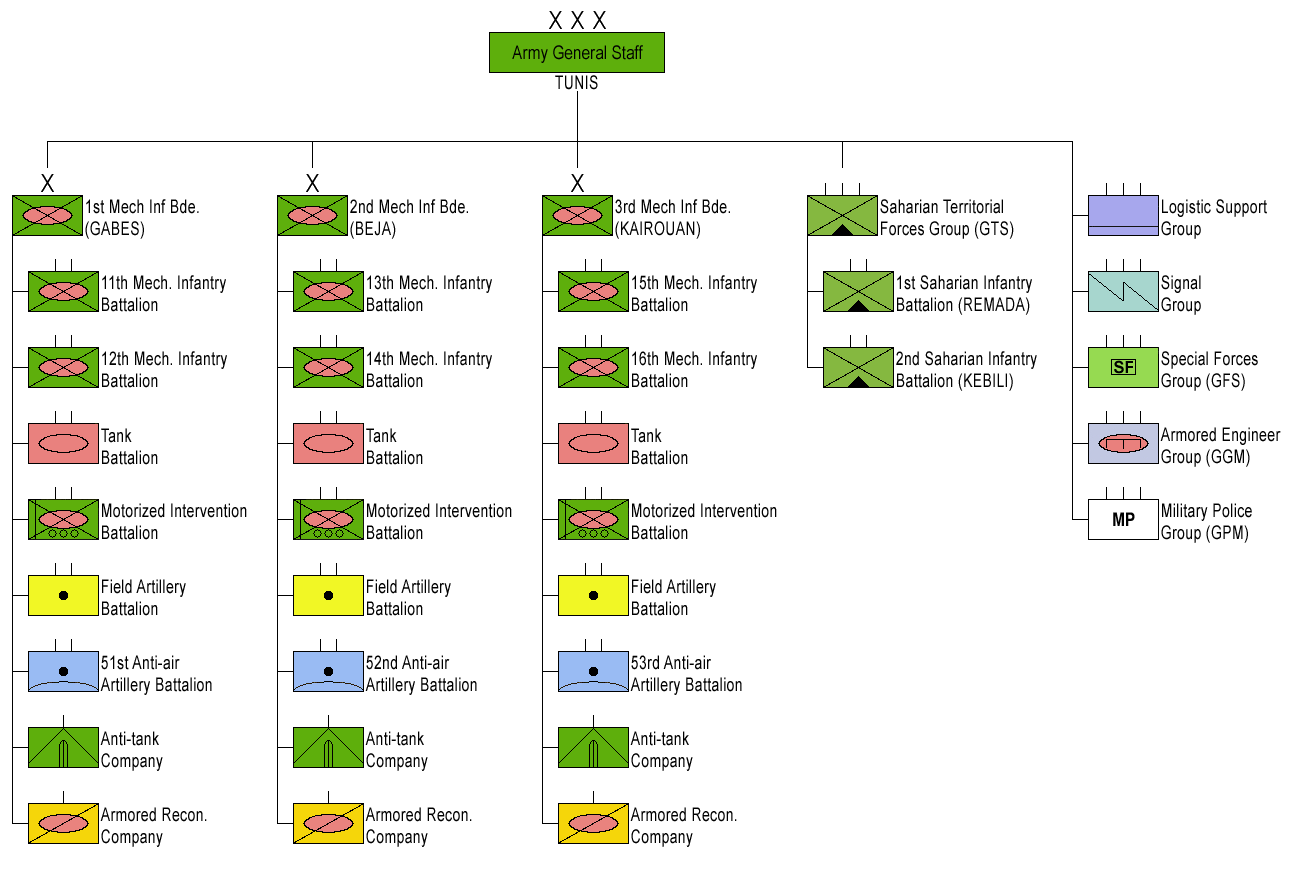
The Tunisian Land Army (, ) is the ground component of the Tunisian Armed Forces . The Land Forces Command is located in Bizerte. The TAF itself was created on June 30, 1956. The Land Army is the largest service branch within the Tunisian Armed Forces and has a dominant presence in the current General Staff. It is estimated to number around 90,000, in addition to 60,000 reservists for a total of 150,000 strong. The modern army was created in the 1830s. It has seen substantive combat on one occasion: against France during the 1961 Bizerte crisis. The mission of the Tunisian army is to defend the country against any foreign attack, to allow the development of a diplomatic counterattack and encourage the involvement of the United Nations, protect Tunisian nationals around the world and participate in peacekeeping missions. History During the Beylical period The modern Tunisian army was formed in 1831 by Al-Husayn II ibn Mahmud. The first battalions of the regular modern T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunisian Armed Forces
The Tunisian Armed Forces () consist of the Tunisian Army, Tunisian Air Force, Air Force and Navy. As of 2019, Tunisia had armed forces with more than 150,000 active-duty personnel, of which 80,000 were conscripts. Paramilitary forces consisted of a 12,000-member national guard. Tunisia participates in United Nations peacekeeping efforts in the DROC (MONUSCO) and Côte d'Ivoire.Military Balance 2013, p.406 Previous United Nations peacekeeping deployments for the Tunisian armed forces have included Cambodia (UNTAC), Namibia (UNTAG), Somalia, Rwanda, Burundi, Ethiopia/Eritrea (UNMEE), and the 1960s mission in the Congo, ONUC. History The modern Tunisian army was formed in 1831 by Al-Husayn II ibn Mahmud. During the period of the French Protectorate of Tunisia, French Protectorate (1881–1956) Tunisians were recruited in significant numbers into the French Army, serving as tirailleurs (infantry) and spahis (cavalry). These units saw active service in Europe during both World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spahis
Spahis () were light-cavalry regiments of the French army recruited primarily from the Arab and Berber populations of Algeria, Tunisia and Morocco. The modern French Army retains one regiment of Spahis as an armoured unit, with personnel now recruited in mainland France. Senegal also maintains a mounted unit with spahi origins as a presidential escort: the Red Guard. Etymology The name is the French form of the Ottoman Turkish word , a word derived from Persian , "soldier", "horseman", ultimately from Persian meaning "army", "cavalry". Early history Following the French occupation of Algiers in 1830, detachments of locally recruited irregular horsemen were attached to the regiments of light cavalry assigned to North African service. These auxiliaries were designated as '' chasseurs spahis''. Between 1834 and 1836 they were organised into four squadrons of regular spahis. In 1841 the 14 squadrons by then in existence were brought together in a single corps of spahis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammamet, Tunisia
Hammamet ( ', literally " Baths") is a town in the Nabeul Governorate of Tunisia. Due to its beaches, it is a popular destination for swimming and water sports and is one of the primary tourist destinations in Tunisia. It is located in the south-eastern section of Cape Bon. The reported number of inhabitants varies from 100,000 to 400,000 and the population quadruples due to tourists' arrival in the summer. It is particularly known for jasmine, which is the namesake of the tourist resort of Yasmine Hammamet. All over Hammamet, souvenirs crafted from jasmine can be found. Around Hammamet, suburbs are being built as migrants from the southern region of the country come to find employment. As a popular tourist destination, the city is economically important to Tunisia. The 2005 World Scout Conference was held in Hammamet. History In the 1st century, there was a settlement here known as Pupput. It was a town (now in the suburbs of Hammamet) that became a Roman colony in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kélibia
Kelibia (Kélibia) ( '), often referred to as Klibia or Gallipia by European writers, is a coastal town on the Cap Bon peninsula, Nabeul Governorate in the far north-eastern part of Tunisia. Its sand beaches are considered some of the finest in the Mediterranean. History Known in Roman times as Clypia or Clypea, () the town was founded by the Carthaginians as the fortified town of Aspis () in the 5th century BC. The Siege of Aspis in 255BC was the first battle of the First Punic War fought on African soil. Clypea was also the seat of an ancient Christian bishopric. At the Council of Carthage (411), which brought together Catholic and Donatist bishops, Clypea was represented by Bishop Leodicius and the Donatist Geminius. Aurilius was one of the bishops whom the Arian Vandal king Huneric summoned to Carthage in 484 and then exiled. Two other bishops of Clypia took part in the Council of Carthage (525) (Bishop Crescentius) and Council of Carthage (645) (Bishop Stephanus). No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Béja
Béja ( ') is a city in Tunisia. It is the capital of the Béja Governorate. It is located from Tunis, between the Medjerdah River and the Mediterranean, against the foothills of the Khroumire, the town of Béja is situated on the sides of Djebel Acheb, facing the greening meadows, its white terraces and red roofs dominated by the imposing ruins of the old Roman fortress. History Etymology Classical era period The city endured brutal assaults by the Carthaginians, the Numidians, the Romans, and, later on, by the Vandals. The Numidian king Jugurtha made the town his governing headquarters. Originally the town was named Waga, which became Vacca and then Vaga under the Romans and eventually Baja under the Arabs and Béja under the French. The Romans destroyed the old Carthaginian citadel and replaced it with a new one; they built fortifications that are still standing today. Under the Roman domination, Béja became prosperous and was the center of a diocese. Acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zarzis
Zarzis, also known as Jarjis ( '), is a coastal commune (municipality) in southeastern Tunisia, former bishopric and Latin Catholic titular see under its ancient name Gergis. To the Phoenicians, Romans and Arabs the port was of strategic importance. Geography It lies on the coast of the Mediterranean, where the climate is mainly dry and sunny, making it a popular tourist destination mixing the old and the traditional. It has a major port where park of economic activitiesis based. Located at the southern end of the eastern peninsula that bears his name, the ''délégation'' (district) of Zarzis has a very large coastline. There are a variety of landscapes reflecting a great diversity of climatic conditions. Buildings and structures * 320-metre-high guyed mast for FM/TV-broadcasting, tallest structure in Tunisia. History The city was known in Antiquity as Gergis and located at the western end of the Lesser Syrtis (Gulf of Gabès), not far from the island of Meninx (curr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabès
Gabès (, ; ), also spelled Cabès, Cabes, and Kabes, is the capital of the Gabès Governorate in Tunisia. Situated on the coast of the Gulf of Gabès, the city has a population of 167,863, making it the 6th largest city in Tunisia. Located 327 km southeast of Tunis and 113 km from Sfax, Gabès lies at the delta of the Wadi Qabis, which originates 10 kilometers upstream at Ras El Oued, Algeria, Ras al-Oued and serves as its primary water source. Historically, the town was a Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian settlement known as Tacapae before falling under Roman Empire, Roman control. It was later ruined during the 7th-century Arab invasion but was recovered by Sidi Boulbaba, a revered companion of the Muhammad, Prophet Muhammad and a patron of the town. Although it experienced decline under the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans, Gabès saw significant growth under French rule from 1881 to 1955, with the development of key infrastructure, including a railway, road network, and port. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Hamma
El Hamma ( ') is an oasis town located in the Gabès Governorate, 30 kilometers west of Gabès, Tunisia and near the eastern end of Chott el Fejej. Its population in 2014 was 73,512. Etymology The Arabic name (حامة) comes from the word for "hot water" (الماء الحام), a reference to the thermal springs that are widespread in the region. The similar names Hamma or Hammamet (the spas) are given to other towns and villages across North Africa. Geography Located along the Gabès- Kébili road, and at an altitude of about fifty meters, the town borders the Chott el-Fejej. It is one of the natural outlets of the great Albian Aquifer. The oasis has several sources which together form the El Hamma ouads which are 300 meters from each other. Among these are Aïn El Bordj, Aïn Chaaliya and Aïn Abdelkader. A small mountain range 220 meters above sea level separates El Hamma from the Gabès. History The town is in the ancestral lands of the Beni Zid tribe and their neig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabarka
Tabarka ( ') is a coastal town located in north-western Tunisia, close to the Algeria–Tunisia border, border with Algeria. Tabarka was occupied at various times by Punic people, Punics, Greeks, Roman people, Romans, Arabs, Genoa, Genoese and Ottoman Turks, Ottomans. The town is dominated by an offshore rock on which there remains a Republic of Genoa, Genoese castle. Nationalist leader Habib Bourguiba, later president of post-independence Tunisia, was exiled on Tabarka by the French Fourth Republic, French colonial authorities in 1952. Tourist attractions include coral fishing, the Coralis Festival of underwater photography, and its annual jazz festival. Name Tabarka was known to the Carthaginians as (). This was transcribed into ancient Greek language, Greek as ''Thaúbraka'' () and into Latin as ''Thabraca''. In modern day Berber language, Berber it is known as ''Tabarka'' or ''Tbarga'', while its Arabic language, Arabic name is ''Ṭbarqa'' (). History Although older so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djerba
Djerba (; , ; ), also transliterated as Jerba or Jarbah, is a Tunisian island and the largest island of North Africa at , in the Gulf of Gabès, off the coast of Tunisia. Administratively, it is part of Medenine Governorate. The island had a population of 139,544 at the 2004 census, which rose to 163,726 at the 2014 census. Citing its long and unique history, Tunisia has sought UNESCO World Heritage status protections for the island, and, in 2023, Djerba was officially designated a World Heritage Site. History Djerba is speculated to have been the island of the lotus-eaters where Odysseus was stranded on his voyage through the Mediterranean Sea. Djerba was known as the island of Lytos in the time of the Greeks. It was possible to locate one of its villages from the Qantara Tower, and the name Djerba was given to the area near Houmt Souk. Antiquity The Berbers are indigenous to the Maghreb. They inhabited the coasts and mountains and worked in cultivating the land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahdia
Mahdia ( ') is a Tunisian coastal city with 76,513 inhabitants, south of Monastir, Tunisia, Monastir and southeast of Sousse. Mahdia is a provincial centre north of Sfax. It is important for the associated fish-processing industry, as well as weaving. It is the capital of Mahdia Governorate. History Antiquity The old part of Mahdia corresponds to the Ancient Rome, Roman city called Aphrodisium and, later, called Africa (a name perhaps derived from the older name), or Cape Africa. The Catholic Church's list of titular sees includes a no longer residential bishopric called Africa and, since there is no record of an episcopal see in Roman Empire, Roman times called by either of these names (nor by that of Alipota, another Roman town that Charles Tissot suggested tentatively might be represented by present-day Mehdia), it is supposed that the episcopal see of Africa was established when the city was held by the Kingdom of Sicily, as a part of the Kingdom of Africa (1147–1160) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chikly
Chikly () is a small island located in the northern part of Lake of Tunis which houses Fort Santiago Chikly, a former Roman citadel which was reconstructed by the Spanish Governor of Goletta, Luys Peres Varga, between 1546 and 1550. The fort was completely abandoned in 1830 and was left to deteriorate. Chikly was declared a national cultural heritage asset in December 1993 and is owned by the Ministry of Culture of Tunisia. The fort is being restored througTunisian-Spanish cooperationinvolving the National Heritage Institute and the University of Madrid. Excavation and cleaning took place in 1994 followed by archaeological excavations in 1995. These found mosaics and charts dating back to the Roman and Byzantine The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ... periods in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |