|
Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy
Tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS, sometimes referred to as TDLS, TLS or TLAS) is a technique for measuring the concentration of certain species such as methane, water vapor and many more, in a gaseous mixture using tunable diode lasers and laser absorption spectrometry. The advantage of TDLAS over other techniques for concentration measurement is its ability to achieve very low detection limits (of the order of Parts per billion, ppb). Apart from concentration, it is also possible to determine the temperature, pressure, velocity and mass flux of the gas under observation. TDLAS is by far the most common Laser absorption spectrometry, laser based absorption technique for quantitative assessments of species in gas phase. Working A basic TDLAS setup consists of a tunable diode laser light source, transmitting (i.e. beam shaping) optics, optically accessible absorbing medium, receiving optics and detector/s. The emission wavelength of the tunable diode laser, viz. Vert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes it an economically attractive fuel, although capturing and storing it is difficult because it is a gas at standard temperature and pressure. In the Earth's atmosphere methane is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. Methane is an Organic chemistry, organic Organic compound, compound, and among the simplest of organic compounds. Methane is also a hydrocarbon. Naturally occurring methane is found both below ground and under the seafloor and is formed by both geological and biological processes. The largest reservoir of methane is under the seafloor in the form of methane clathrates. When methane reaches the surface and the Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere, it is known as atmospheric methane. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mbar
The bar is a metric unit of pressure defined as 100,000 Pa (100 kPa), though not part of the International System of Units (SI). A pressure of 1 bar is slightly less than the current average atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level (approximately 1.013 bar). By the barometric formula, 1 bar is roughly the atmospheric pressure on Earth at an altitude of 111 metres at 15 °C. The bar and the millibar were introduced by the Norwegian meteorologist Vilhelm Bjerknes, who was a founder of the modern practice of weather forecasting, with the bar defined as one megadyne per square centimetre. The SI brochure, despite previously mentioning the bar, now omits any mention of it.. The bar has been legally recognised in countries of the European Union since 2004.British Standard BS 350:2004 ''Conversion Factors for Units''. The US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) deprecates its use except for "limited use in meteorology" and lists it a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption Spectroscopy
Absorption spectroscopy is spectroscopy that involves techniques that measure the absorption of electromagnetic radiation, as a function of frequency or wavelength, due to its interaction with a sample. The sample absorbs energy, i.e., photons, from the radiating field. The intensity of the absorption varies as a function of frequency, and this variation is the absorption spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is performed across the electromagnetic spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is employed as an analytical chemistry tool to determine the presence of a particular substance in a sample and, in many cases, to quantify the amount of the substance present. Infrared and ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy are particularly common in analytical applications. Absorption spectroscopy is also employed in studies of molecular and atomic physics, astronomical spectroscopy and remote sensing. There is a wide range of experimental approaches for measuring absorption spectra. The most commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scramjet
A scramjet (supersonic combustion ramjet) is a variant of a ramjet airbreathing jet engine in which combustion takes place in supersonic airflow. As in ramjets, a scramjet relies on high vehicle speed to compress the incoming air forcefully before combustion (hence ''ram''jet), but whereas a ramjet decelerates the air to speed of sound, subsonic velocities before combustion using shock cones, a scramjet has no shock cone and slows the airflow using shockwaves produced by its ignition source in place of a shock cone. This allows the scramjet to operate efficiently at extremely high speeds. Although scramjet engines have been used in a handful of operational military vehicles, scramjets have so far mostly been demonstrated in research test articles and experimental vehicles. History Before 2000 The Bell X-1 attained Supersonic speed#Supersonic flight, supersonic flight in 1947 and, by the early 1960s, rapid progress toward faster aircraft suggested that operational aircraft wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypersonic Speed
In aerodynamics, a hypersonic speed is one that exceeds five times the speed of sound, often stated as starting at speeds of Mach 5 and above. The precise Mach number at which a craft can be said to be flying at hypersonic speed varies, since individual physical changes in the airflow (like molecular dissociation and ionization) occur at different speeds; these effects collectively become important around Mach 5–10. The hypersonic regime can also be alternatively defined as speeds where specific heat capacity changes with the temperature of the flow as kinetic energy of the moving object is converted into heat. Characteristics of flow While the definition of hypersonic flow can be quite vague and is generally debatable (especially because of the absence of discontinuity between supersonic and hypersonic flows), a hypersonic flow may be characterized by certain physical phenomena that can no longer be analytically discounted as in supersonic flow. The peculiarities in hyperso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
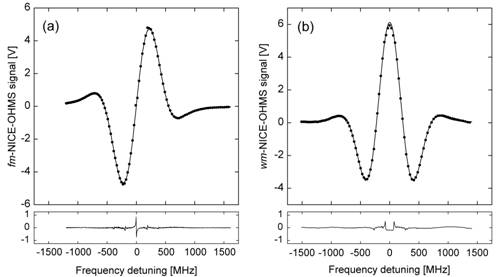
Noise-Immune Cavity-Enhanced Optical-Heterodyne Molecular Spectroscopy
Noise-immune cavity-enhanced optical-heterodyne molecular spectroscopy (NICE-OHMS) is an ultra-sensitive laser-based absorption technique that utilizes laser light to assess the concentration or the amount of a species in gas phase by absorption spectrometry (AS). Principles The NICE-OHMS technique combines cavity enhanced absorption spectrometry (CEAS) for prolonged interaction length with the sample with frequency modulation (fm) spectrometry FMS for reduction of 1/f noise. By choosing the fm-modulation frequency equal to the free spectral range (FSR) of the cavity, all components of the spectral fm-triplet are transmitted through the cavity in an identical manner. Therefore, the cavity does not compromise the balance of the fm-triplet, which otherwise would give rise to fm-background signals. It also does not convert any fluctuations of the laser frequency with respect to the transmission mode of the cavity to intensity modulation, which would deteriorate the detectability b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavity Ring-down Spectrometry
Cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS) is a highly sensitive optical spectroscopic technique that enables measurement of absolute optical extinction by samples that scatter and absorb light. It has been widely used to study gaseous samples which absorb light at specific wavelengths, and in turn to determine mole fractions down to the parts per trillion level. The technique is also known as cavity ring-down laser absorption spectroscopy (CRLAS). A typical CRDS setup consists of a laser that is used to illuminate a high-finesse optical cavity, which in its simplest form consists of two highly reflective mirrors. When the laser is in resonance with a cavity mode, intensity builds up in the cavity due to constructive interference. The laser is then turned off in order to allow the measurement of the exponentially decaying light intensity leaking from the cavity. During this decay, light is reflected back and forth thousands of times between the mirrors giving an effective path length ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Cell (spectroscopy)
Multiple-pass or long path absorption cells are commonly used in spectroscopy to measure low-concentration components or to observe weak spectra in gases or liquids. Several important advances were made in this area beginning in the 1930s, and research into a wide range of applications continues to the present day. Functional Overview Generally the goal of this type of sample cell is to improve detection sensitivity by increasing the total optical path length that travels through a small, constant sample volume. In principle, a longer Optical path length, path length results in greater detection sensitivity. Focusing mirrors must be used to redirect the beam at each reflection point, resulting in the beam being restricted to a predefined space along a controlled path until it exits the optical cavity. The output of the cell is the input of an optical detector (a specialized type of transducer), which senses specific changes in the properties of the beam that occur during interactio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas In Scattering Media Absorption Spectroscopy
Gas in scattering media absorption spectroscopy (GASMAS) is an optical technique for sensing and analysis of gas located within porous and highly scattering solids, e.g. powders, ceramics, wood, fruit, translucent packages, pharmaceutical tablets, foams, human paranasal sinuses etc. It was introduced in 2001 by Prof. Sune Svanberg and co-workers at Lund University (Sweden). The technique is related to conventional high-resolution laser spectroscopy for sensing and spectroscopy of gas (e.g. tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy, TDLAS), but the fact that the gas here is "hidden" inside solid materials give rise to important differences. Basic Principles Free gases exhibit very sharp spectral features, and different gas species have their own unique spectral fingerprints. At atmospheric pressure, absorption linewidths are typically on the order of 0.1 cm−1 (i.e. ~3 GHz in optical frequency or 0.006 nm in wavelength), while solid media have dull spectral behavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multipass Spectroscopic Absorption Cells
Multiple-pass or long path absorption cells are commonly used in spectroscopy to measure low-concentration components or to observe weak spectra in gases or liquids. Several important advances were made in this area beginning in the 1930s, and research into a wide range of applications continues to the present day. Functional Overview Generally the goal of this type of sample cell is to improve detection sensitivity by increasing the total optical path length that travels through a small, constant sample volume. In principle, a longer path length results in greater detection sensitivity. Focusing mirrors must be used to redirect the beam at each reflection point, resulting in the beam being restricted to a predefined space along a controlled path until it exits the optical cavity. The output of the cell is the input of an optical detector (a specialized type of transducer), which senses specific changes in the properties of the beam that occur during interaction with the test sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pink Noise
Pink noise, noise, fractional noise or fractal noise is a signal (information theory), signal or process with a frequency spectrum such that the power spectral density (power per frequency interval) is inversely proportional to the frequency of the signal. In pink noise, each Octave (electronics), octave interval (halving or doubling in frequency) carries an equal amount of noise energy. Pink noise sounds like a waterfall. It is often used to tune loudspeaker systems in professional audio. Pink noise is one of the most commonly observed signals in biological systems. The name arises from the pink appearance of visible light with this power spectrum. This is in contrast with white noise which has equal intensity per frequency interval. Definition Within the scientific literature, the term "1/f noise" is sometimes used loosely to refer to any noise with a power spectral density of the form S(f) \propto \frac, where is frequency, and , with exponent usually close to 1. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |