|
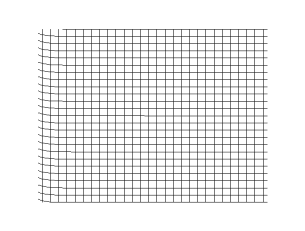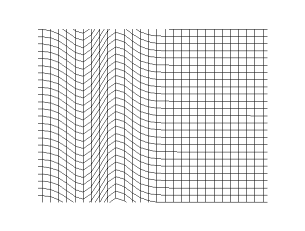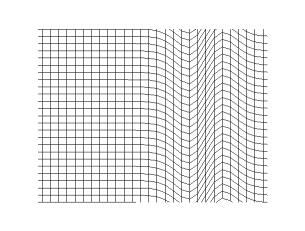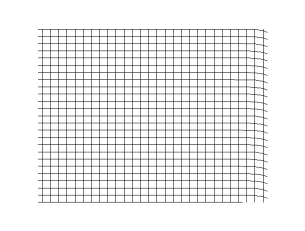
Transverse Wave
In physics, a transverse wave is a wave that oscillates perpendicularly to the direction of the wave's advance. In contrast, a longitudinal wave travels in the direction of its oscillations. All waves move energy from place to place without transporting the matter in the transmission medium if there is one. Electromagnetic waves are transverse without requiring a medium. The designation “transverse” indicates the direction of the wave is perpendicular to the displacement of the particles of the medium through which it passes, or in the case of EM waves, the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of the wave. A simple example is given by the waves that can be created on a horizontal length of string by anchoring one end and moving the other end up and down. Another example is the waves that are created on the membrane of a drum. The waves propagate in directions that are parallel to the membrane plane, but each point in the membrane itself gets displaced up and dow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onde Cisaillement Impulsion 1d 30 Petit
Onde means ''wave'' in French and ''the same'' (ಒಂದೇ) in Kannada language. It may refer to * Onde, Vikramgad, a village in India *'' Onde Balliya Hoogalu'', a 1967 Indian Kannada film *'' Onde Roopa Eradu Guna'', a 1975 Indian Kannada film *'' Onde Guri'', a 1983 Indian Kannada film *'' Le Onde'', a 1996 album by the Italian pianist Ludovico Einaudi * Mille Lune Mille Onde, a single from Andrea Bocelli's 2001 album ''Cieli di Toscana'' *'' Onde (film)'', a 2005 Italian film * Onde 2000, a motorcycle racing team based in Spain See also * Ondes (other) * Onde-onde (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Wave
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid. In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the brain. Only acoustic waves that have frequencies lying between about 20 Hz and 20 kHz, the audio frequency range, elicit an auditory percept in humans. In air at atmospheric pressure, these represent sound waves with wavelengths of to . Sound waves above 20 kHz are known as ultrasound and are not audible to humans. Sound waves below 20 Hz are known as infrasound. Different animal species have varying hearing ranges, allowing some to even hear ultrasounds. Definition Sound is defined as "(a) Oscillation in pressure, stress, particle displacement, particle velocity, etc., propagated in a medium with internal forces (e.g., elastic or viscous), or the superposition of such propagated oscillation. (b) Auditory sens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Polarization
In electrodynamics, circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization state in which, at each point, the electromagnetic field of the wave has a constant magnitude and is rotating at a constant rate in a plane perpendicular to the direction of the wave. In electrodynamics, the strength and direction of an electric field is defined by its electric field vector. In the case of a circularly polarized wave, the tip of the electric field vector, at a given point in space, relates to the phase of the light as it travels through time and space. At any instant of time, the electric field vector of the wave indicates a point on a helix oriented along the direction of propagation. A circularly polarized wave can rotate in one of two possible senses: ''right-handed circular polarization (RHCP)'' in which the electric field vector rotates in a right-hand sense with respect to the direction of propagation, and ''left-handed circular polarization (LHCP)'' in which the vecto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antinodes
A node is a point along a standing wave where the wave has minimum amplitude. For instance, in a vibrating guitar string, the ends of the string are nodes. By changing the position of the end node through frets, the guitarist changes the effective length of the vibrating string and thereby the note played. The opposite of a node is an antinode, a point where the amplitude of the standing wave is at maximum. These occur midway between the nodes. Explanation Standing waves result when two sinusoidal wave trains of the same frequency are moving in opposite directions in the same space and interfere with each other. They occur when waves are reflected at a boundary, such as sound waves reflected from a wall or electromagnetic waves reflected from the end of a transmission line, and particularly when waves are confined in a resonator at resonance, bouncing back and forth between two boundaries, such as in an organ pipe or guitar string. In a standing wave the nodes are a se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standing Waves
In physics, a standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave that oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. The peak amplitude of the wave oscillations at any point in space is constant with respect to time, and the oscillations at different points throughout the wave are in phase. The locations at which the absolute value of the amplitude is minimum are called nodes, and the locations where the absolute value of the amplitude is maximum are called antinodes. Standing waves were first described scientifically by Michael Faraday in 1831. Faraday observed standing waves on the surface of a liquid in a vibrating container. Franz Melde coined the term "standing wave" (German: ''stehende Welle'' or ''Stehwelle'') around 1860 and demonstrated the phenomenon in his classic experiment with vibrating strings. This phenomenon can occur because the medium is moving in the direction opposite to the movement of the wave, or it can arise in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
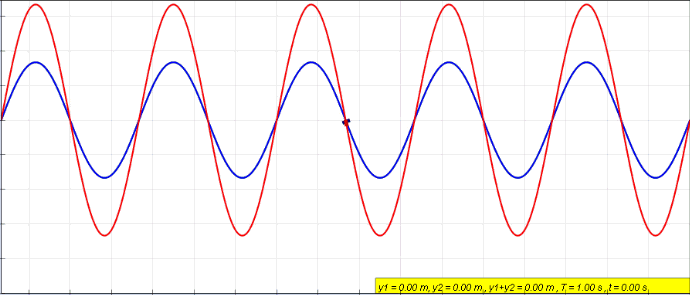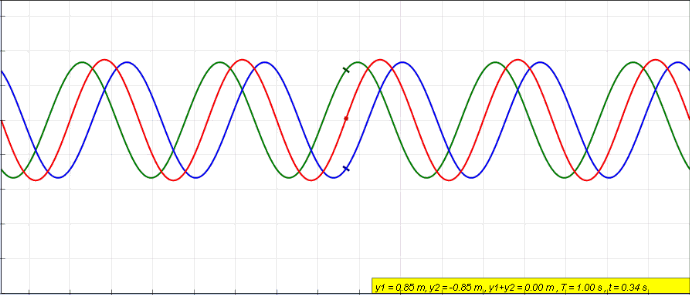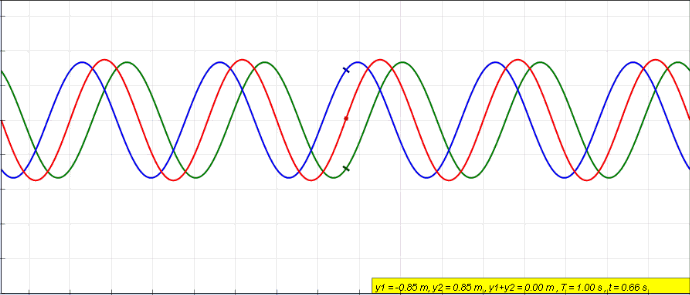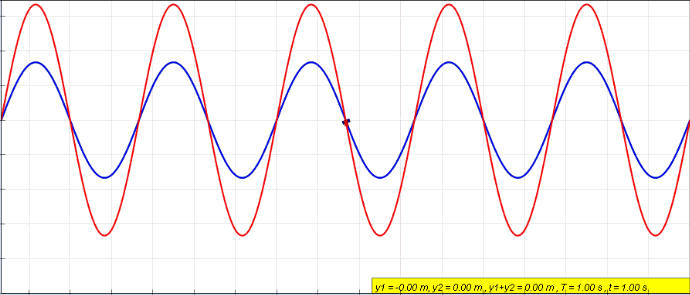
Wave Superposition
The superposition principle, also known as superposition property, states that, for all linear systems, the net response caused by two or more stimuli is the sum of the responses that would have been caused by each stimulus individually. So that if input ''A'' produces response ''X'', and input ''B'' produces response ''Y'', then input (''A'' + ''B'') produces response (''X'' + ''Y''). A function F(x) that satisfies the superposition principle is called a linear function. Superposition can be defined by two simpler properties: additivity F(x_1 + x_2) = F(x_1) + F(x_2) and homogeneity F(ax) = a F(x) for scalar . This principle has many applications in physics and engineering because many physical systems can be modeled as linear systems. For example, a beam can be modeled as a linear system where the input stimulus is the load on the beam and the output response is the deflection of the beam. The importance of linear systems is that they are easier to analyze mathematica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Combination
In mathematics, a linear combination or superposition is an Expression (mathematics), expression constructed from a Set (mathematics), set of terms by multiplying each term by a constant and adding the results (e.g. a linear combination of ''x'' and ''y'' would be any expression of the form ''ax'' + ''by'', where ''a'' and ''b'' are constants). The concept of linear combinations is central to linear algebra and related fields of mathematics. Most of this article deals with linear combinations in the context of a vector space over a field (mathematics), field, with some generalizations given at the end of the article. Definition Let ''V'' be a vector space over the field ''K''. As usual, we call elements of ''V'' ''vector space, vectors'' and call elements of ''K'' ''scalar (mathematics), scalars''. If v1,...,v''n'' are vectors and ''a''1,...,''a''''n'' are scalars, then the ''linear combination of those vectors with those scalars as coefficients'' is :a_1 \mathbf v_1 + a_2 \mathbf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homogeneous
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts relating to the uniformity of a substance, process or image. A homogeneous feature is uniform in composition or character (i.e., color, shape, size, weight, height, distribution, texture, language, income, disease, temperature, radioactivity, architectural design, etc.); one that is heterogeneous is distinctly nonuniform in at least one of these qualities. Etymology and spelling The words ''homogeneous'' and ''heterogeneous'' come from Medieval Latin ''homogeneus'' and ''heterogeneus'', from Ancient Greek ὁμογενής (''homogenēs'') and ἑτερογενής (''heterogenēs''), from ὁμός (''homos'', "same") and ἕτερος (''heteros'', "other, another, different") respectively, followed by γένος (''genos'', "kind"); -ous is an adjectival suffix. Alternate spellings omitting the last ''-e-'' (and the associated pronunciations) are common, but mistaken: ''homogenous'' is strictly a biological/pathological term whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Harmonic Motion
In mechanics and physics, simple harmonic motion (sometimes abbreviated as ) is a special type of periodic motion an object experiences by means of a restoring force whose magnitude is directly proportional to the distance of the object from an equilibrium position and acts towards the equilibrium position. It results in an oscillation that is described by a sinusoid which continues indefinitely (if uninhibited by friction or any other dissipation of energy). Simple harmonic motion can serve as a mathematical model for a variety of motions, but is typified by the oscillation of a mass on a spring when it is subject to the linear elastic restoring force given by Hooke's law. The motion is sinusoidal in time and demonstrates a single resonant frequency. Other phenomena can be modeled by simple harmonic motion, including the motion of a simple pendulum, although for it to be an accurate model, the net force on the object at the end of the pendulum must be proportional to the dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Product
In mathematics, an inner product space (or, rarely, a Hausdorff pre-Hilbert space) is a real vector space or a complex vector space with an operation called an inner product. The inner product of two vectors in the space is a scalar, often denoted with angle brackets such as in \langle a, b \rangle. Inner products allow formal definitions of intuitive geometric notions, such as lengths, angles, and orthogonality (zero inner product) of vectors. Inner product spaces generalize Euclidean vector spaces, in which the inner product is the dot product or ''scalar product'' of Cartesian coordinates. Inner product spaces of infinite dimension are widely used in functional analysis. Inner product spaces over the field of complex numbers are sometimes referred to as unitary spaces. The first usage of the concept of a vector space with an inner product is due to Giuseppe Peano, in 1898. An inner product naturally induces an associated norm, (denoted , x, and , y, in the pictu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Number
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a continuous one- dimensional quantity such as a duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that pairs of values can have arbitrarily small differences. Every real number can be almost uniquely represented by an infinite decimal expansion. The real numbers are fundamental in calculus (and in many other branches of mathematics), in particular by their role in the classical definitions of limits, continuity and derivatives. The set of real numbers, sometimes called "the reals", is traditionally denoted by a bold , often using blackboard bold, . The adjective ''real'', used in the 17th century by René Descartes, distinguishes real numbers from imaginary numbers such as the square roots of . The real numbers include the rational numbers, such as the integer and the fraction . The rest of the real numbers are called irrational numbers. Some irrational numbers (as well as all the rationals) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector (mathematics)
In mathematics and physics, vector is a term that refers to quantities that cannot be expressed by a single number (a scalar), or to elements of some vector spaces. Historically, vectors were introduced in geometry and physics (typically in mechanics) for quantities that have both a magnitude and a direction, such as displacements, forces and velocity. Such quantities are represented by geometric vectors in the same way as distances, masses and time are represented by real numbers. The term ''vector'' is also used, in some contexts, for tuples, which are finite sequences (of numbers or other objects) of a fixed length. Both geometric vectors and tuples can be added and scaled, and these vector operations led to the concept of a vector space, which is a set equipped with a vector addition and a scalar multiplication that satisfy some axioms generalizing the main properties of operations on the above sorts of vectors. A vector space formed by geometric vectors is called a Euc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |