|
Tropomodulin
Tropomodulin (TMOD) is a protein which binds and caps the minus end of actin (the "pointed" end), regulating the length of actin filaments in muscle and non-muscle cells. The protein functions by physically blocking the spontaneous dissociation of Adenosine diphosphate, ADP-bound actin monomers from the minus end of the actin fibre. This, along with plus end capping proteins, such as capZ stabilise the structure of the actin filament. End capping is particularly important when long-lived actin filaments are necessary, for example: in myofibrils. Inhibition of tropomodulin capping activity leads to dramatic increase in thin filament length from its pointed end. Actin filaments have two differing ends where one is the fast-acting barbed end and the other is the slow growing pointed end. Since TMOD binds to the pointed end of actin it is essential in cell morphology, cell movement, and muscle contraction. TMOD has been identified as an erythrocyte with 359 amino acids and it is a glob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of over 100 μM; its mass is roughly 42 kDa, with a diameter of 4 to 7 nm. An actin protein is the monomeric subunit of two types of filaments in cells: microfilaments, one of the three major components of the cytoskeleton, and thin filaments, part of the contractile apparatus in muscle cells. It can be present as either a free monomer called G-actin (globular) or as part of a linear polymer microfilament called F-actin (filamentous), both of which are essential for such important cellular functions as the mobility and contraction of cells during cell division. Actin participates in many important cellular processes, including muscle contraction, cell motility, cell division and cytokinesis, vesicle and organelle mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PDB 1pgv EBI
PDB or pdb may refer to: Organizations * Party of German-speaking Belgians (German: '), a former Belgian political party * Promised Day Brigade, a former Iraqi organization Science and technology * Protein Data Bank, a biological molecule database ** Protein Data Bank (file format) * Potato dextrose broth, a microbiological growth medium * Pee Dee Belemnite, a reference standard for isotopes; see ''δ''13C Computing * PDB (Palm OS), a record database format * Pluggable database, in Oracle Database * Program database, a debugging information format * Python Debugger (pdb), of the Python programming language; see Stepping Other uses * Chess Problem Database Server (PDB Server), a repository for chess problems * Pousette-Dart Band, an American band * President's Daily Brief, a US intelligence document See also * 1,4-Dichlorobenzene or ''para''-dichlorobenzene (PDCB), a chemical * Bangladesh Power Development Board The Bangladesh Power Development Board (BPDB) is a governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
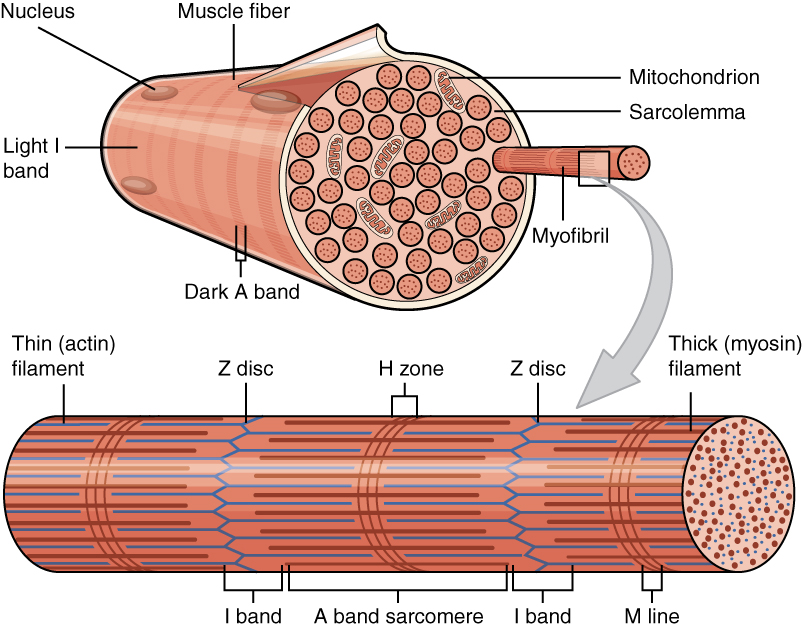
Muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contraction, contract. Muscle tissue contains special Muscle contraction, contractile proteins called actin and myosin which interact to cause movement. Among many other muscle proteins, present are two regulatory proteins, troponin and tropomyosin. Muscle is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle tissue is striated consisting of elongated, multinucleate muscle cells called muscle fibers, and is responsible for movements of the body. Other tissues in skeletal muscle include tendons and perimysium. Smooth and cardiac muscle contract involuntarily, without conscious intervention. These muscle types may be activated both through the interaction of the central nervous system as well as by innervation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Diphosphate
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP), also known as adenosine pyrophosphate (APP), is an important organic compound in metabolism and is essential to the flow of energy in living cells. ADP consists of three important structural components: a sugar backbone attached to adenine and two phosphate groups bonded to the 5 carbon atom of ribose. The diphosphate group of ADP is attached to the 5’ carbon of the sugar backbone, while the adenine attaches to the 1’ carbon. ADP can be interconverted to adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and adenosine monophosphate (AMP). ATP contains one more phosphate group than ADP, while AMP contains one fewer phosphate group. Energy transfer used by all living things is a result of dephosphorylation of ATP by enzymes known as ATPases. The cleavage of a phosphate group from ATP results in the coupling of energy to metabolic reactions and a by-product of ADP. ATP is continually reformed from lower-energy species ADP and AMP. The biosynthesis of ATP is achieved th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CapZ
CapZ, also known as CAPZ, CAZ1 and CAPPA1, is a capping protein that caps the barbed end of actin filaments in muscle cells. Structure CapZ is a heterodimeric molecule, made up of an α and β subunit. The α and β subunits are similar in structure. Each subunit is divided into three domains and a shared C-terminal extension. Helix 1-3 is an N-terminal that is composed of three antiparallel helices that are arranged in an up, down, up pattern. Helix 4 is a C-terminal made up of an antiparallel β sheet which is composed of five β strands. On one side of the C-terminal, there is a shorter N-terminal helix and a long C-terminal helix. This long C-terminal helix makes up helix 5. The final helix, helix 6 differs in the α and β subunits. The β subunit is longer than the α subunit. Function Actin stabilisation The main function of CapZ is to cap the barbed (plus) end of actin filaments in muscle cells. It is located in the Z band of the muscle sarcomere. This protein helps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myofibrils
A myofibril (also known as a muscle fibril or sarcostyle) is a basic rod-like organelle of a muscle cell. Skeletal muscles are composed of long, tubular cells known as muscle fibers, and these cells contain many chains of myofibrils. Each myofibril has a diameter of 1–2 micrometres. They are created during embryonic development in a process known as myogenesis. Myofibrils are composed of long proteins including actin, myosin, and titin, and other proteins that hold them together. These proteins are organized into thick, thin, and elastic myofilaments, which repeat along the length of the myofibril in sections or units of contraction called sarcomeres. Muscles contract by sliding the thick myosin, and thin actin myofilaments along each other. Structure Each myofibril has a diameter of between 1 and 2 micrometres (μm). The filaments of myofibrils, myofilaments, consist of three types, thick, thin, and elastic filaments. *Thin filaments consist primarily of the protein act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |