|
Triodia Earless Skink
The ''Hemiergis millewae'', commonly known as the Millewa skink or Triodia earless skink, is a species of hemiergis lizards that is endemic to Australia. It is a specialist species, highly dependent on Spinifex (Triodia scariosa) for food and shelter, and has only been observed in semi-arid Mallee woodlands of southern and eastern Australia. It is considered endangered throughout parts of its range. Description ''Hermiergis millewae'' is a small, terrestrial (ground-dwelling) skink which is native to Australia. It is characterised by dark brown shiny scales with a burnt orange stripe along its back, from above the ear to its hindlimbs, and pale grey underbelly. The Millewa skink has an elongated body, with four short limbs each containing five digits and a long tail similar in length to its torso. As with other Hemiergis (earless) skinks, its ears are not visible and it has an ear depression entirely covered by scales. It has a fifth supralabial scale contacting the eye. ''He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert John Coventry
Albert may refer to: Companies * Albert (supermarket), a supermarket chain in the Czech Republic * Albert Heijn, a supermarket chain in the Netherlands * Albert Market, a street market in The Gambia * Albert Productions, a record label * Albert Computers, Inc., a computer manufacturer in the 1980s Entertainment * ''Albert'' (1985 film), a Czechoslovak film directed by František Vláčil * ''Albert'' (2015 film), a film by Karsten Kiilerich * ''Albert'' (2016 film), an American TV movie * ''Albert'' (Ed Hall album), 1988 * "Albert" (short story), by Leo Tolstoy * Albert (comics), a character in Marvel Comics * Albert (''Discworld''), a character in Terry Pratchett's ''Discworld'' series * Albert, a character in Dario Argento's 1977 film ''Suspiria'' Military * Battle of Albert (1914), a WWI battle at Albert, Somme, France * Battle of Albert (1916), a WWI battle at Albert, Somme, France * Battle of Albert (1918), a WWI battle at Albert, Somme, France People * Albert (given n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovoviviparity
Ovoviviparity, ovovivipary, ovivipary, or aplacental viviparity is a term used as a "bridging" form of reproduction between egg-laying oviparous and live-bearing viviparous reproduction. Ovoviviparous animals possess embryos that develop inside eggs that remain in the mother's body until they are ready to hatch. The young of some ovoviviparous amphibians, such as '' Limnonectes larvaepartus'', are born as larvae, and undergo further metamorphosis outside the body of the mother. Members of genera '' Nectophrynoides'' and '' Eleutherodactylus'' bear froglets, not only the hatching, but all the most conspicuous metamorphosis, being completed inside the body of the mother before birth. Among insects that depend on opportunistic exploitation of transient food sources, such as many Sarcophagidae and other carrion flies, and species such as many Calliphoridae, that rely on fresh dung, and parasitoids such as tachinid flies that depend on entering the host as soon as possibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biological species. It uses a set of precise criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of thousands of species and subspecies. These criteria are relevant to all species and all regions of the world. With its strong scientific base, the IUCN Red List is recognized as the most authoritative guide to the status of biological diversity. A series of Regional Red Lists are produced by countries or organizations, which assess the risk of extinction to species within a political management unit. The aim of the IUCN Red List is to convey the urgency of conservation issues to the public and policy makers, as well as help the international community to reduce species extinction. According to IUCN the formally stated goals of the Red List are to provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barrier Ranges
The Barrier Ranges or sometimes the Barrier Range and historically the Stanley's Barrier Range, is a mountain range that comprises a series of hills and higher grounds in the far western region of New South Wales, Australia, surrounding the city of Broken Hill. Location and features The Barrier Ranges comprise the whole system of ranges and ridges associated with the main watershed named the Main Barrier Range - including Coko Range, Floods Range, Slate Range, Robe Range, Mundi Mundi Range, Coonbaralba Range and Mount Darling Range. The city of Broken Hill lies within these ranges. The ranges is oriented in a roughly north-south direction, east of the border between New South Wales and South Australia. It is an area of slightly higher ground lying between the lower lands along the Darling River, and lower ground in South Australia. The Barrier Ranges contains a number of mineral deposits, most notably Broken Hill. It was reported in October 1856 that, 'within the last year or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murray-Sunset National Park
The Murray-Sunset National Park is the second largest national park in Victoria, Australia, located in the Mallee district in the northwestern corner of the state, bordering South Australia. The national park is situated approximately northwest of Melbourne and was proclaimed in 1991. It is in the northwestern corner of the state, bordering South Australia to the west and the Murray River to the north. The Sturt Highway passes through the northern part of the park, but most of the park is in the remote area between the Sturt Highway and the Mallee Highway, west of the Calder Highway. History The park was created in 1991, and expanded to encompass Pink Lakes State Park in 1999. The lakes are dubbed "pink" after the beta-carotene pigment that colours it in late summer, caused by the algae ''Dunaliella salina''. This area was the site of a major salt industry from 1916 to 1975. At its peak, ten thousand tons of salt was harvested and railed from Lake Crosbie, Lake Becking an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikara–Flinders Ranges National Park
The Ikara–Flinders Ranges National Park, formerly Flinders Ranges National Park,Flinders Ranges to be renamed in recognition of traditional Aboriginal owners ''ABC News'', 12 February 2016. Retrieved 12 February 2016. is situated approximately 400 km north of Adelaide, Australia, Adelaide in the northern central part of South Australia's largest mountain range, the Flinders Ranges. The park covers an area of 912 km², northeast of the small town of Hawker, South Australia, Hawker. The Heysen Trail and Mawson Trails pass through the park. The park's most characteristic landmark is Wilpena Pound, a large, sickle-shaped, natural amphitheatre covering nearly 80 km², containing the range's highest peak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eyre Peninsula
The Eyre Peninsula is a triangular peninsula in South Australia. It is bounded by the Spencer Gulf on the east, the Great Australian Bight on the west, and the Gawler Ranges to the north. Originally called Eyre’s Peninsula, it was named after explorer Edward John Eyre, who explored parts of the peninsula in 1839–41. The coastline was first charted by the expeditions of Matthew Flinders in 1801–02 and French explorer Nicolas Baudin around the same time. Flinders also named the nearby Yorke Peninsula, Yorke’s Peninsula and Spencer Gulf, Spencer’s Gulph on the same voyage. The peninsula's economy is primarily agricultural, with growing aquaculture, mining, and tourism sectors. The main towns are Port Lincoln in the south, Whyalla and Port Augusta in the northeast, and Ceduna, South Australia, Ceduna in the northwest. Port Lincoln (''Galinyala'' in Barngarla language, Barngarla), Whyalla and Port Augusta (''Goordnada'') are part of the Barngarla Aboriginal country. Cedu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
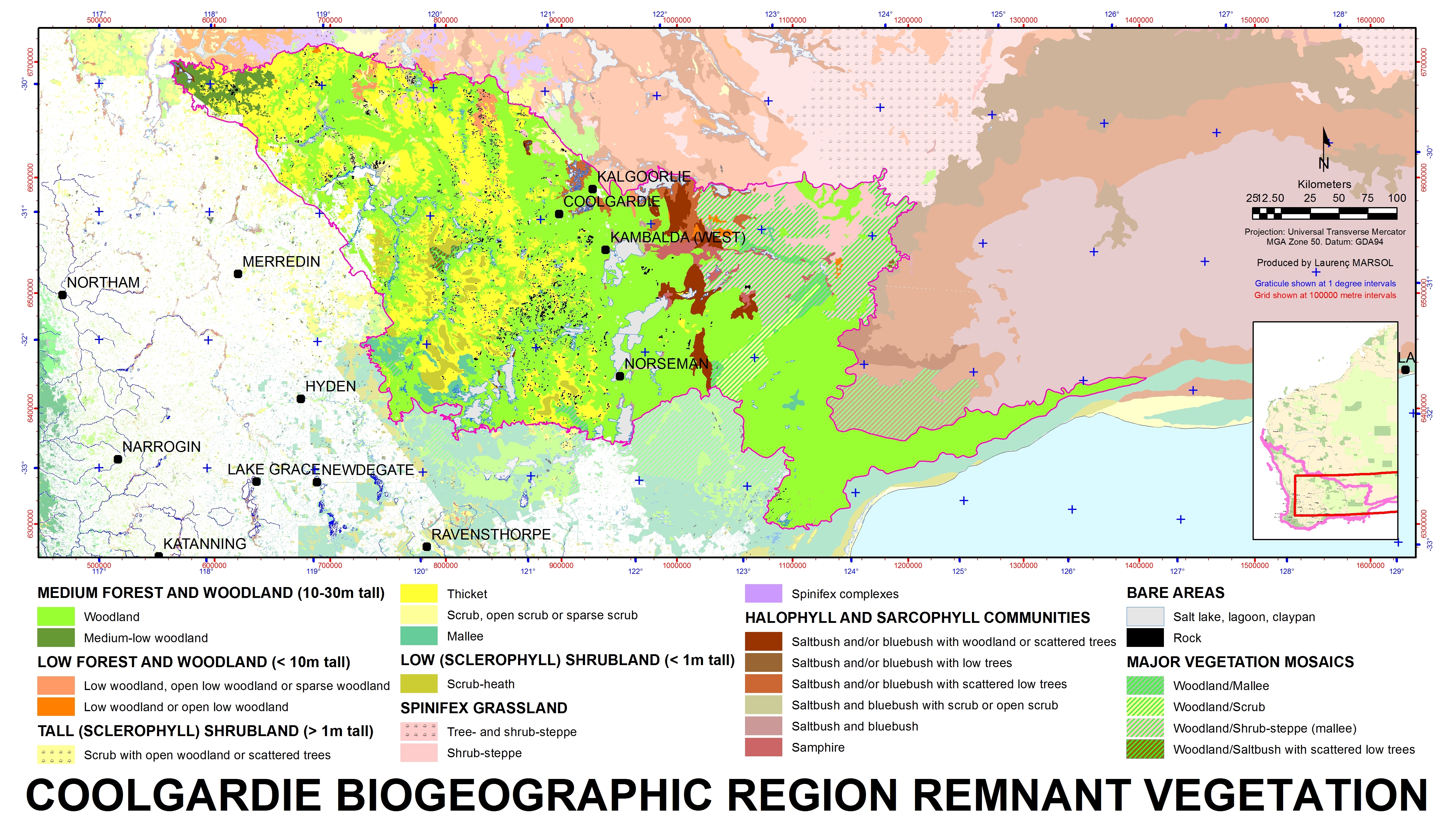
Coolgardie Bioregion
Coolgardie is an Australian bioregion consisting of an area of low hills and plains of infertile sandy soil in Western Australia. It has an area of . It includes much of the Great Western Woodlands. Location and description This is a transition zone between the Mediterranean climate of Australia's south-west coast and the country's dry interior. The poor soil makes it unsuitable for agriculture but Coolgardie has been a gold and nickel mining area. It is bounded on the north by the arid Murchison bioregion, characterised by open Mulga woodlands and steppe. The low shrublands of the arid Nullarbor Plain lie to the east. The Mallee bioregion adjoins Coolgardie on the south. The Avon Wheatbelt bioregion is to the west. The Coolgardie bioregion, together with the coastal Hampton bioregion to the southeast, constitute the Coolgardie woodlands ecoregion defined by the World Wildlife Fund. Flora and fauna The low hills are home to woodland of endemic species of eucal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insectivore
A robber fly eating a hoverfly An insectivore is a carnivorous animal or plant that eats insects. An alternative term is entomophage, which can also refer to the human practice of eating insects. The first vertebrate insectivores were amphibians. When they evolved 400 million years ago, the first amphibians were piscivores, with numerous sharp conical teeth, much like a modern crocodile. The same tooth arrangement is however also suited for eating animals with exoskeletons, thus the ability to eat insects is an extension of piscivory. At one time, insectivorous mammals were scientifically classified in an order called Insectivora. This order is now abandoned, as not all insectivorous mammals are closely related. Most of the Insectivora taxa have been reclassified; those that have not yet been reclassified and found to be truly related to each other remain in the order Eulipotyphla. Although individually small, insects exist in enormous numbers. Insects make u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earless Skink
The earless skinks form the genus ''Hemiergis'' in the skink family Scincidae. All earless skinks are native to Australia. Species There are seven species: * '' Hemiergis decresiensis'' (Cuvier, 1829) — three-toed earless skink * '' Hemiergis gracilipes'' (Steindachner, 1870) — south-western mulch-skink * '' Hemiergis initialis'' (Werner, 1910) — southwestern earless skink * '' Hemiergis millewae'' Coventry, 1976 — Triodia earless skink * ''Hemiergis peronii'' (Gray, 1831) — four-toed earless skink The four-toed earless skink (''Hemiergis peronii''), also known commonly as Péron's earless skink, the lowlands earless skink, or the four-toed mulch skink, is a viviparous earless skink endemic to southern Australia. Etymology The specific ..., Peron's earless skink, or lowlands earless skink * '' Hemiergis quadrilineatus'' (Duméril & Bibron, 1839) — two-toed earless skink * '' Hemiergis talbingoensis'' (Copland, 1946) — eastern three-toed earless skink Two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mallee (habit)
Mallee are trees or shrubs, mainly certain species of eucalypts, which grow with multiple stems springing from an underground lignotuber, usually to a height of no more than . The term is widely used for trees with this growth habit across southern Australia, in the states of Western Australia, South Australia, New South Wales and Victoria, and has given rise to other uses of the term, including the ecosystems where such trees predominate, specific geographic areas within some of the states and as part of various species' names. Etymology The word is thought to originate from the word ''mali'', meaning water, in the Wemba Wemba language, an Aboriginal Australian language of southern New South Wales and Victoria. The word is also used in the closely related Woiwurrung language and other Aboriginal languages of Victoria, South Australia, and southern New South Wales. Overview The term ''mallee'' is used describe various species of trees or woody plants, mainly of the genus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |