|
Tree Diagram (other)
Tree diagram may refer to: * Tree structure, a way of representing the hierarchical nature of a structure in a graphical form Mathematics and logic * Tree diagram (probability theory), a diagram to represent a probability space in probability theory * Decision tree, a decision support tool that uses a tree-like graph or model of decisions and their possible consequences * Event tree, inductive analytical diagram in which an event is analyzed using Boolean logic * Game tree, a tree diagram used to find and analyze potential moves in a game Linguistics * Language tree, representation of a group of languages related through descent from a common ancestor * Parse tree, a representation of the syntactic structure of a string according to some formal grammar in linguistics ** Sentence diagram, a pictorial representation of the grammatical structure of a sentence showing the relationships of phrase structures Biology * Dendrogram, a tree diagram used to illustrate clusters of gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Chart/doc
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are usable as lumber or plants above a specified height. In wider definitions, the taller palms, tree ferns, bananas, and bamboos are also trees. Trees are not a taxonomic group but include a variety of plant species that have independently evolved a trunk and branches as a way to tower above other plants to compete for sunlight. The majority of tree species are angiosperms or hardwoods; of the rest, many are gymnosperms or softwoods. Trees tend to be long-lived, some reaching several thousand years old. Trees have been in existence for 370 million years. It is estimated that there are some three trillion mature trees in the world. A tree typically has many secondary branches supported clear of the ground by the trunk. This trunk typically con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault Tree Diagram
Fault tree analysis (FTA) is a type of failure analysis in which an undesired state of a system is examined. This analysis method is mainly used in safety engineering and reliability engineering to understand how systems can fail, to identify the best ways to reduce risk and to determine (or get a feeling for) event rates of a safety accident or a particular system level (functional) failure. FTA is used in the aerospace, nuclear power, chemical and process, pharmaceutical, petrochemical and other high-hazard industries; but is also used in fields as diverse as risk factor identification relating to social service system failure. FTA is also used in software engineering for debugging purposes and is closely related to cause-elimination technique used to detect bugs. In aerospace, the more general term "system failure condition" is used for the "undesired state" / top event of the fault tree. These conditions are classified by the severity of their effects. The most severe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Diagram
Graph drawing is an area of mathematics and computer science combining methods from geometric graph theory and information visualization to derive two-dimensional depictions of graphs arising from applications such as social network analysis, cartography, linguistics, and bioinformatics. A drawing of a graph or network diagram is a pictorial representation of the vertices and edges of a graph. This drawing should not be confused with the graph itself: very different layouts can correspond to the same graph., p. 6. In the abstract, all that matters is which pairs of vertices are connected by edges. In the concrete, however, the arrangement of these vertices and edges within a drawing affects its understandability, usability, fabrication cost, and aesthetics. The problem gets worse if the graph changes over time by adding and deleting edges (dynamic graph drawing) and the goal is to preserve the user's mental map. Graphical conventions Graphs are frequently drawn as node–li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outliners
An outliner (or outline processor) is a specialized type of text editor (word processor) used to create and edit outlines, which are text files which have a tree structure, for organization. Textual information is contained in discrete sections called "nodes", which are arranged according to their topic–subtopic (parent–child) relationships, like the members of a family tree. When loaded into an outliner, an outline may be collapsed or expanded to display as few or as many levels as desired. Outliners are used for storing and retrieving textual information, with terms, phrases, sentences, or paragraphs attached to a tree. So rather than being arranged by document, information is arranged by topic or content. An outline in an outliner may contain as many topics as desired. This eliminates the need to have separate documents, as outlines easily include other outlines just by adding to the tree. The main difference between a hand-written outline and a digital one is that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feynman Diagram
In theoretical physics, a Feynman diagram is a pictorial representation of the mathematical expressions describing the behavior and interaction of subatomic particles. The scheme is named after American physicist Richard Feynman, who introduced the diagrams in 1948. The interaction of subatomic particles can be complex and difficult to understand; Feynman diagrams give a simple visualization of what would otherwise be an arcane and abstract formula. According to David Kaiser, "Since the middle of the 20th century, theoretical physicists have increasingly turned to this tool to help them undertake critical calculations. Feynman diagrams have revolutionized nearly every aspect of theoretical physics." While the diagrams are applied primarily to quantum field theory, they can also be used in other fields, such as solid-state theory. Frank Wilczek wrote that the calculations that won him the 2004 Nobel Prize in Physics "would have been literally unthinkable without Feynman dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Diagram (physics)
Tree diagram may refer to: * Tree structure, a way of representing the hierarchical nature of a structure in a graphical form Mathematics and logic * Tree diagram (probability theory), a diagram to represent a probability space in probability theory * Decision tree, a decision support tool that uses a tree-like graph or model of decisions and their possible consequences * Event tree, inductive analytical diagram in which an event is analyzed using Boolean logic * Game tree, a tree diagram used to find and analyze potential moves in a game Linguistics * Language tree, representation of a group of languages related through descent from a common ancestor * Parse tree, a representation of the syntactic structure of a string according to some formal grammar in linguistics ** Sentence diagram, a pictorial representation of the grammatical structure of a sentence showing the relationships of phrase structures Biology * Dendrogram, a tree diagram used to illustrate clusters of genes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Topology
A tree topology, or star-bus topology, is a hybrid network topology in which star network A star network is an implementation of a spoke–hub distribution paradigm in computer networks. In a star network, every host is connected to a central hub. In its simplest form, one central hub acts as a conduit to transmit messages. The ...s are interconnected via bus networks. Tree networks are hierarchical, and each node can have an arbitrary number of child nodes. Regular tree networks A regular tree network's topology is characterized by two parameters: the branching, d, and the number of generations, G. The total number of the nodes, N, and the number of peripheral nodes N_p, are given by : N= \frac,\quad N_p=d^G Random tree networks Three parameters are crucial in determining the statistics of random tree networks, first, the branching probability, second the maximum number of allowed progenies at each branching point, and third the maximum number of generat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toaru Majutsu No Index
is a Japanese light novel series written by Kazuma Kamachi and illustrated by Kiyotaka Haimura, which has been published by ASCII Media Works under their Dengeki Bunko imprint since April 2004 in a total of three separate series. The first ran from April 2004 to October 2010, the second from March 2011 to July 2019, and the third from February 2020 to present. The plot is set in a world where supernatural abilities exist. The light novels focus on Toma Kamijo, a young high school student in Academy City with an unusual ability in his right hand as he encounters an English nun named Index. His ability, which allows him to cancel other powers by touching them, and relationship with Index prove dangerous to other sorcerers and espers who wanted to discover the secrets behind him and Index, as well as the city. A manga adaptation by Chuya Kogino began serialization in ''Monthly Shōnen Gangan'' since April 2007. J.C.Staff produced two 24-episode anime seri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
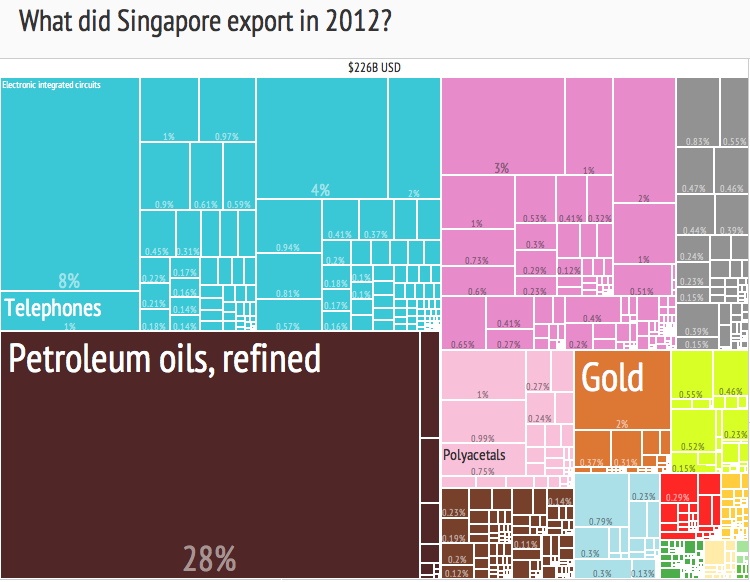
Treemapping
In information visualization and computing, treemapping is a method for displaying hierarchical data using nested figures, usually rectangles. Treemaps display hierarchical ( tree-structured) data as a set of nested rectangles. Each branch of the tree is given a rectangle, which is then tiled with smaller rectangles representing sub-branches. A leaf node's rectangle has an area proportional to a specified dimension of the data. Often the leaf nodes are colored to show a separate dimension of the data. When the color and size dimensions are correlated in some way with the tree structure, one can often easily see patterns that would be difficult to spot in other ways, such as whether a certain color is particularly relevant. A second advantage of treemaps is that, by construction, they make efficient use of space. As a result, they can legibly display thousands of items on the screen simultaneously. Tiling algorithms To create a treemap, one must define a tiling algorithm, that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Program Structure Tree
A program structure tree (PST) is a hierarchical diagram that displays the nesting relationship of single-entry single-exit (SESE) fragments/regions, showing the organization of a computer program A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to execute. Computer programs are one component of software, which also includes documentation and other intangible components. A computer progra .... Nodes in this tree represent SESE regions of the program, while edges represent nesting regions. The PST is defined for all control flow graphs. Bibliographical notes These notes list important works which fueled research on parsing of programs and/or (work)flow graphs (adapted from Section 3.5 in ). *The connectivity properties are the basic properties of graphs and are useful when testing whether a graph is planar or when determining if two graphs are isomorphic. John Hopcroft and Robert Endre Tarjan (1973) developed an optimal (to wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attack Tree
Attack trees are conceptual diagrams showing how an asset, or target, might be attacked. Attack trees have been used in a variety of applications. In the field of information technology, they have been used to describe threats on computer systems and possible attacks to realize those threats. However, their use is not restricted to the analysis of conventional information systems. They are widely used in the fields of defense and aerospace for the analysis of threats against tamper resistant electronics systems (e.g., avionics on military aircraft). Attack trees are increasingly being applied to computer control systems (especially relating to the electric power grid). Attack trees have also been used to understand threats to physical systems. Some of the earliest descriptions of attack trees are found in papers and articles by Bruce Schneier, when he was CTO of Counterpane Internet Security. Schneier was clearly involved in the development of attack tree concepts and was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Structure
A tree structure, tree diagram, or tree model is a way of representing the hierarchical nature of a structure in a graphical form. It is named a "tree structure" because the classic representation resembles a tree, although the chart is generally upside down compared to a biological tree, with the "stem" at the top and the "leaves" at the bottom. A tree structure is conceptual, and appears in several forms. For a discussion of tree structures in specific fields, see Tree (data structure) for computer science; insofar as it relates to graph theory, see tree (graph theory) or tree (set theory). Other related articles are listed below. Terminology and properties The tree elements are called " nodes". The lines connecting elements are called "branches". Nodes without children are called leaf nodes, "end-nodes", or "leaves". Every finite tree structure has a member that has no superior. This member is called the "root" or root node. The root is the starting node. But the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |