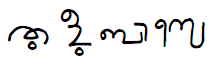|
Tuluver
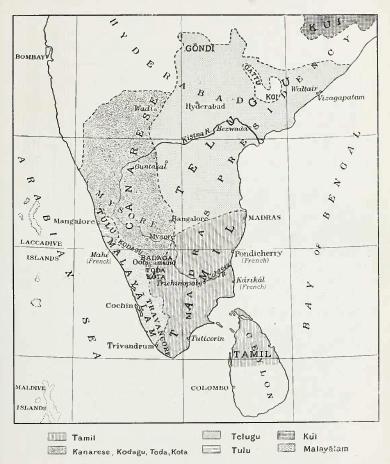
The Tulu people or Tuluvas are an ethno-linguistic group from Southern India. They are native speakers of the Tulu language and the region they traditionally inhabit is known as Tulu Nadu. This region comprises the districts of Dakshina Kannada and Udupi in Karnataka and a part of Kasaragod district in Kerala, with Mangalore, Karnataka being the commercial hub. The Census report of 2011 reported a population of 1,846,427 native Tulu speakers living in India. Etymology According to '' Keralolpathi'', the name ''Tuluva'' comes from that of one of the Cheraman Perumal kings of Kerala, who fixed his residence in the northern portion of his dominions just before its separation from Kerala, and who was called ''Tulubhan Perumal''. Mythology According to mythology, Tulu Nadu was reclaimed by Parashurama from the sea. According to the 17th-century Malayalam work '' Keralolpathi'', the lands of Kerala and Tulu Nadu were recovered from the Arabian Sea by the axe-wielding w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulu Nadu
Tulunad or Tulu Nadu, also called Bermere sristi or Parashurama Srishti, is a region and a proposed state on the southwestern coast of India. The Tulu people, known as 'Tuluva' (plural 'Tuluver'), speakers of Tulu, a Dravidian language, are the preponderant ethnic group of this region. South Canara, an erstwhile district and a historical area, encompassing the undivided territory of the contemporary Dakshina Kannada and Udupi districts of Karnataka State and Kasaragod district of Kerala state forms the cultural area of the Tuluver. Historically, Tulu Nadu lay between the Gangavalli River (Uttara Kannada district) in the north and the Chandragiri River (Kasaragod district) in the south. Currently, Tulu Nadu consists of the Dakshina Kannada and Udupi districts of Karnataka state and Kasaragod district of Kerala state. This region is not an official administrative entity. Mangalore, the fourth largest (in terms of area and population) and a major city of Karnataka is the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulu Language
Tulu () in Kannada script, ml, തുളു ഭാഷെ in Malayalam script. ''bhāṣe'', , ''bhāśe'', and ''bāśe'' are alternative spellings for the Tulu word ''bāse'' in the Kannada script. The correct spelling for the word "language" in Kannada is kn, ಭಾಷೆ ''bhāṣe'', but that is not necessarily true in Tulu. Männer's ''Tulu-English and English-Tulu Dictionary'' (1886) says, " bāšè, bāsè, ''see'' ." (vol. 1, p. 478), " bhāšè, bhāshè, ''s''. Speech, language." (vol. 1, p. 508), meaning that the four spellings are more or less acceptable. The word is actually pronounced ''bāse'' in Tulu. Note that š and sh in his dictionary correspond to ''ś'' and ''ṣ'', respectively, in ISO 15919 is a Dravidian language whose speakers are concentrated in Dakshina Kannada and the southern part of Udupi of Karnataka in south-western India and in the northern parts of the Kasaragod district of Kerala. The native speakers of T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keralolpathi
The Keralolpathi ( ml, കേരളോല്പത്തി; IAST:''kēraḷōlpatti''; ) is a Malayalam Brahmanical literary work that deals with the origin and legends of the land of Kerala. P. Shungunny Menon ascribes the authorship of this work to Thunchaththu Ramanujan Ezhuthachan, a 17th-century scholar of the Malabar region of India. A. Sreedhara Menon dates the work to 18th or 19th century. The Keralolpathi is mostly an expansion from an earlier Sanskrit work known as the ''Kerala Mahatmayam''. That work is classed among the Hindu Puranas as an ''Upa Purana'' (or sub Purana) of the ''Bhoogola Purana''. The Keralolpathi covers the ancestry of the Namboodiri Brahmins and other castes of Kerala and is sometimes called the "Kerala Ulpathy". While the "Kerala Mahatmayam" deals with the origin of Kerala and its people alone, the Keralolpathi gives a history of Kerala down to the modern age, including reference to the British in Kerala. Perumals mentioned in Keralolpathi P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunt (community)
Bunt () is an Indian community, who traditionally inhabit the coastal districts of Karnataka. Bunts were originally a warrior class community with agrarian origins, and form the landed gentry of the region. They are the dominant, land-owning farming community of Tulu Nadu and speak Tulu as well as Kundagannada as their mother tongue. The Bunts today are a largely urbanised community with a population size of 1 million worldwide. Etymology The word ''Bunt'' means ''powerful man'' or ''warrior'' in Tulu language. Bunts are also referred to as ''okkelme,'' which means farmers or cultivators and references their agrarian origins. History American anthropologist Sylvia Vatuk states that the Bunt community was a loosely defined social group. The matrilineal kin groups that constituted the caste were linguistically, geographically and economically diverse, which were united by their arrogation of aristocratic status and power. The Bunts speak Tulu and Kannada as their native ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Billava
The Billava, Billoru, Biruveru people are an ethnic group of India. They are found traditionally in Tulu Nadu region and engaged in toddy tapping, cultivation and other activities. They have used both missionary education and Sri Narayana Guru's reform movement to upgrade themselves. Etymology and origins L. K. Ananthakrishna Iyer recounted the community's belief that ''billava'' means ''bowmen'' and that it "applied to the castemen who were largely employed as soldiers by the native rulers of the district". Edgar Thurston had reached a similar conclusion in 1909. The Billavas are first recorded in inscriptions dating from the fifteenth century AD but Amitav Ghosh notes that "... this is merely an indication of their lack of social power; there is every reason to suppose that all the major Tuluva castes share an equally long history of settlement in the region". The earliest epigraphy for the Tuluva Bunt community dates to around 400 years earlier. Language There is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senguttuvan
Cheran Chenkuttuvan ( ml, ചേരൻ ചെങ്കുട്ടുവൻ ; ta, சேரன் செங்குட்டுவன்) (''c.'' 2nd century CE), literally 'the Alluring Kuttuvan Chera', identified with Katal Pirakottiya Vel Kezhu Kuttuvan,K.G. Sesha Aiyar, ''Chera Kings of the Sangam Period'', London, 1937. 21-23. was the most celebrated Chera dynasty ruler of the early land of Kerala in early historic South India. The Kuttuvan is eulogized by Paranar in the fifth decad of '' Patitrupattu'' of the '' Ettutokai'' anthology (early Tamil texts).Zvelebil, Kamil. ''The Smile of Murugan: On Tamil Literature of South India''. Leiden: E. J. Brill, 1973. 52–53. The Kuttuvan successfully intervened in a succession dispute in the Chola country and established his relative on the Chola throne. The Kadambas ― helped by the Yavanas (perhaps Greek or Roman mariners) ― attacked the kuttuvan by sea, but the Chera ruler destroyed their fleet. He is said to have defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasuki (snake)
Vasuki ( IAST: ) is the second king of the nagas in Hinduism. He is described as having a gem called ''Nagamani'' (serpent's ornament) on his head. Adishesha, the first king of the serpents and the mount of Narayana, is his elder brother, and Manasa, another ''naga'', is his sister. Vasuki is Shiva's snake, depicted around his neck. He is known in Chinese and Japanese mythology as being one of the "eight Great Dragon Kings" (八大龍王 pinyin: Bādà lóngwáng; Japanese: Hachidai Ryūō), amongst Nanda (Nāgarāja), Upananda, Sāgara (Shakara), Takshaka, Balavan, Anavatapta, and Utpala. Legends Vasuki is famous for coiling around Shiva's neck, who blessed and wore him as an ornament. Vasuki took part in the incident of Samudra Manthana by allowing both the devas and the asuras to bind him to Mount Mandara, so that they could use him as their churning rope to extract the amrita from the ocean of milk. Vasuki is also mentioned in other Hindu scriptures, such as the ''Ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
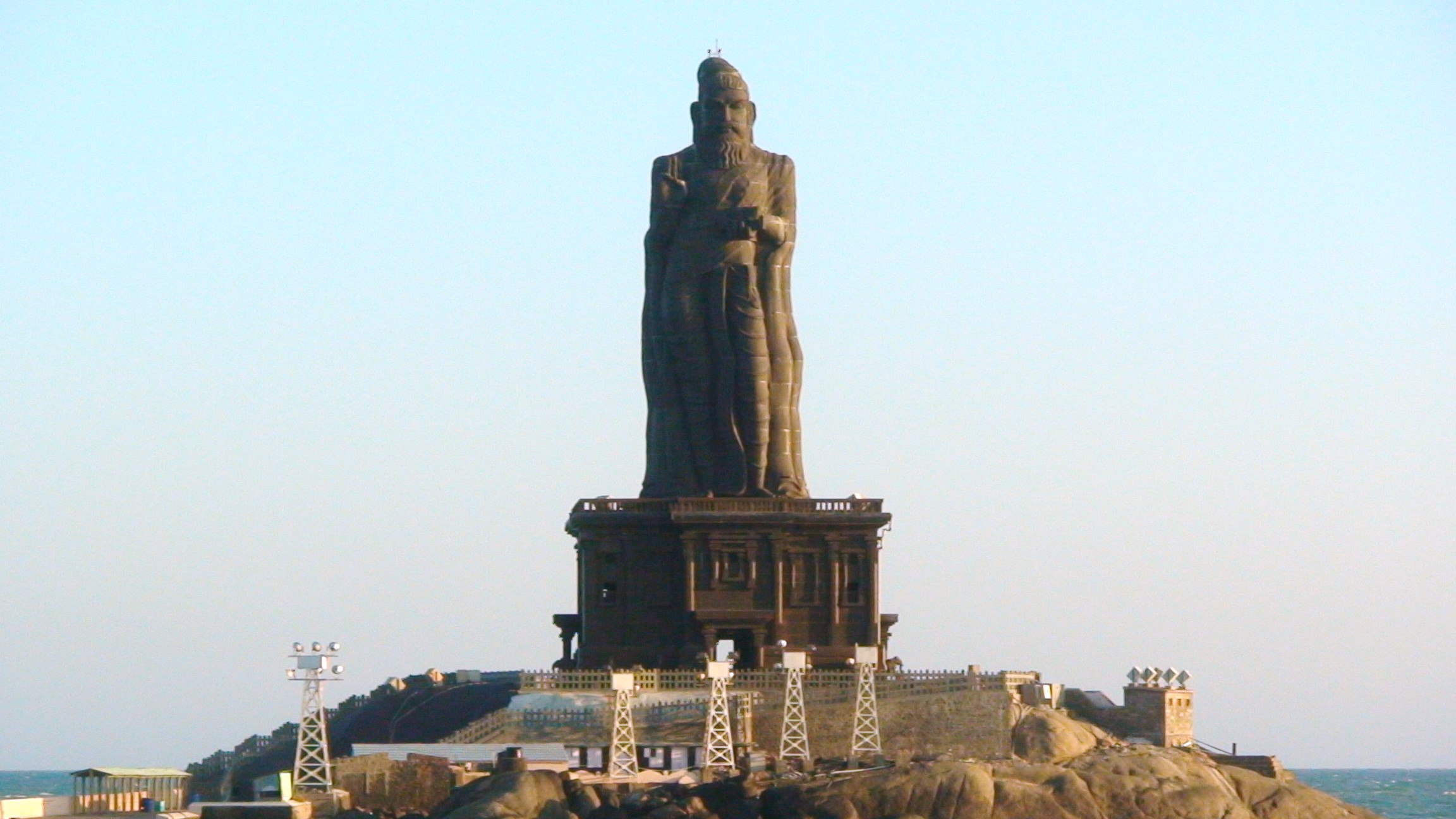
Kanyakumari
Kanniyakumari (; , referring to Devi Kanya Kumari), also known as Cape Comorin, is a city in Kanniyakumari district in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is the southern tip of the Indian subcontinent and the southernmost city in mainland India, thus referred to as 'The Land's End'. The city is situated south of Thiruvananthapuram city, and about south of Nagercoil, the headquarters of Kanniyakumari district. Kanniyakumari is a popular tourist destination and pilgrimage centre in India. Notable tourist spots include its unique sunrise and sunset points, the Thiruvalluvar Statue and Vivekananda Rock Memorial off the coast. Lying at the tip of peninsular India, the town is bordered on the west, south and east by the Laccadive Sea. It has a coastal line of stretched on the three sides. On the shores of the city is a temple dedicated to Goddess Kanniyakumari (the virgin Goddess), after which the town is named.https://thehinduimages.com/details-page.php?id=1579 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
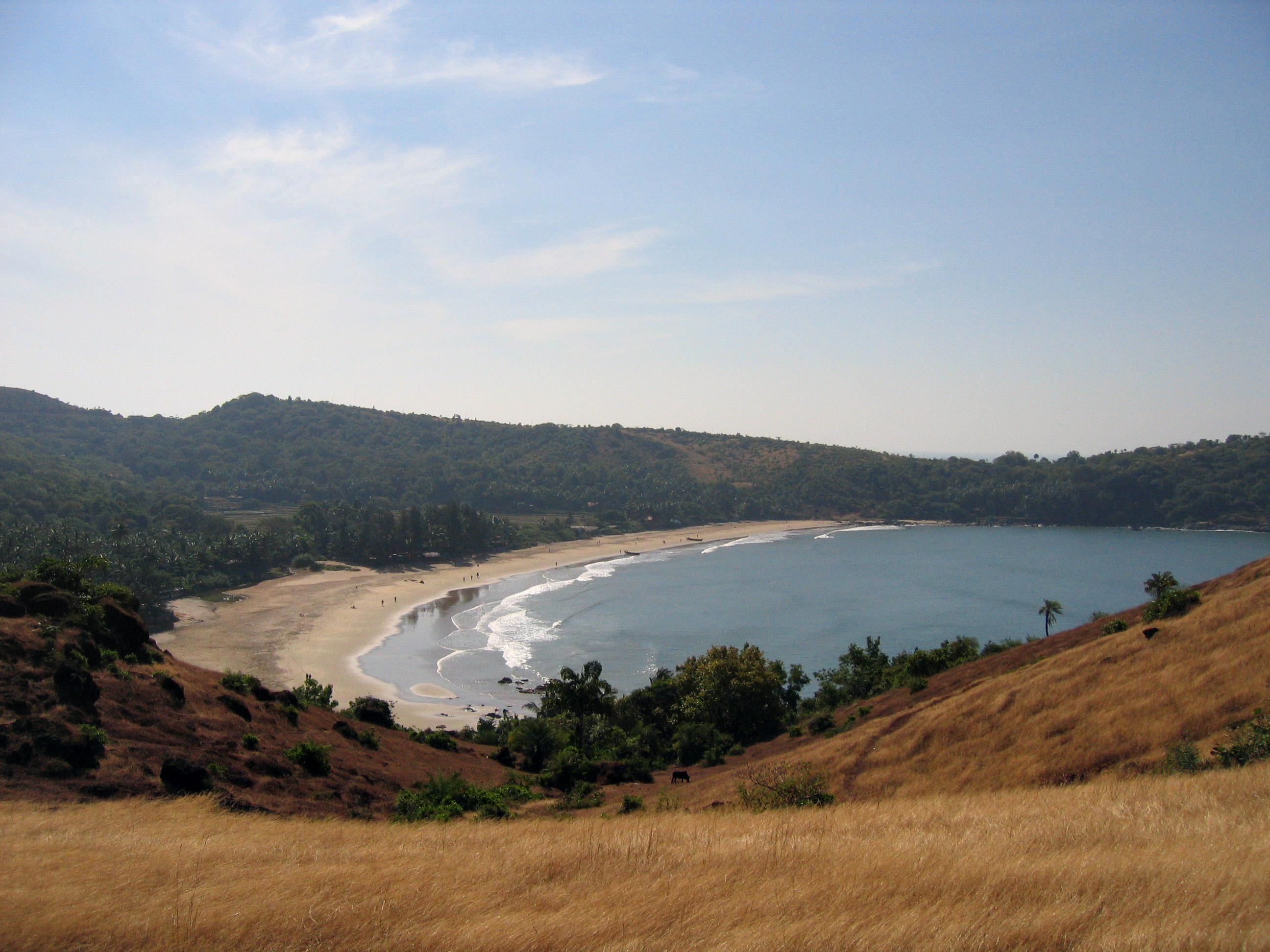
Gokarna, India
Gokarna is a small temple town located in Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka state in India, It has a population of around 20,000. The main temple and deity is Shiva, who is also known as Mahabaleshwara. This temple houses what is believed to be original image of Shiva's ''linga'' (Atmalinga). Gokarna is known as one of the seven important Hindu pilgrimage centers. It is on what was once an unspoiled beach near the estuary of the river Aghanashini. Recently, due to the influx of tourists, the character of the town has changed; it is no longer just a centre of pilgrimage, though large numbers of devotees visit to offer prayers and worship to Shiva. Due to its laid-back, unspoiled and rustic nature many younger western tourists started visiting Gokarna about three decades ago. Enterprising locals started stores and restaurants. Later the onset of millennial youth increased the tourism. Now the resorts also cater to wealthier tourists. Etymology Gokarna means ''cow's ear'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism. Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" within the Trimurti, the triple deity of supreme divinity that includes Brahma and Shiva. Gavin Flood, An Introduction to Hinduism' (1996), p. 17. In Vaishnavism, Vishnu is the supreme being who creates, protects, and transforms the universe. In the Shaktism tradition, the Goddess, or Adi Shakti, is described as the supreme Para Brahman, yet Vishnu is revered along with Shiva and Brahma. Tridevi is stated to be the energy and creative power ( Shakti) of each, with Lakshmi being the equal complementary partner of Vishnu. He is one of the five equivalent deities in Panchayatana puja of the Smarta tradition of Hinduism. According to Vaishnavism, the highest form of Ishvara is with qualities ( Saguna), and have certain form, but is limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daśāvatāra
The Dashavatara ( sa, दशावतार, ) are the ten primary avatars of Vishnu, a principal Hindu god. Vishnu is said to descend in the form of an avatar to restore cosmic order. The word ''Dashavatara'' derives from , meaning "ten", and , roughly equivalent to "incarnation". The list of included avatars varies across sects and regions, particularly in respect to the inclusion of Balarama (brother of Krishna) or Gautama Buddha. Though no list can be uncontroversially presented as standard, the "most accepted list found in Puranas and other texts is ..Krishna, Buddha." Most draw from the following set of figures, in this order: Matsya; Kurma; Varaha; Narasimha; Vamana; Parashurama; Rama; Krishna or Balarama; Buddha or Krishna; and Kalki. In traditions that omit Krishna, he often replaces Vishnu as the source of all avatars. Some traditions include a regional deity such as Vithoba or Jagannath in penultimate position, replacing Krishna or Buddha. All avatars have appeare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasurama
Parashurama (), also referred to as Rama Jamadagnya, Rama Bhargava and Veerarama, is the sixth avatar among the Dashavatara of the preserver god Vishnu in Hinduism. He is believed to be one of the ''Chiranjeevis'' (Immortals), who will appear at the end of the ''Kali Yuga'' to be the guru of Vishnu's tenth and last incarnation, Kalki. Born to Jamadagni and Renuka, the Brahmin Parashurama was foretold to appear at a time when overwhelming evil prevailed on the earth. The Kshatriya class, with weapons and power, had begun to abuse their power, take what belonged to others by force and tyrannise people. He corrected the cosmic equilibrium by destroying the Kshatriya warriors twenty-one times. He is married to Dharani, an incarnation of Lakshmi, the wife of Vishnu. He is present in the Ramayana due to the conflict with Rama (the protagonist of the Ramayana) over Shiva's broken bow. He is mentioned in the Mahabharata as the guru of Bhisma, Drona, Rukmi, and Karna. Legend A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |