|
Triple Test Score
The triple test score is a diagnostic tool for examining potentially breast cancer, cancerous breasts. Diagnostic accuracy of the triple test score is nearly 100%. Scoring includes using the procedures of physical examination, mammography and needle biopsy. If the results of a triple test score are greater than five, an excisional biopsy is indicated. The term ''triple test scoring'' (TSS) was first noted in 1975 as a means of rapidly diagnosing and examining breast malignancies. TSS developed as a useful and accurate clinical tool for breast masses because it was cheaper and it cut down on the diagnosis time. Scoring To obtain the triple test score, a number from 1 through 3 is assigned to each one of the procedures. A score of 1 is assigned to a benign test result, 2 applies to a suspicious test result, and 3 applies to a malignant result. The sum of the scores of all three procedures is the triple test score. If the total summed score from the three tests is 3 to 4 then the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple Test
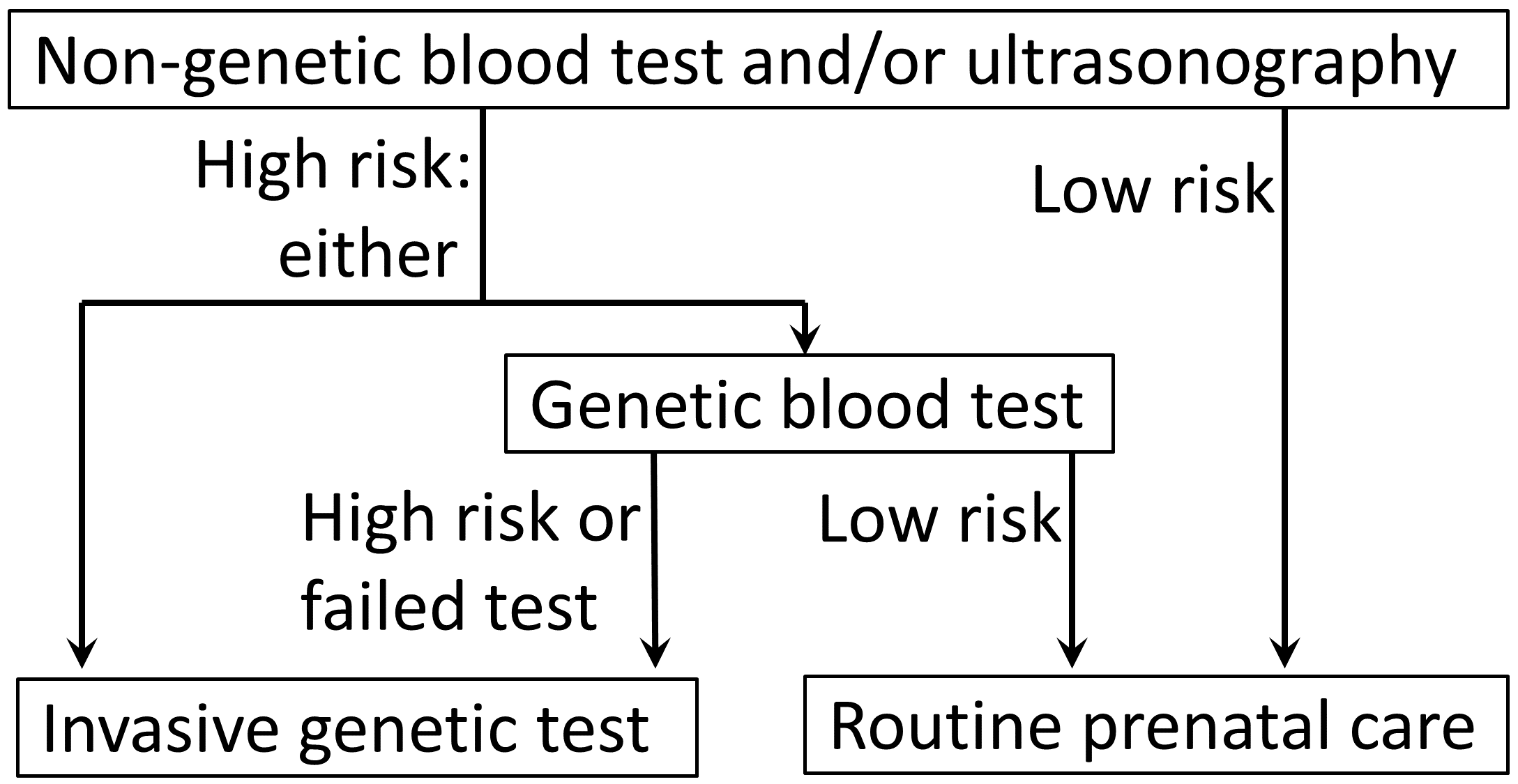
The triple test, also called triple screen, the Kettering test or the Bart's test, is an investigation performed during pregnancy in the second trimester to classify a patient as either high-risk or low-risk for chromosomal abnormalities (and neural tube defects). The term "multiple-marker screening test" is sometimes used instead. This term can encompass the "double test" and "quadruple test" (described below). The Triple screen measures serum levels of AFP, estriol, and beta-hCG, with a 70% sensitivity and 5% false-positive rate. It is complemented in some regions of the United States, as the ''Quad screen'' (adding inhibin A to the panel, resulting in an 81% sensitivity and 5% false-positive rate for detecting Down syndrome when taken at 15–18 weeks of gestational age) and other prenatal diagnosis techniques, although it remains widely used in Canada and other countries. A positive screen indicates an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities (and neural tube defec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast MRI
One alternative to mammography, breast MRI or contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), has shown substantial progress in the detection of breast cancer. Uses Some of the uses of MRI of the breasts are: screening for malignancy in women with greater than 20% lifetime risk of breast cancer (especially those with high risk genes such as BRCA1 and BRCA2), evaluate breast implants for rupture, screening the opposite side breast for malignancy in women with known one sided breast malignancy, extent of disease and the presence of multifocality and multicentricity in patients with invasive carcinoma and ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), and evaluate response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. MRI of the breasts has the highest sensitivity to detect breast cancer when compared with other imaging modalities such as breast ultrasound or mammography. In the screening for breast cancer for high-risk women, sensitivity of MRI ranges from 83 to 94% while specificity (the confidence that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with Metastatic breast cancer, distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin. Risk factors for developing breast cancer include obesity, a Sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical exercise, alcohol consumption, hormone replacement therapy during menopause, ionizing radiation, an early age at Menarche, first menstruation, having children late in life (or not at all), older age, having a prior history of breast cancer, and a family history of breast cancer. About five to ten percent of cases are the result of an inherited genetic predisposition, including BRCA mutation, ''BRCA'' mutations among others. Breast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensitivity And Specificity
In medicine and statistics, sensitivity and specificity mathematically describe the accuracy of a test that reports the presence or absence of a medical condition. If individuals who have the condition are considered "positive" and those who do not are considered "negative", then sensitivity is a measure of how well a test can identify true positives and specificity is a measure of how well a test can identify true negatives: * Sensitivity (true positive rate) is the probability of a positive test result, conditioned on the individual truly being positive. * Specificity (true negative rate) is the probability of a negative test result, conditioned on the individual truly being negative. If the true status of the condition cannot be known, sensitivity and specificity can be defined relative to a " gold standard test" which is assumed correct. For all testing, both diagnoses and screening, there is usually a trade-off between sensitivity and specificity, such that higher sensiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Needle Breast Biopsy
Needle or Needles may refer to: Crafting * Crochet needle, a tool for making loops in thread or yarn * Knitting needle, a tool for knitting, not as sharp as a sewing needle * Sewing needle, a long slender tool with a pointed tip * Trussing needle, a long slender tool, sometimes with a flattened point, to tie poultry for cooking * Upholstery needle, a tool for upholstery, generally thick and curved Science and technology Botany * Needle (botany), of conifers Medicine * Acupuncture needle, in alternative medicine * Hypodermic needle, a hollow needle commonly used with a syringe to inject fluid into or extract fluid from the body * Surgical needle, several types of needles used for surgical suture * Tuohy needle, a needle used to administer epidural catheters Technology * Gramophone needle, used for playing records * Indicator needle, of a measuring instrument * Needle valve People * Dave Needle (1947–2016), American engineer * Sharon Needles (born 1981), American drag quee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blausen 0628 Mammogram
Blausen Medical Communications, Inc. (BMC) is the creator and owner of a library of two- and three-dimensional medical and scientific images and animations, a developer of information technology allowing access to that content, and a business focused on licensing and distributing the content. It was founded by Bruce Blausen in Houston, Texas, in 1991, and is privately held. Background Blausen Medical Communications is a privately held company founded by Bruce Blausen in Houston, Texas in 1991. BMC created and owns a library of medical and scientific images and animations, and has developed information technology tools allowing access to the library; as well, it licenses and otherwise works to distribute the content. As of this date, BMC's animation library comprised approximately 1,500 animations and over 27,000 two- and three-dimensional images designed for point-of-care patient education, which could be accessed by consumers or professional caregivers (primarily via hospital o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BI-RADS
The Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) is a quality assurance tool originally designed for use with mammography. The system is a collaborative effort of many health groups but is published and trademarked by the American College of Radiology (ACR). The system is designed to standardize reporting and is used by medical professionals to communicate a patient's risk of developing breast cancer, particularly for patients with dense breast tissue. The document focuses on patient reports used by medical professionals, not "lay reports" that are provided to patients. Published documents The BI-RADS is published by ACR in the form of the ''BI-RADS Atlas''. the ''Atlas'' is divided into three publications: * Mammography, Fifth Edition * Ultrasound, Second Edition * MRI, Second Edition Assessment categories While BI-RADS is a quality control system, in day-to-day usage the term ''BI-RADS'' refers to the mammography assessment categories. These are standardized numerical c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dense Breast Tissue
Dense breast tissue, also known as dense breasts, is a condition of the breasts where a higher proportion of the breasts are made up of glandular tissue and fibrous tissue than fatty tissue. Around 40–50% of women have dense breast tissue and one of the main medical components of the condition is that mammograms are unable to differentiate tumorous tissue from the surrounding dense tissue. This increases the risk of late diagnosis of breast cancer in women with dense breast tissue. Additionally, women with such tissue have a higher likelihood of developing breast cancer in general, though the reasons for this are poorly understood. Definition and prevalence Dense breast tissue is defined based on the amount of glandular and fibrous tissue as compared to the percentage of fatty tissue. The current mammography classifications split up the density of breasts into four categories. Approximately 10% of women have almost entirely fatty breasts, 40% with small pockets of dense tiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Ultrasound
Breast ultrasound is a medical imaging technique that uses medical ultrasonography to perform imaging of the breast. It can be performed for either diagnostic or screening purposes and can be used with or without a mammogram. In particular, breast ultrasound may be useful for younger women who have denser fibrous breast tissue that may make mammograms more challenging to interpret. Automated whole-breast ultrasound (AWBU) is a technique that produces volumetric images of the breast and is largely independent of operator skill. It utilizes high-frequency ultrasound to help perform a diagnostic evaluation of the lactiferous ducts (duct sonography) and make dilated ducts and intraductal masses visible. Galactography is another technique that can be used to visualize the system of lactiferous ducts and allows a wider area to be visualized. Elastography is a type of ultrasound examination that measures tissue stiffness and can be used to detect tumours. Breast ultrasound is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TTS Components Diagram
TTS may refer to: Places * Taman Tasik Semenyih, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, a student town * Toba Tek Singh District, a district in the Punjab province of Pakistan * Toba Tek Singh Tehsil * Toba Tek Singh, Punjab, Pakistan Schools * Tamil Nadu Theological Seminary * Tanglin Trust School, Singapore * Thomas Telford School, a City Technology College in Telford, Shropshire Science Medicine * Temporary threshold shift, auditory fatigue * Tarsal tunnel syndrome, a foot condition * Transdermal therapeutic system, a drug delivery system * Thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome, a rare condition of blood clotting Other uses in science * T Tauri star, in astronomy * Three-taxon analysis, in phylogenetics * Time-temperature superposition, in polymer physics * Time translation symmetry, invariabilty of the laws of physics Technology *Text-to-speech, in speech synthesis *Teletypesetter, in telegraphy * Transaction Tracking System, on the Novell NetWare OS * Technology Transformatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytopathology
Cytopathology (from Greek , ''kytos'', "a hollow"; , ''pathos'', "fate, harm"; and , ''-logia'') is a branch of pathology that studies and diagnoses diseases on the cellular level. The discipline was founded by George Nicolas Papanicolaou in 1928. Cytopathology is generally used on samples of free cells or tissue fragments, in contrast to histopathology, which studies whole tissues. Cytopathology is frequently, less precisely, called "cytology", which means "the study of cells". Cytopathology is commonly used to investigate diseases involving a wide range of body sites, often to aid in the diagnosis of cancer but also in the diagnosis of some infectious diseases and other inflammatory conditions. For example, a common application of cytopathology is the Pap smear, a screening tool used to detect precancerous cervical lesions that may lead to cervical cancer. Cytopathologic tests are sometimes called smear tests because the samples may be smeared across a glass microscop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excisional Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle aspiration biopsy. Biopsies are most commonly performed for insight into possible cancerous or inflammatory conditions. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |