|
Trichodesmium Clevei
''Trichodesmium'', also called sea sawdust, is a genus of Filamentation, filamentous cyanobacteria. They are found in nutrient poor tropical and subtropical ocean waters (particularly around Australia and in the Red Sea, where they were first described by Captain Cook). ''Trichodesmium'' is a diazotroph; that is, it nitrogen fixation, fixes atmospheric nitrogen into ammonium, a nutrient used by other organisms. ''Trichodesmium'' is thought to fix nitrogen on such a scale that it accounts for almost half of the nitrogen fixation in marine systems globally. ''Trichodesmium'' is the only known diazotroph able to fix nitrogen in daylight under aerobic conditions without the use of heterocysts. ''Trichodesmium'' can live as individual filaments, with tens to hundreds of cells strung together, or in colonies consisting of tens to hundreds of filaments clustered together. These colonies are visible to the naked eye and sometimes form blooms, which can be extensive on surface waters. Thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Barrier Reef
The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest coral reef system, composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands stretching for over over an area of approximately . The reef is located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Queensland, Australia, separated from the coast by a channel wide in places and over deep. The Great Barrier Reef can be seen from outer space and is the world's biggest single structure made by living organisms. This reef structure is composed of and built by billions of tiny organisms, known as coral polyp (zoology), polyps. It supports a wide diversity of life and was selected as a World Heritage Site in 1981. CNN labelled it one of the Seven Wonders of the World#Seven Natural Wonders of the World, Seven Natural Wonders of the World in 1997. Australian World Heritage places included it in its list in 2007. The Queensland National Trust named it a state icon of Queensland in 2006. A large part of the reef is protected by the Great Barrier Reef Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copepods
Copepods (; meaning 'oar-feet') are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic (living in the water column), some are benthic (living on the sediments), several species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses of plants ( phytotelmata) such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as biodiversity indicators. As with other crustaceans, copepods have a larval form. For copepods, the egg hatches into a nauplius form, with a head and a tail but no true thorax or abdomen. The larva molts several times until it resembles the adult and then, after more molts, achieves adult development. The nauplius form is so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycoerythrin
Phycoerythrin (PE) is a red protein-pigment complex from the light-harvesting phycobiliprotein family, present in cyanobacteria, red algae and Cryptomonad, cryptophytes, accessory to the main chlorophyll pigments responsible for photosynthesis.The red pigment is due to the prosthetic group, phycoerythrobilin, which gives phycoerythrin its red color. Like all phycobiliproteins, it is composed of a protein part covalently binding chromophores called phycobilins. In the phycoerythrin family, the most known phycobilins are: phycoerythrobilin, the typical phycoerythrin acceptor chromophore. Phycoerythrobilin is a linear tetrapyrrole molecule found in cyanobacteria, red algae, and cryptomonads. Together with other bilins such as phycocyanobilin it serves as a light-harvesting pigment in the photosynthetic light-harvesting structures of cyanobacteria called phycobilisomes. Phycoerythrins are composed of (αβ) monomers, usually organised in a disk-shaped Protein quaternary structure, trim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
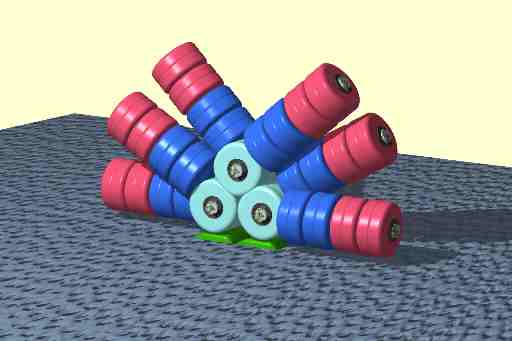
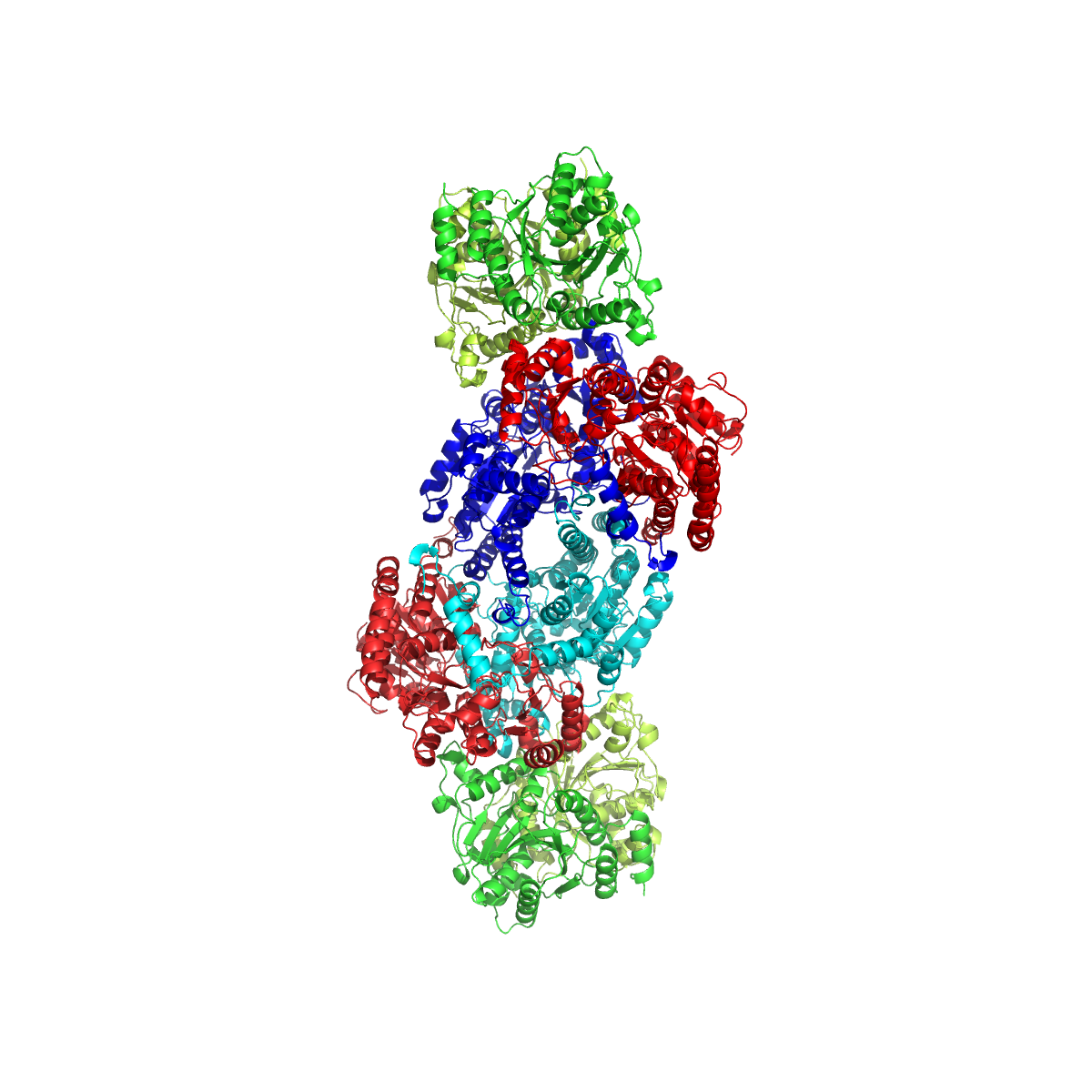
Nitrogenase
Nitrogenases are enzymes () that are produced by certain bacteria, such as cyanobacteria (blue-green bacteria) and rhizobacteria. These enzymes are responsible for the reduction of nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3). Nitrogenases are the only family of enzymes known to catalyze this reaction, which is a step in the process of nitrogen fixation. Nitrogen fixation is required for all forms of life, with nitrogen being essential for the biosynthesis of molecules (nucleotides, amino acids) that create plants, animals and other organisms. They are encoded by the Nif genes or homologs. They are related to protochlorophyllide reductase. Classification and structure Although the equilibrium formation of ammonia from molecular hydrogen and nitrogen has an overall negative enthalpy of reaction ( \Delta H^ = -45.2 \ \mathrm \, \mathrm \; \mathrm ), the activation energy is very high ( E_\mathrm = 230-420 \ \mathrm \, \mathrm ). Nitrogenase acts as a catalyst, reducing this energy barrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative Bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the Crystal violet, crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists of a thin peptidoglycan gram-negative cell wall, cell wall sandwiched between an inner (Cytoplasm, cytoplasmic) Cell membrane, membrane and an Bacterial outer membrane, outer membrane. These bacteria are found in all environments that support life on Earth. Within this category, notable species include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', along with various pathogenic bacteria, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', ''Chlamydia trachomatis'', and ''Yersinia pestis''. They pose significant challenges in the medical field due to their outer membrane, which acts as a protective barrier against numerous Antibiotic, antibiotics (including penicillin), Detergent, detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lectotype
In biology, a type is a particular specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally associated. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage (pre-1900 in botany), a type was a taxon rather than a specimen. A taxon is a scientifically named grouping of organisms with other like organisms, a set that includes some organisms and excludes others, based on a detailed published description (for example a species description) and on the provision of type material, which is usually available to scientists for examination in a major museum research collection, or similar institution. Type specimen According to a precise set of rules laid down in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) and the ''International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (ICN), the scientific name of every taxon is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichodesmium Thiebautii
''Trichodesmium thiebautii'' is a cyanobacteria that is often found in open oceans of tropical and subtropical regions and is known to be a contributor to large oceanic surface blooms. This microbial species is a diazotroph, meaning it fixes nitrogen gas (N2), but it does so without the use of heterocysts. ''T. thiebautii'' is able to simultaneously perform oxygenic photosynthesis. ''T. thiebautii'' was discovered in 1892 by M.A. Gomont. ''T. thiebautii'' are important for nutrient cycling in marine habitats because of their ability to fix N2, a limiting nutrient in ocean ecosystems. Discovery In 1830 the cyanobacteria genus '' Trichodesmium'' was first found in samples collected in marine waters surrounding Egypt and Syria, and described based on morphological features. In 1892, approximately sixty years following the initial discovery of the genus, Gomont described two new species, ''T. thiebautii'' and ''T. hildebrandtii'', based on specific morphological characteristics, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichodesmium Scoboideum
''Trichodesmium'', also called sea sawdust, is a genus of Filamentation, filamentous cyanobacteria. They are found in nutrient poor tropical and subtropical ocean waters (particularly around Australia and in the Red Sea, where they were first described by Captain Cook). ''Trichodesmium'' is a diazotroph; that is, it nitrogen fixation, fixes atmospheric nitrogen into ammonium, a nutrient used by other organisms. ''Trichodesmium'' is thought to fix nitrogen on such a scale that it accounts for almost half of the nitrogen fixation in marine systems globally. ''Trichodesmium'' is the only known diazotroph able to fix nitrogen in daylight under aerobic conditions without the use of heterocysts. ''Trichodesmium'' can live as individual filaments, with tens to hundreds of cells strung together, or in colonies consisting of tens to hundreds of filaments clustered together. These colonies are visible to the naked eye and sometimes form blooms, which can be extensive on surface waters. Thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichodesmium Lenticulare
''Trichodesmium'', also called sea sawdust, is a genus of filamentous cyanobacteria. They are found in nutrient poor tropical and subtropical ocean waters (particularly around Australia and in the Red Sea, where they were first described by Captain Cook). ''Trichodesmium'' is a diazotroph; that is, it fixes atmospheric nitrogen into ammonium, a nutrient used by other organisms. ''Trichodesmium'' is thought to fix nitrogen on such a scale that it accounts for almost half of the nitrogen fixation in marine systems globally. ''Trichodesmium'' is the only known diazotroph able to fix nitrogen in daylight under aerobic conditions without the use of heterocysts. ''Trichodesmium'' can live as individual filaments, with tens to hundreds of cells strung together, or in colonies consisting of tens to hundreds of filaments clustered together. These colonies are visible to the naked eye and sometimes form blooms, which can be extensive on surface waters. These large blooms led to widespread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichodesmium Lacustre
''Trichodesmium'', also called sea sawdust, is a genus of Filamentation, filamentous cyanobacteria. They are found in nutrient poor tropical and subtropical ocean waters (particularly around Australia and in the Red Sea, where they were first described by Captain Cook). ''Trichodesmium'' is a diazotroph; that is, it nitrogen fixation, fixes atmospheric nitrogen into ammonium, a nutrient used by other organisms. ''Trichodesmium'' is thought to fix nitrogen on such a scale that it accounts for almost half of the nitrogen fixation in marine systems globally. ''Trichodesmium'' is the only known diazotroph able to fix nitrogen in daylight under aerobic conditions without the use of heterocysts. ''Trichodesmium'' can live as individual filaments, with tens to hundreds of cells strung together, or in colonies consisting of tens to hundreds of filaments clustered together. These colonies are visible to the naked eye and sometimes form blooms, which can be extensive on surface waters. Thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |