|
Tregami
Tregami is a Nuristani language spoken in the villages of Gambir, Kaṭâr, and Devoz in the Tregâm Valley off the lower Pech River in the Watapur District of Kunar Province in Afghanistan. The area is in the Hindu Kush along the border with Pakistan. Tregami belongs to the Nuristani group of the Indo-Iranian language family. It is spoken by approximately 3,500 people (2011). Most individuals speak Pashto in addition to Tregami. Tregami is a close relative of Nuristani Kalasha, spoken in Ghaziabad District to the east, with which it has a lexical similarity of 75% to 80%. Although Tregami villages are close in proximity, there is a slight difference between the dialects of Katar and Gambir. The language has been influenced by the neighboring Indo-Aryan languages like Wotapuri-Katarqalai, Grangali, and by the Nuristani Katë dialects. Name The native name is unknown. The exonym ''Tregâm'', from Wotapuri-Katarqalai, literally means "three villages", referencing Gambir, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuristani Language
The Nuristani languages are one of the three groups within the Indo-Iranian language family, alongside the Indo-Aryan and Iranian languages. They have approximately 214,000 speakers primarily in Nuristan and Kunar provinces in northeastern Afghanistan and a few adjacent valleys in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa's Chitral District, Pakistan. The region inhabited by the Nuristanis is located in the southern Hindu Kush mountains, and is drained by the Alingar River in the west, the Pech River in the center, and the Landai Sin and Kunar rivers in the east. More broadly, the Nuristan region is located at the northern intersection of the Indian subcontinent and the Iranian plateau. The Nuristani languages were not described in literature until the 19th century. The older name for the region was Kafiristan due to the pre-Islamic religious practices of its residents, but this term has been abandoned in favor of Nuristan ("land of light") after the region's people were converted to Islam. La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuristani Languages
The Nuristani languages are one of the three groups within the Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian language family, alongside the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan and Iranian languages, Iranian languages. They have approximately 214,000 speakers primarily in Nuristan and Kunar Province, Kunar provinces in northeastern Afghanistan and a few adjacent valleys in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa's Chitral District, Pakistan. The region inhabited by the Nuristanis is located in the southern Hindu Kush mountains, and is drained by the Alingar River in the west, the Pech River in the center, and the Landai Sin River, Landai Sin and Kunar River, Kunar rivers in the east. More broadly, the Nuristan region is located at the northern intersection of the Indian subcontinent and the Iranian plateau. The Nuristani languages were not described in literature until the 19th century. The older name for the region was Kafiristan due to the pre-Islamic religious practices of its residents, but this term has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waigali Language
Nuristani Kalasha ('), also known as ''Waigali'', is a Nuristani language spoken by about 10,000 people in the Nuristan Province of Afghanistan. The native name is ''Kalaṣa-alâ'' 'Kalasha-language'. "Waigali" refers to the dialect of the Väi people of the upper part of the Waigal Valley, centered on the town of Waigal, which is distinct from the dialect of the Čima-Nišei people who inhabit the lower valley. The word 'Kalasha' is the native ethnonym for all the speakers of the southern Nuristani languages. Nuristani Kalasha belongs to the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, and is in the southern Nuristani languages, Nuristani group of the Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian branch. It is closely related to Zemiaki language, Zemiaki and to Tregami language, Tregami, the lexical similarity with the latter being approximately 76% to 80%. It shares its name with the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan Kalasha language (''Kalaṣa-mun''), spoken in Pakist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Indo-European Language
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists; its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. Far more work has gone into reconstructing PIE than any other proto-language, and it is the best understood of all proto-languages of its age. The majority of linguistic work during the 19th century was devoted to the reconstruction of PIE and its daughter languages, and many of the modern techniques of linguistic reconstruction (such as the comparative method) were developed as a result. PIE is hypothesized to have been spoken as a single language from approximately 4500 BCE to 2500 BCE during the Late Neolithic to Early Bronze Age, though estimates vary by more than a thousand years. According to the prevailing Kurgan hypothesis, the original homeland of the Proto-Indo-Europeans may have been in the Pon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Nuristani Language
Proto-Nuristani is the reconstructed proto-language of the Nuristani languages. Proto-Nuristani is descended from Proto-Indo-Iranian, which in turn is descended from Proto-Indo-European. History Proto-Nuristani is the latest common form of all modern-day Nuristani languages. Since diverging from the other Indo-Iranian languages, the Nuristani-speaking peoples have maintained social interactions with other Indo-Iranian peoples, influencing each other's linguistic and cultural landscapes. There have been some phonological developments that were shared with Indo-Aryan and Iranian languages at different stages of development, as well as sound changes specific to the Nuristani languages. Due to the lack of direct attestation of Nuristani languages until the 19th century, it is difficult to deduce much detail about Proto-Nuristani, without resorting to extensive internal comparisons between the modern-day Nuristani languages, and external comparisons with earlier forms of atteste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuristan Province
Nuristan, also spelled as Nurestan or Nooristan (Pashto: ; Katë: ), is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in the eastern part of the country. It is divided into seven districts and is Afghanistan's least populous province, with a population of around 167,000. Parun serves as the provincial capital. Nuristan is bordered on the south by Laghman and Kunar provinces, on the north by Badakhshan province, on the west by Panjshir province, and on the east by Pakistan. The origin of the local Nuristani people has been disputed, ranging from being the indigenous inhabitants forced to flee to this region after refusing to surrender to invaders, to being linked to various ancient groups of people and the Turk Shahi kings. Some Nuristanis claim being descendants of the Greek occupying forces of Alexander the Great. It was formerly called Kafiristan () ("Land of the Infidels") until the inhabitants were forcibly converted from an animist religion with elements from In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
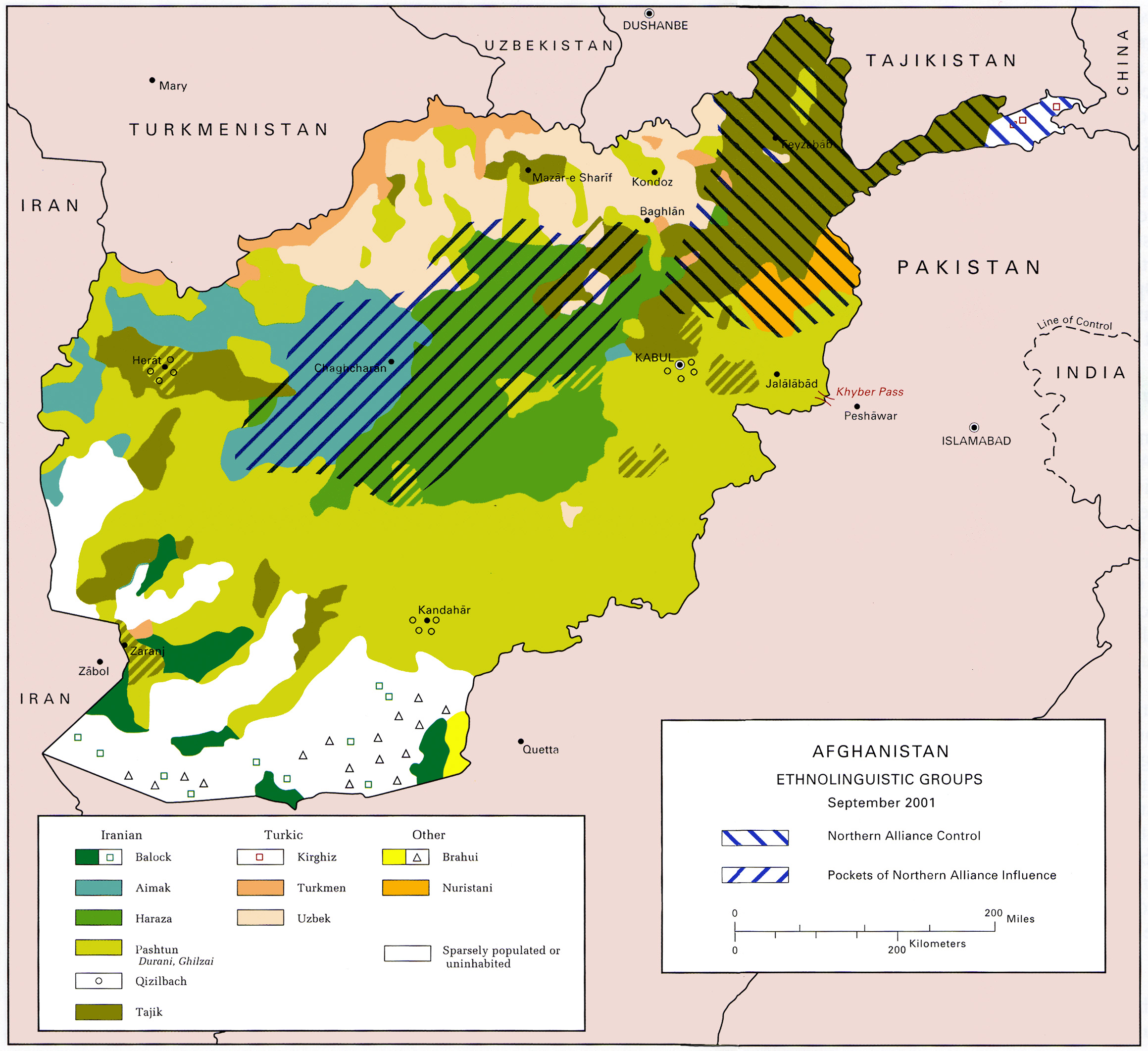
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran border, west, Turkmenistan to the Afghanistan–Turkmenistan border, northwest, Uzbekistan to the Afghanistan–Uzbekistan border, north, Tajikistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, northeast, and China to the Afghanistan–China border, northeast and east. Occupying of land, the country is predominantly mountainous with plains Afghan Turkestan, in the north and Sistan Basin, the southwest, which are separated by the Hindu Kush mountain range. Kabul is the country's capital and largest city. Demographics of Afghanistan, Afghanistan's population is estimated to be between 36 and 50 million. Ancient history of Afghanistan, Human habitation in Afghanistan dates to the Middle Paleolithic era. Popularly referred to as the graveyard of empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Shift
Language shift, also known as language transfer, language replacement or language assimilation, is the process whereby a speech community shifts to a different language, usually over an extended period of time. Often, languages that are perceived to be of higher-status stabilize or spread at the expense of other languages that are perceived—even by their own speakers—to have lower status. An example is the shift from Gaulish to Latin during the time of the Roman Empire. Language assimilation may operate alongside other aspects of cultural assimilation when different cultures meet and merge. Mechanisms Prehistory For prehistory, Forster ''et al''. (2004) and Forster and Renfrew (2011) observe that there is a correlation of language shift with intrusive male Y chromosomes but not necessarily with intrusive female mtDNA. They conclude that technological innovation (the transition from hunting-gathering to farming, or from stone to metal tools) or military prowess (as in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moribund Language
An endangered language or moribund language is a language that is at risk of disappearing as its speakers die out or shift to speaking other languages. Language loss occurs when the language has no more native speakers and becomes a " dead language". If no one can speak the language at all, it becomes an "extinct language". A dead language may still be studied through recordings or writings, but it is still dead or extinct unless there are fluent speakers left. Although languages have always become extinct throughout human history, endangered languages are currently dying at an accelerated rate because of globalization, mass migration, cultural replacement, imperialism, neocolonialism and linguicide (language killing). Language shift most commonly occurs when speakers switch to a language associated with social or economic power or one spoken more widely, leading to the gradual decline and eventual death of the endangered language. The process of language shift is often influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wotapuri-Katarqalai Language
Wotapuri-Katarqalai is an Indo-Aryan language documented to have been spoken in Afghanistan Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde .... It is unknown if the language still has active speakers, or is extinct. The most recent documentation of its use was published in 1983, when it was proposed that the language was in use in and unlikely to be extinct in . In September 2023, there were just 3 senior male speakers (1 in Katar-qala and 2 in Quro) living in the valley reported to Sviatoslav Kaverin who was conducting field research there. Phonology Below is set out the phonology of the Wotapuri-Katarqalai language. Vowels Consonants References Dardic languages Extinct languages of Asia {{IndoAryan-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exonym
An endonym (also known as autonym ) is a common, name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used inside a particular group or linguistic community to identify or designate themselves, their place of origin, or their language. An exonym (also known as xenonym ) is an established, ''non-native'' name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used primarily outside the particular place inhabited by the group or linguistic community. Exonyms exist not only for historico-geographical reasons but also in consideration of difficulties when pronouncing foreign words, or from non-systematic attempts at transcribing into a different writing system. For instance, is the endonym for the country that is also known by the exonyms ''Germany'' and in English and Italian, respectively, and in Spanish and French, respectively, in Polish, and and in Finni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |