|
Troy VIIa
Troy in the Late Bronze Age was a thriving coastal city consisting of a steep fortified citadel and a sprawling lower town below it. It had a considerable population and extensive foreign contacts, including with Mycenaean Greece. Geographic and linguistic evidence suggests that it corresponds to the city of Wilusa known from Hittite texts. Its Stratigraphy (archaeology), archaeological sublayers Troy VIh and Troy VIIa are among the candidates for a historicity of the Iliad, potential historical setting for the myths of the Trojan War, since aspects of their architecture are consistent with the ''Iliad'' description of mythic Troy and they show potential signs of violent destruction. Periodization Late Bronze Age Troy includes parts of the archaeological layers known as Troy VI and Troy VII. Troy VI was built . Its final sublayer, Troy VIh, was destroyed . The early sublayers of Troy VII were contemporary with the late period of Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean culture and the Hittite Em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troy
Troy (/; ; ) or Ilion (; ) was an ancient city located in present-day Hisarlik, Turkey. It is best known as the setting for the Greek mythology, Greek myth of the Trojan War. The archaeological site is open to the public as a tourist destination, and was added to the List of World Heritage Sites in Turkey, UNESCO World Heritage list in 1998. Troy was repeatedly destroyed and rebuilt during its 4000 years of occupation. As a result, the site is divided into nine Stratigraphy (archaeology), archaeological layers, each corresponding to a city built on the ruins of the previous. Archaeologists refer to these layers using Roman numerals, Troy I being the earliest and Troy IX being the latest. Troy was first settled around 3600 BC and grew into a small fortified city around 3000 BC (Troy I). Among the early layers, Troy II is notable for its wealth and imposing architecture. During the Late Bronze Age, Troy was called Wilusa and was a vassal of the Hittite Empire. The final layer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
950s BC
The 950s BC is a decade which lasted from 959 BC to 950 BC. Events and trends * 959 BC—Psusennes II succeeds Siamun as king of Egypt. * 957 BC– Solomon's Temple is completed. 959 BC is also a proposed date. * 957 BC—The reign of Mu Wang of the Zhou dynasty begins. * 952 BC— Thersippus, King of Athens dies after a reign of 41 years and is succeeded by his son Phorbas. * 950 BC—Northern Egypt starts to be ruled by Libyan pharaohs. The Libyans build cities and for the first time a sturdy urban life grows up in the Nile Delta. * c. 950 BC- 800 BC—Some early parts of the Bible are written. * c. 950 BC—Kurukshetra War Births * Osorkon I, pharaoh of Egypt Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ..., is born (approximate date). * King Parikshit of Kuru dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troy (Ilion), Turkey (7446656654)
Troy (/; ; ) or Ilion (; ) was an ancient city located in present-day Hisarlik, Turkey. It is best known as the setting for the Greek myth of the Trojan War. The archaeological site is open to the public as a tourist destination, and was added to the UNESCO World Heritage list in 1998. Troy was repeatedly destroyed and rebuilt during its 4000 years of occupation. As a result, the site is divided into nine archaeological layers, each corresponding to a city built on the ruins of the previous. Archaeologists refer to these layers using Roman numerals, Troy I being the earliest and Troy IX being the latest. Troy was first settled around 3600 BC and grew into a small fortified city around 3000 BC (Troy I). Among the early layers, Troy II is notable for its wealth and imposing architecture. During the Late Bronze Age, Troy was called Wilusa and was a vassal of the Hittite Empire. The final layers (Troy VIII-IX) were Greek and Roman cities which served as tourist attractions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
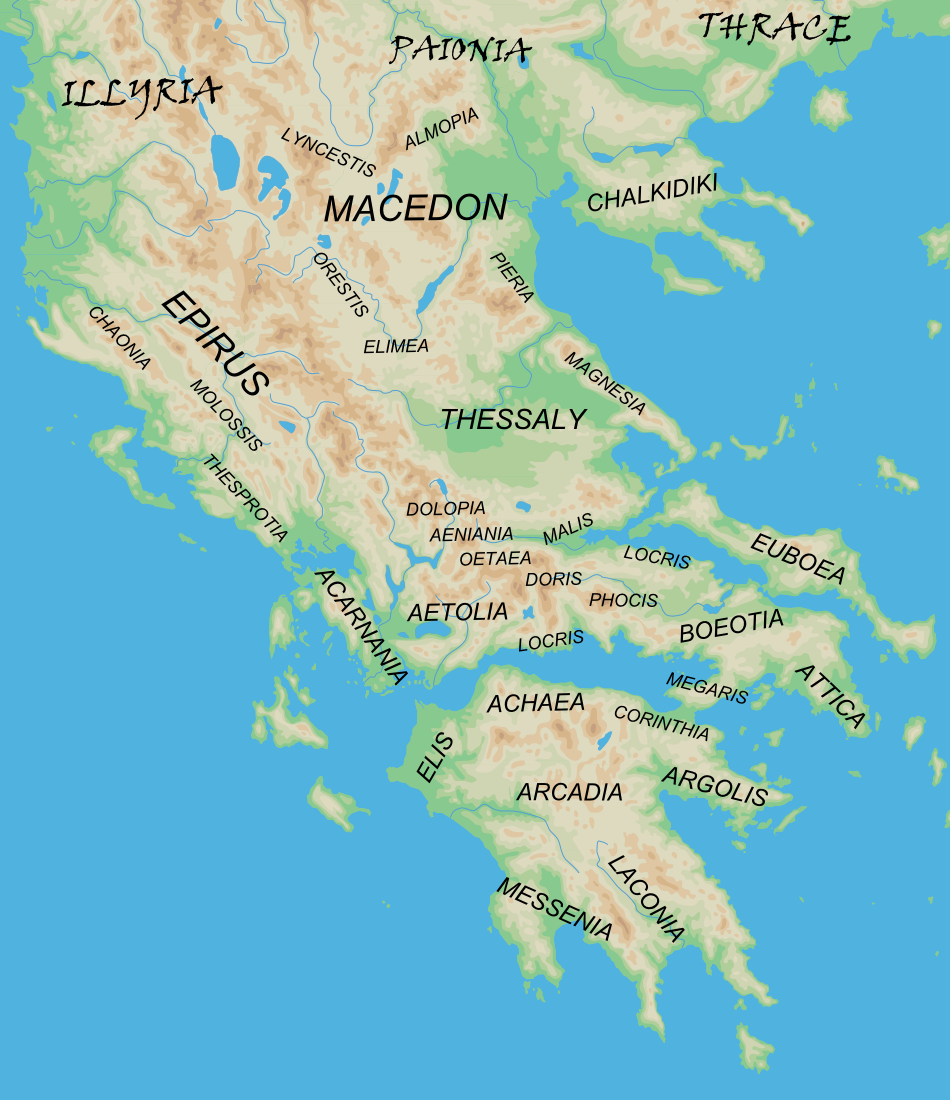
Argolid
The regions of ancient Greece were sub-divisions of the Hellenic world as conceived by the ancient Greeks, shown by their presence in the works of ancient historians and geographers or in surviving legends and myths. Conceptually, there is no clear theme to the structure of these regions. Some, particularly in the Peloponnese, can be seen primarily as distinct geo-physical units, defined by physical boundaries such as mountain ranges and rivers. Conversely, the division of central Greece between Boeotia, Phocis, Doris and the three parts of Locris, seems to be attributable to ancient tribal divisions and not major geographical features. Both types of regions retained their identity throughout the Greek Dark Ages and its tumultuous changes in the local population and culture, giving them a less political and more symbolic presence. Other geographical divisions not identified with the aforementioned areas did, however, change over time, suggesting a closer connection with tribal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midea (Argolid)
Midea () or Mideia (Μίδεια) was a city of ancient Argolis. Mythology and proto-history Midea was originally called Perseuspolis (Περσέως πόλις), and is mentioned by Pseudo-Apollodorus in connection with its eponymous hero Perseus. It was said to have derived its name from the wife of Electryon, and was celebrated as the residence of Electryon and the birthplace of his daughter Alcmena, best known as the mother of Heracles. But it is mentioned in the earliest division of the country, along with the Heraeum and Tiryns, as belonging to Proetus. It was the residence of Hippodameia in her banishment. History It was destroyed by Argos, probably at the same time as Tiryns, soon after the Greco-Persian Wars. Strabo describes Midea as near Tiryns; and from its mention by Pausanias, in connection with the Heraeum and Tiryns, it must be placed on the eastern edge of the Argeian plain. The only clue in the ancient authors to its exact position a statement by Pausani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megaron
The ''megaron'' (; , , : ''megara'' ) was the great hall in very early Mycenae, Mycenean and Ancient Greece, ancient Greek palace complexes. Architecturally, it was a rectangular hall that was supported by four columns, fronted by an open, two-columned portico, and had a central, open hearth that vented though an Oculus (architecture), oculus in the roof. The ''megaron'' also contained the Throne room, throne-room of the ''Anax, wanax'', or Mycenaean ruler, whose throne was located in the main room with the central hearth. Similar architecture is found in the Ancient Near East, though the presence of the open portico, generally supported by columns, is particular to the Aegean civilization, Aegean. ''Megara'' are sometimes referred to as "long-rooms", as defined by their rectangular (non-square) shape and the position of their entrances, which are always along the shorter wall so that the depth of the space is larger than the width.. There were often many rooms around the centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dardanelles
The Dardanelles ( ; ; ), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli (after the Gallipoli peninsula) and in classical antiquity as the Hellespont ( ; ), is a narrow, natural strait and internationally significant waterway in northwestern Turkey that forms part of the continental boundary between Asia and Europe and separates Asian Turkey from European Turkey. Together with the Bosporus, the Dardanelles forms the Turkish Straits. One of the world's narrowest straits used for International waterway, international navigation, the Dardanelles connects the Sea of Marmara with the Aegean Sea, Aegean and Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean seas while also allowing passage to the Black Sea by extension via the Bosporus. The Dardanelles is long and wide. It has an average depth of with a maximum depth of at its narrowest point abreast the city of Çanakkale. The first fixed crossing across the Dardanelles opened in 2022 with the completion of the 1915 Çanakkale Bridge. Most of the northe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age in West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in modern-day Turkey in the early 2nd millennium BC. The Hittites formed a series of Polity, polities in north-central Anatolia, including the kingdom of Kussara (before 1750 BC), the Kültepe, Kanesh or Nesha Kingdom (–1650 BC), and an empire centered on their capital, Hattusa (around 1650 BC). Known in modern times as the Hittite Empire, it reached its peak during the mid-14th century BC under Šuppiluliuma I, when it encompassed most of Anatolia and parts of the northern Levant and Upper Mesopotamia, bordering the rival empires of the Hurri-Mitanni and Assyrians. Between the 15th and 13th centuries BC, the Hittites were one of the dominant powers of the Near East, coming into conflict with the New Kingdom of Egypt, the Middle Assyrian Empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Century BC
The 10th century BC comprises the years from 1000 BC to 901 BC. This period followed the Late Bronze Age collapse in the Near East, and the century saw the Early Iron Age take hold there. The Greek Dark Ages which had come about in 1200 BC continued. The Neo-Assyrian Empire is established towards the end of the 10th century BC. In the Iron Age in India, the Vedic period is ongoing. In China, the Zhou dynasty is in power. Bronze Age Europe continued with Urnfield culture. Japan was inhabited by an evolving hunter-gatherer society during the Jōmon period. The world in the 10th century BC Events * 1000 BC: India— Iron Age of India. Indian kingdoms rule India— Panchala, Kuru, Kosala, Pandya and Videha. * 1000 BC: The Sa Huỳnh culture started in central and southern Vietnam. * 993 BC: Amenemope succeeds Psusennes I as king of Egypt. * 993 BC: Archippus, King of Athens dies after a reign of 19 years and is succeeded by his son Thersippus. * 984 BC: Osorkon th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1050s BC
The 1050s BC is a decade which lasted from 1059 BC to 1050 BC. Events and trends * 1057 BC—According to Josephus, Solomon's Temple finishes construction on January 19. This predates secular estimates by more than 120 years and is not considered reliable or accurate. * 1054 BC—Shamshi-Adad IV, son of Tiglath-Pileser I, usurps the Assyrian throne from his nephew, Eriba-Adad II. * 1053 BC—Death of Kang, king of the Zhou of ancient China. In September, a five-planetary alignment occurs. * 1052 BC— Zhao succeeds Kang. * 1051 BC—Saul becomes the first King of ancient Israel. * 1050 BC—Death of Shamshi-Adad IV; his son, Ashurnasirpal I, succeeds him as King of Assyria. * 1050 BC—Philistines capture the Ark of the Covenant from Israel in battle. (Approximate date) * —The Shang dynasty ends in ancient China and is replaced by the Zhou dynasty. * —Proto-Geometric period starts in ancient Greece. Significant people * Simbar-shipak, king of Babylon, is born (appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
11th Century BC
The 11th century BC comprises all years from 1100 BC to 1001 BC. Although many human societies were literate in this period, some of the individuals mentioned below may be apocryphal rather than historically accurate. The world in the 11th century BC Events * 1089 BC: Melanthus, legendary King of Athens, dies after a reign of 37 years and is succeeded by his son Codrus. * 1069 BC: Ramses XI dies, ending the Twentieth Dynasty. He is succeeded by Smendes I, who founds the Twenty-first Dynasty. * 1068 BC: Codrus, legendary King of Athens, dies in battle against Dorian invaders after a reign of 21 years. Athenian tradition considers him the last king to have held absolute power. Modern historians consider him the last king whose life account is part of Greek mythology. He is succeeded by his son Medon. * 1050 BC: Philistines capture the Ark of the Covenant from Israel in battle. (Approximate date) * 1048 BC: Medon, King of Athens, dies after a reign of 20 years and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1100s BC (decade)
The 1100s BC is a decade which lasted from 1109 BC to 1100 BC. Events and trends * 1104 BC—Foundation of Cadiz, Spain.Strabo, ''Geographica'' 3.5.5 * 1100 BC—Tiglath-Pileser I of Assyria conquers the Hittites. * —Maya Calendar counts time from this point. * —The Dorians invade Ancient Greece. * — Mycenaean era ends with the destruction of that civilization. The collapse of Mycenaean dominance starts. * — Late Minoan culture ends. * —Greek Dark Ages begin. * —Beginning of the proto-Villanovan culture in northern Italy. * —The New Kingdom in Egypt comes to an end. * —The Shang dynasty ends in China. * —Kurukshetra War begins in Later Vedic period in Kuru Kingdom. Significant people * c. 1102 BC—Samuel is born. * c. 1100 BC—Zarathustra is born. Inventions, discoveries, introductions * Alphabet, developed by Phoenicians. * MUL.APIN, developed by Assyrians: an ancient catalog of constellation A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |