|
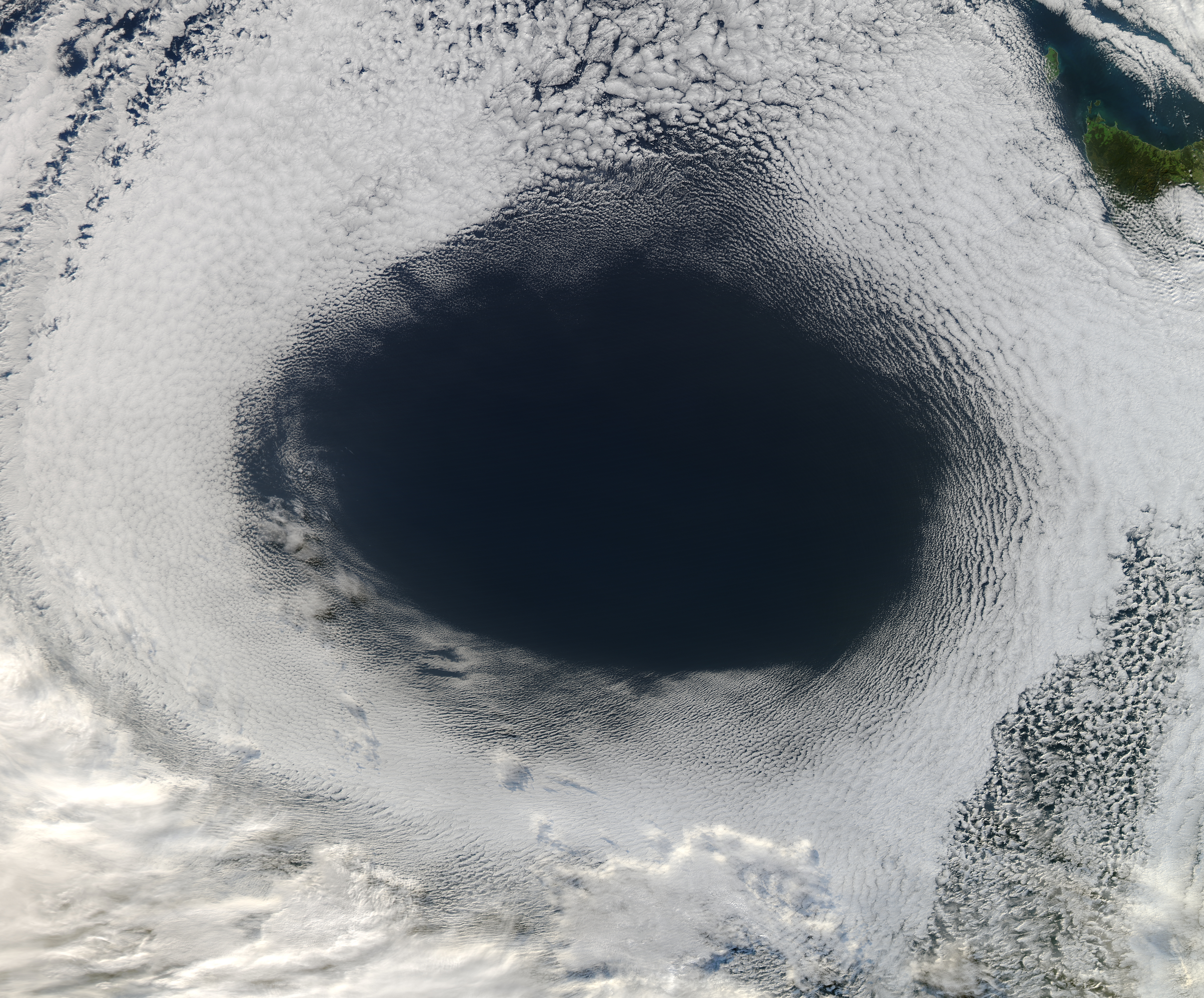
Tropical Depression Five (2010)
Tropical Depression Five was an Atlantic tropical cyclone that lasted for 12 hours, although its remnants persisted for almost another week. Its precursor was from a non-tropical trough east of Florida, and on August 10 it developed in the southeastern Gulf of Mexico. It was the fifth depression of the 2010 Atlantic hurricane season. The system was declassified as a tropical cyclone the following day, a remnant circulation later moved over Louisiana and Mississippi, producing heavy rainfall and causing flooding. Along the Florida coast, the system produced heavy waves that contributed to two deaths. Moving inland, the remnants of the depression reached central Alabama before turning southward. The system nearly redeveloped into a tropical cyclone on August 16 after it again reached the Gulf of Mexico, but it became disorganized and turned northward into Mississippi. The depression twice caused BP to delay work in building a relief well to combat the Deepwater Horiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Coast Of The United States
The Gulf Coast of the United States, also known as the Gulf South or the South Coast, is the coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The list of U.S. states and territories by coastline, coastal states that have a shoreline on the Gulf of Mexico are Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, and these are known as the ''Gulf States''. The economy of the Gulf Coast area is dominated by industries related to energy, petrochemicals, fishing, aerospace, agriculture, and tourism. The large cities of the region are (from west to east) Brownsville, Texas, Brownsville, Corpus Christi, Texas, Corpus Christi, Houston, Galveston, Texas, Galveston, Beaumont, Texas, Beaumont, Lake Charles, Louisiana, Lake Charles, Lafayette, Louisiana, Lafayette, Baton Rouge, Louisiana, Baton Rouge, New Orleans, Gulfport, Mississippi, Gulfport, Biloxi, Mississippi, Biloxi, Mobile, Alabama, Mobile, Pensacola, Florida, Pensacola, Panama City, Florida, Panama Ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Circulation
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of Atmosphere of Earth, air and together with ocean circulation is the means by which thermal energy is redistributed on the surface of the Earth. The Earth's atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, but the large-scale structure of its circulation remains fairly constant. The smaller-scale weather systems – middle latitudes, mid-latitude low-pressure area, depressions, or tropical convective cells – occur chaotically, and long-range weather predictions of those cannot be made beyond ten days in practice, or a month in theory (see chaos theory and the butterfly effect). The Earth's weather is a consequence of its illumination by the Sun and the laws of thermodynamics. The atmospheric circulation can be viewed as a heat engine driven by the Sun's energy and whose heat sink, energy sink, ultimately, is the blackness of space. The work produced by that engine causes the motion of the masses of air, and in that process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palm Beach International Airport
Palm Beach International Airport – also known as PBI Airport and historically as Morrison Field & Palm Beach Air Force Base – is a public airport in Palm Beach County, Florida, United States located just west of the city of West Palm Beach, for which it serves as the primary airport. It is also the primary airport for most of Palm Beach County, serving the suburbs and cities of Boca Raton, Wellington, Boynton Beach, Jupiter, and Palm Beach Gardens. It is the third busiest airport in the Miami metropolitan area after Miami International Airport and Fort Lauderdale–Hollywood International Airport. Palm Beach Airport is operated by the Palm Beach County Department of Airports. Road access to the airport is direct from I-95, Southern Boulevard, and Congress Avenue. The airport is bordered on the west by Military Trail. History Palm Beach International Airport began operations in 1936 as Morrison Field. It was named in honor of Grace Morrison, a key participant in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
05L Aug 16 2010
5L or 5-L can refer to: Transportation * AeroSur (IATA code) * 5L, a model of Toyota L engine * Curtiss F-5L, see Felixstowe F5L * SSH 5L (WA), former name of U.S. Route 12 in Washington * Atlantic coast F-5L, see Felixstowe F.5 * Auster J/5L, a model of Auster Aiglet Trainer * British Rail Class 202 Diesel-electric multiple units (6L) when reduced to a five-carriage configuration * British Rail Class 203 Diesel-electric multiple units (6B) when reduced to a five-carriage configuration by the removal of their buffet cars Science and technology * ORC5L * TAF5L * 5L, a model of HP LaserJet 5 * AIX 5L, see IBM AIX AIX (pronounced ) is a series of Proprietary software, proprietary Unix operating systems developed and sold by IBM since 1986. The name stands for "Advanced Interactive eXecutive". Current versions are designed to work with Power ISA based ... Other uses * '' The Horns of Nimon'' (production code: 5L), a 1979–80 ''Doctor Who'' serial See also * L5 (disamb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the southwest, and Arkansas to the northwest. Mississippi's western boundary is largely defined by the Mississippi River, or its historical course. Mississippi is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 32nd largest by area and List of U.S. states by population, 35th-most populous of the 50 U.S. states and has the lowest per-capita income. Jackson, Mississippi, Jackson is both the state's List of capitals in the United States, capital and largest city. Jackson metropolitan area, Mississippi, Greater Jackson is the state's most populous Metropolitan statistical area, metropolitan area, with a population of 591,978 2020 United States census, in 2020. Other major cities include Gulfport, Mississippi, Gulfport, Southaven, Mississippi, South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florida Panhandle
The Florida panhandle (also known as West Florida and Northwest Florida) is the northwestern part of the U.S. state of Florida. It is a Salient (geography), salient roughly long, bordered by Alabama on the west and north, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia on the north, and the Gulf of Mexico to the south. Its eastern boundary is arbitrarily defined. It is defined by its Culture of the Southern United States, southern culture and Rural area, rural demographics in contrast to urbanized central and southern Florida, as well as closer cultural links to Alabama and Georgia. Its major communities include Pensacola, Florida, Pensacola, Navarre, Florida, Navarre, Destin, Florida, Destin, Panama City Beach, Florida, Panama City Beach, and Tallahassee, Florida, Tallahassee. As is the case with the other eight U.S. states that have Salient (geography)#Panhandles in the United States, panhandles, the geographic meaning of the term is inexact and elastic. References to the Florida panhandle a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticyclone
A high-pressure area, high, or anticyclone, is an area near the surface of a planet where the atmospheric pressure is greater than the pressure in the surrounding regions. Highs are middle-scale meteorological features that result from interplays between the relatively larger-scale dynamics of an entire planet's atmospheric circulation. The strongest high-pressure areas result from masses of cold air which spread out from polar regions into cool neighboring regions. These highs weaken once they extend out over warmer bodies of water. Weaker—but more frequently occurring—are high-pressure areas caused by atmospheric subsidence: Air becomes cool enough to precipitate out its water vapor, and large masses of cooler, drier air descend from above. Within high-pressure areas, winds flow from where the pressure is highest, at the center of the area, towards the periphery where the pressure is lower. However, the direction is not straight from the center outwards, but curved du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deformation (meteorology)
Deformation is the rate of change of shape of fluid bodies. Meteorologically, this quantity is very important in the formation of atmospheric fronts, in the explanation of cloud shapes, and in the diffusion of materials and properties.Djurić, D: "Weather Analysis". Prentice Hall, 1994. . Equations The deformation of horizontal wind is defined as \operatorname \mathbf = \sqrt, where \ A = \frac + \frac and \ B = \frac - \frac, representing the derivatives of wind component. Because these derivatives vary greatly with the rotation of the coordinate system, so do \ A and \ B. Stretching direction The deformation elements \ A and \ B (above) can be used to find the ''direction of the dilatation axis'', the line along which the material elements stretch (also known as the ''stretching direction''). Several flow patterns are characteristic of large deformation: confluence, diffluence, and shear flow. , also known as ''stretching'', is the elongating of a fluid body along the flow ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, map weather formations, and terrain. The term ''RADAR'' was coined in 1940 by the United States Navy as an acronym for "radio detection and ranging". The term ''radar'' has since entered English and other languages as an anacronym, a common noun, losing all capitalization. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwave domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Depression Five 2010 Rainfall
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's axial tilt; the width of the tropics (in latitude) is twice the tilt. The tropics are also referred to as the tropical zone and the torrid zone (see geographical zone). Due to the overhead sun, the tropics receive the most solar energy over the course of the year, and consequently have the highest temperatures on the planet. Even when not directly overhead, the sun is still close to overhead throughout the year, therefore the tropics also have the lowest seasonal variation on the planet; "winter" and "summer" lose their temperature contrast. Instead, seasons are more commonly divided by precipitation variations than by temperature variations. The tropics maintain wide diversity of local climates, such as rain forests, monsoons, savannahs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bar (unit)
The bar is a metric unit of pressure defined as 100,000 Pa (100 kPa), though not part of the International System of Units (SI). A pressure of 1 bar is slightly less than the current average atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level (approximately 1.013 bar). By the barometric formula, 1 bar is roughly the atmospheric pressure on Earth at an altitude of 111 metres at 15 °C. The bar and the millibar were introduced by the Norwegian meteorologist Vilhelm Bjerknes, who was a founder of the modern practice of weather forecasting, with the bar defined as one megadyne per square centimetre. The SI brochure, despite previously mentioning the bar, now omits any mention of it.. The bar has been legally recognised in countries of the European Union since 2004. British Standard BS 350:2004 ''Conversion Factors for Units''. The US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) deprecates its use except for "limited use in meteorology" and lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1,013.25 millibars, 760 mm Hg, 29.9212 inchesHg, or 14.696 psi.International Civil Aviation Organization. ''Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere'', Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993. . The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm. In most circumstances, atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. As elevation increases, there is less overlying atmospheric mass, so atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing elevation. Because the atmosphere is thin relative to the Earth's radius—especially the dense atmospheric layer at low altitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |