|
Tucatinib
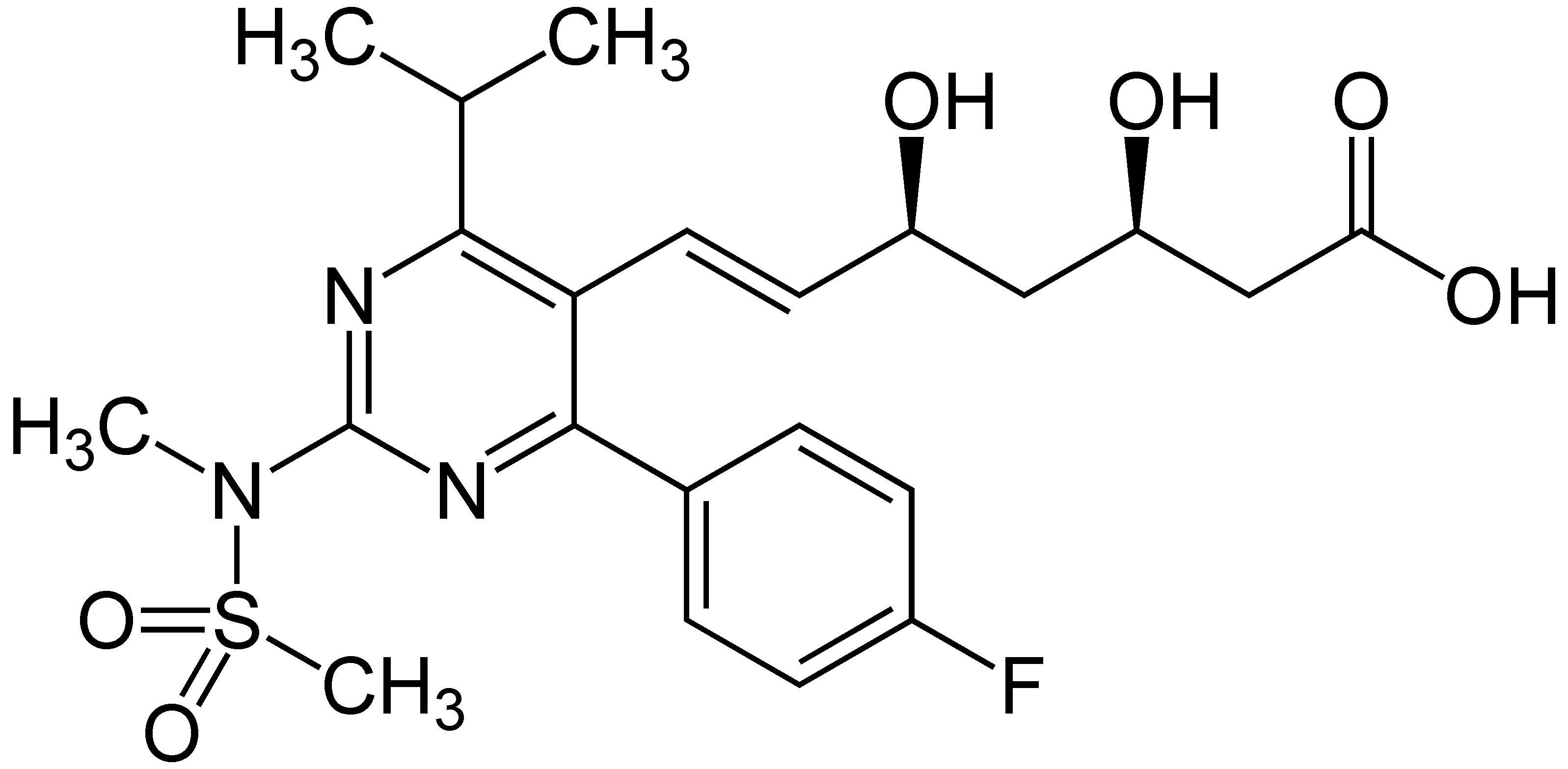
Tucatinib, sold under the brand name Tukysa, is an anticancer medication used for the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer. It is a small molecule inhibitor of HER2. It was developed by Array BioPharma and licensed to Cascadian Therapeutics (formerly Oncothyreon, subsequently part of Seattle Genetics). Common side effects include diarrhea, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (burning or tingling discomfort in the hands and feet), nausea, fatigue, hepatotoxicity (liver damage), vomiting, stomatitis (inflammation of the mouth and lips), decreased appetite, abdominal pain, headache, anemia and rash. Tucatinib may cause harm to a developing fetus or baby. Tucatinib was approved for medical use in the United States in April 2020, in Australia in August 2020, and in the European Union in February 2021. Medical uses Tucatinib is a kinase inhibitor indicated in combination with trastuzumab and capecitabine for the treatment of adults with advanced unresectable or metastatic HER ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Cytochrome P450 3A4 (abbreviated CYP3A4) () is an important enzyme in the body, mainly found in the liver and in the intestine. It oxidizes small foreign organic molecules ( xenobiotics), such as toxins or drugs, so that they can be removed from the body. It is highly homologous to CYP3A5, another important CYP3A enzyme. While many drugs are deactivated by CYP3A4, there are also some drugs which are ''activated'' by the enzyme. Some substances, such as some drugs and furanocoumarins present in grapefruit juice, interfere with the action of CYP3A4. These substances will therefore either amplify or weaken the action of those drugs that are modified by CYP3A4. CYP3A4 is a member of the cytochrome P450 family of oxidizing enzymes. Several other members of this family are also involved in drug metabolism, but CYP3A4 is the most common and the most versatile one. Like all members of this family, it is a hemoprotein, i.e. a protein containing a heme group with an iron atom. In humans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HER2-positive Breast Cancer
Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ERBB2'' gene. ERBB is abbreviated from erythroblastic oncogene B, a gene originally isolated from the avian genome. The human protein is also frequently referred to as ''HER2'' (human epidermal growth factor receptor 2) or CD340 (cluster of differentiation 340). HER2 is a member of the human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER/EGFR/ERBB) family. But contrary to other member of the ERBB family, HER2 does not directly bind ligand. HER2 activation results from heterodimerization with another ERBB member or by homodimerization when HER2 concentration are high, for instance in cancer. Amplification or over-expression of this oncogene has been shown to play an important role in the development and progression of certain aggressive types of breast cancer. In recent years the protein has become an important biomarker and target of therapy for approximately 30% of breast cancer patients. Name ''H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pertuzumab
Pertuzumab, sold under the brand name Perjeta, is a monoclonal antibody used in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel for the treatment of metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer; it also used in the same combination as a neoadjuvant in early HER2-positive breast cancer. Side effects in more than half the people taking it include diarrhea, hair loss, and loss of neutrophils; more than 10% experience loss of red blood cells, hypersensitivity or allergic reaction, infusion reactions, decreased appetite, insomnia, distortions in the sense of taste, inflammation of the mouth or lips, constipation, rashes, nail disease, and muscle pain. Women who are pregnant or planning on getting pregnant should not take it, it was not studied in people with certain heart conditions and should be used in caution in such people, and it should not be used with an anthracycline. It is unknown if pertuzumab interacts with doxorubicin. It is the first-in-class of a kind of drug called a "HER dimer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer Treatments
Cancer can be treated by surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, targeted therapy (including immunotherapy such as monoclonal antibody therapy) and synthetic lethality, most commonly as a series of separate treatments (e.g. chemotherapy before surgery). The choice of therapy depends upon the location and grade of the tumor and the stage of the disease, as well as the general state of the patient ( performance status). Cancer genome sequencing helps in determining which cancer the patient exactly has for determining the best therapy for the cancer. A number of experimental cancer treatments are also under development. Under current estimates, two in five people will have cancer at some point in their lifetime. Complete removal of the cancer without damage to the rest of the body (that is, achieving cure with near-zero adverse effects) is the ideal, if rarely achieved, goal of treatment and is often the goal in practice. Sometimes this can be accomplished ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakthrough Therapy
Breakthrough therapy is a United States Food and Drug Administration designation that expedites drug development that was created by Congress under Section 902 of the 9 July 2012 Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act. The FDA's "breakthrough therapy" designation is not intended to imply that a drug is actually a "breakthrough" or that there is high-quality evidence of treatment efficacy for a particular condition; rather, it allows the FDA to grant priority review to drug candidates if preliminary clinical trials indicate that the therapy may offer substantial treatment advantages over existing options for patients with serious or life-threatening diseases. The FDA has other mechanisms for expediting the review and approval process for promising drugs, including fast track designation, accelerated approval, and priority review. Requirements A breakthrough therapy designation can be assigned to a drug if "it is a drug which is intended alone or in combinatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antineoplastic Drugs
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms (palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Committee For Medicinal Products For Human Use
The Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), formerly known as Committee for Proprietary Medicinal Products (CPMP), is the European Medicines Agency's committee A committee or commission is a body of one or more persons subordinate to a deliberative assembly. A committee is not itself considered to be a form of assembly. Usually, the assembly sends matters into a committee as a way to explore them more ... responsible for elaborating the agency's opinions on all issues regarding medicinal products for human use. See also * Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use References External links Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Health and the European Union {{eu-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme
The Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) is a program of the Australian Government that subsidises prescription medication for Australian citizens and permanent residents, as well as international visitors covered by a reciprocal health care agreement. The PBS is separate to the Medicare Benefits Schedule, a list of health care services that can be claimed under Medicare, Australia's universal health care insurance scheme. The out-of-pocket amount for some medications has increased since 1960, with increased subsidies for concession holders beginning in 1983. Safety nets were introduced in 2000 and expanded in 2004, limiting the total out-of-pocket expense singles or families would pay per year for health care in Australia. History In 1944, the Chifley Labor Government passed the ''Pharmaceutical Benefits Act 1944'' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphan Drug
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent developed to treat medical conditions which, because they are so rare, would not be profitable to produce without government assistance. The conditions are referred to as orphan diseases. The assignment of orphan status to a disease and to drugs developed to treat it is a matter of public policy in many countries and has yielded medical breakthroughs that might not otherwise have been achieved, due to the economics of drug research and development. In the U.S. and the EU, it is easier to gain marketing approval for an orphan drug. There may be other financial incentives, such as an extended period of exclusivity, during which the producer has sole rights to market the drug. All are intended to encourage development of drugs which would otherwise lack sufficient profit motive to attract corporate research budgets and personnel. Definition According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an orphan drug is defined as one "intended for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |