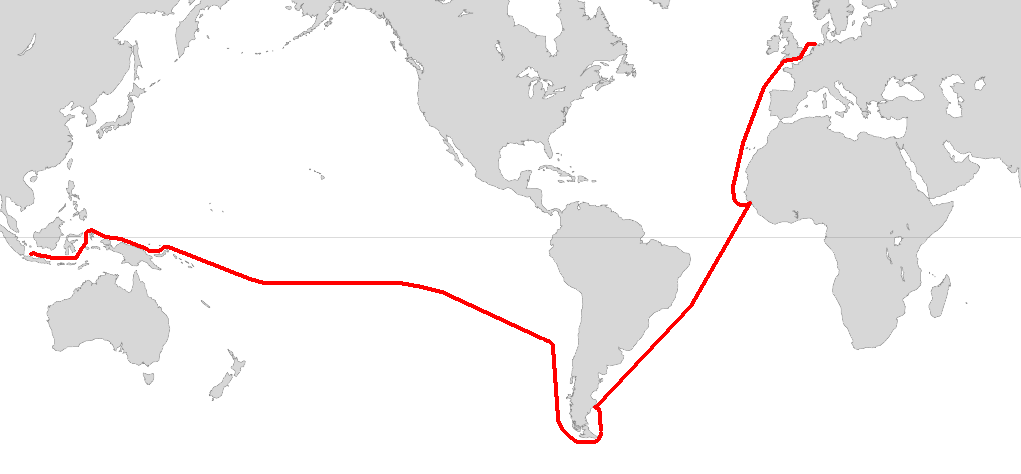
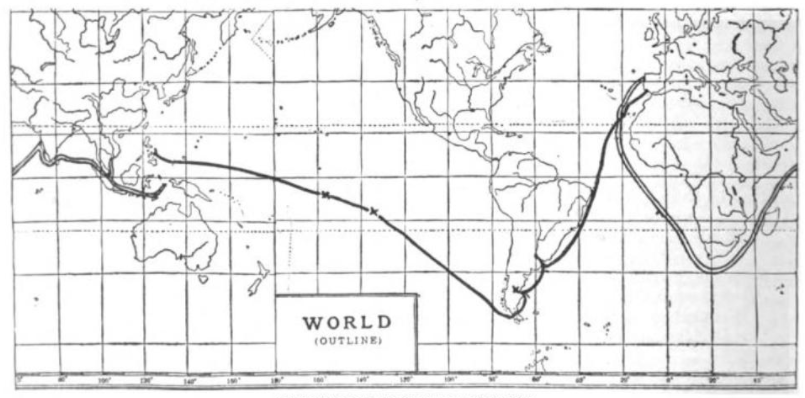
|
Tuamotu Archipelago
The Tuamotu Archipelago or the Tuamotu Islands (, officially ) are a French Polynesian chain of just under 80 islands and atolls in the southern Pacific Ocean. They constitute the largest chain of atolls in the world, extending (from northwest to southeast) over an area roughly the size of Western Europe. Their combined land area is . This archipelago's major islands are Rangiroa, Anaa, Fakarava, Hao (French Polynesia), Hao and Makemo. The Tuamotus have approximately 16,000 inhabitants. The islands were initially settled by Polynesians, and modern Tuamotuans have inherited from them a shared Polynesian culture, culture and the Tuamotuan language. The Tuamotus are a overseas collectivity, French overseas collectivity. History The early history of the Tuamotu islands is generally unknown. Archaeological findings suggest that the western Tuamotus were settled from the Society Islands as early as 900 CE or as late as 1200 CE. DNA evidence suggests that they were settled about 1110 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of French Polynesia
Historical Background and Adoption The flag of French Polynesia features a stylized canoe with five figures under a golden sun on blue waves, symbolizing the region’s cultural identity, maritime heritage, and the unity of its five archipelagos under longstanding French administration. The flag of French Polynesia, adopted officially on 23 November 1984 and replaced the old national flag that was officially adopted in 1958. It is a relatively new national symbol that reflects the region’s changing political and cultural identity. Although it remains an overseas collectivity of France, various political and cultural developments throughout the 20th century contributed to the emergence of local symbols of identity, including the flag. According to the articles of adoption, the flag of French Polynesia must be displayed with the French tricolor, and may be displayed with the flags of the component archipelagos. The French Polynesian flag must be displayed to the left of the F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands. An archipelago may be in an ocean, a sea, or a smaller body of water. Example archipelagos include the Aegean Islands (the origin of the term), the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, the Stockholm Archipelago, the Malay Archipelago (which includes the Indonesian and Philippine Archipelagos), the Lucayan (Bahamian) Archipelago, the Japanese archipelago, and the Hawaiian Archipelago. Etymology The word ''archipelago'' is derived from the Italian ''arcipelago'', used as a proper name for the Aegean Sea, itself perhaps a deformation of the Greek Αιγαίον Πέλαγος. Later, usage shifted to refer to the Aegean Islands (since the sea has a large number of islands). The erudite paretymology, deriving the word from Ancient Greek ἄρχι-(''arkhi-'', "chief") and πέλαγος (''pélagos'', "sea"), proposed by Buondelmonti, can still be found. Geograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob Roggeveen
Jacob Roggeveen (1 February 1659 – 31 January 1729) was a Dutch explorer who was sent to find Terra Australis and Davis Land, but instead found Easter Island (called so because he landed there on Easter Sunday). Jacob Roggeveen also found Bora Bora and Maupiti of the Society Islands, as well as Samoa. He planned the expedition along with his brother Jan Roggeveen, who stayed in the Netherlands. Early career His father, Arend Roggeveen, was a mathematician with much knowledge of astronomy, geography, rhetorics, philosophy, and the theory of navigation as well. He occupied himself with study of the mythical Terra Australis, and even got a patent for an exploratory excursion, but it was to be his son who, at the age of 62, eventually equipped three ships and made the expedition. He became notary of Middelburg (the capital of the province of Zeeland, where he was born). On 12 August 1690, he graduated as a doctor of the law at the University of Harderwijk. About this time he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob Le Maire
Jacob Le Maire (c. 1585 – 22 December 1616) was a Dutch mariner who circumnavigated the Earth in 1615 and 1616. The strait between Tierra del Fuego and Isla de los Estados was named the Le Maire Strait in his honour, though not without controversy. It was Le Maire himself who proposed to the council aboard ''Eendracht'' that the new passage should be called by his name and the council unanimously agreed with Le Maire. The author or authors of ''The Relation'' took ''Eendracht'' captain Willem Schouten's side by proclaiming: :“ ... our men had each of them three cups of wine in signe of ioy for our good hap ... nd the naming ofthe ''Straights of Le Maire'', although by good right it should rather have been called ''Willem Schouten Straight'', after our Masters Name, by whose wise conduction and skill in sayling, the same was found.”. ''Eendracht'' then rounded Cape Horn, proving that Tierra del Fuego was not a continent. Biography Jacob Le Maire was born in either Antwer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willem Schouten
Willem Cornelisz Schouten (1625) was a Dutch navigator for the Dutch East India Company. He was the first to sail the Cape Horn route to the Pacific Ocean. Biography Willem Cornelisz Schouten was born around 1567 in Hoorn, Holland, Seventeen Provinces. In April 1601 Willem Schouten was skipper of the Duyfken in the 'Moluccan fleet' of Wolfert Hermansz, and participated in the Battle of Bantam. On 1 July 1615 Willem Schouten and his younger brother Jan Schouten sailed from Texel in the Netherlands, in an expedition led by Jacob Le Maire and sponsored by Isaac Le Maire and his in equal shares with Schouten. The expedition consisted of two ships: ''Eendracht'' and ''Hoorn''.Quanchi, ''Historical Dictionary of the Discovery and Exploration of the Pacific Islands'', pp. 222–33 A main purpose of the voyage was to search for . A further objective was to explore a western route to the Pacific Ocean to evade the trade restrictions of the Dutch East India Company (VOC) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedro Fernandes De Queirós
Pedro Fernandes de Queirós () (1563–1614) was a Portuguese navigator in the service of Spain. He is best known for leading several Spanish voyages of discovery in the Pacific Ocean, in particular the 1595–1596 voyage of Álvaro de Mendaña y Neira, and for the 1605–1606 expedition that crossed the Pacific in search of '' Terra Australis''. Early life Queirós (or Quirós as he signed) was born in Évora, Portugal in 1563. As the Portuguese and Spanish monarchies had been unified under the king of Spain in 1580 (following the vacancy of the Portuguese throne, which lasted for sixty years, until 1640, when the Portuguese monarchy was restored), Queirós entered Spanish service as a young man and became an experienced seaman and navigator. In April 1595, he joined Álvaro de Mendaña y Neira on his voyage to colonize the Solomon Islands, serving as chief pilot. After Mendaña's death in October 1595, Queirós is credited with taking command and saving the only remaining sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magellan Expedition
The Magellan expedition, sometimes termed the MagellanElcano expedition, was a 16th-century Spanish Empire, Spanish expedition planned and led by Portuguese Empire, Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan. One of the most important voyages in the Age of Discovery, its purpose was to secure a maritime Spice trade, trade route with the Maluku Islands, Moluccas, or Spice Islands, in present-day Indonesia. The expedition departed Spain in 1519 and returned there in 1522 led by Spanish navigator Juan Sebastián Elcano, who crossed the Indian Ocean after Battle of Mactan, Magellan's death in the Philippines. Totaling 60,440 km, or 37,560 mi, the nearly three-year voyage achieved the first circumnavigation of Earth in history. It also marked the first Transpacific crossing, crossing of the Pacific by a European expedition, revealing the vast scale of that ocean, and proved that ships could sail around the world on a western sea route. The five-ship fleet left Spain on 20 September 1519 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer best known for having planned and led the 1519–22 Spanish expedition to the East Indies. During this expedition, he also discovered the Strait of Magellan, allowing his fleet to pass from the Atlantic into the Pacific Ocean and perform the first European navigation to Asia via the Pacific. Magellan was killed in battle in the Philippines and his crew, commanded by the Spanish Juan Sebastián Elcano, completed the return trip to Spain in 1522 achieving the first circumnavigation of Earth in history. Born around 1480 into a family of minor Portuguese nobility, Magellan became a skilled sailor and naval officer in service of the Portuguese Crown in Asia. King Manuel I refused to support Magellan's plan to reach the Moluccas, or Spice Islands, by sailing westwards around the American continent. Magellan then proposed the same plan to King Charles I of Spain, who approved it. In Seville, he married, fathere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marae
A ' (in Māori language, New Zealand Māori, Cook Islands Māori, Tahitian language, Tahitian), ' (in Tongan language, Tongan), ' (in Marquesan language, Marquesan) or ' (in Samoan language, Samoan) is a communal or sacred place that serves religious and social purposes in Polynesian culture, Polynesian societies. In all these languages, the term also means cleared and free of weeds or trees. generally consist of an area of cleared land roughly rectangular (the itself), bordered with stones or wooden posts (called ' in Tahitian and Cook Islands Māori) perhaps with ' (terraces) which were traditionally used for ceremonial purposes; and in some cases, such as Easter Island, a central stone ' or ''a'u'' is placed. In the Easter Island Rapa Nui people, Rapa Nui culture, the term ''ahu'' or ''a'u'' has become a synonym for the whole marae complex. In some modern Polynesian societies, notably that of the Māori people, Māori of New Zealand, the marae is still a vital part of everyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mataiva
Mataiva (meaning "Nine Eyes" in Tuamotuan language, Tuamotuan), Tepoetiriura ("Sparkling Pearl")Mataiva, Eden des Tuamotu Publisher: Air Tahiti: Polynesian Airline - News (''in French''). ''Author: Jean-François Butaud''. Accessed 22 February 2010 or Lazarev atoll is a coral atoll in the Tuamotus, Tuamotu Archipelago. It is located in the Palliser Islands, Palliser group, and is the westernmost of the Tuamotus. The nearest atoll, Tikehau, is located 35 km to the east. Rangiroa is located 79 km to the east, and Tahiti is 311 km to the south. Geography [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manihi
Manihi, or Paeua, is a coral atoll in the Tuamotu Archipelago, part of French Polynesia. It is one of the northernmost of the Tuamotus, located in the King George subgroup. The closest land to Manihi is Ahe Atoll, located 14 km to the west. The population is 648 inhabitants (2022 census). Geography Manihi is a relatively large elongated atoll. Its oval-shaped lagoon measures 27 km in length and 8 km in width, and is ringed by innumerable islets. The lagoon is well known among snorkelers for its beautiful and diverse marine fauna, including, among other species, the manta ray. There is only one pass to enter the lagoon, located close to the atoll's southern end. It is known as ''Passe de Tairapa''. The chief village is Paeua. Another important village, Turipaoa, is located in the south-western part of the atoll, and is home to about 400 inhabitants. Several of the islands are inhabited, by populations ranging from single individuals to as many as 400. Demograp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society Islands
The Society Islands ( , officially ; ) are an archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean that includes the major islands of Tahiti, Mo'orea, Moorea, Raiatea, Bora Bora and Huahine. Politically, they are part of French Polynesia, an overseas country of France, overseas country of the France, French Republic. Geographically, they form part of Polynesia. Name The term ''Society Islands'' was first used by Captain James Cook when he visited the Leeward Islands (Society Islands), Leeward Islands, a subgroup of six of the modern-day Society Islands, during his First voyage of James Cook, expedition to the south Pacific Ocean in 1769. It has been asserted that the name honors the Royal Society, the sponsor of his voyage, but this is disputed. Cook wrote in his journal: History Settlement The first Polynesians are understood to have arrived on these islands around 1000AD. Oral history origin The islanders explain their origins in terms of an oral tradition, orally transmitted sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |