|
Transparent Burnet
''Zygaena purpuralis'', the transparent burnet, is a moth of the family Zygaenidae. Description ''Zygaena purpuralis'' is a medium-sized moth with a wingspan reaching . Usually the forewings show three bright red longitudinal streaks quite variable in shape, with almost transparent greyish-bluish edges. Hindwings are more extensively or almost completely bright red. Head and thorax are black, while the abdomen is dark blue. Larvae are yellow, with some lines of small black spots. Technical description and variation (Seitz) ''Z. purpuralis'' Brunnich (= ''pilosellae'' Esp.; ''minos'' Fuessl.). In this species the hindmargin of the forewing (base included) is all black, while the red wedge-spots situated before it may be shaped entirely as in '' erythrus'' Hbn. An aberration with light yellow instead of red markings, already recorded by Ochsenheimer, has more lately been named by Ruhl ab. ''grossmanni'' (= ''lutescens'' Tutt). It is said to have been observed as a constant or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morten Thrane Brünnich
Morten Thrane Brünnich (30 September 1737 – 19 September 1827) was a Danish zoologist and mineralogist. Biography Brünnich was born in Copenhagen, the son of a portrait painter. He studied oriental languages and theology, but soon became interested in natural history. He contributed his observations of insects to Erik Pontoppidan's ''Danske Atlas'' (1763–81). After being put in charge of the natural history collection of Christian Fleischer he became interested in ornithology, and in 1764 he published ''Ornithologia Borealis'', which included the details of many Scandinavian birds, some described for the first time. The publication of ''Ornithologia Borealis'' was aided by his insight in the collection. Brünnich corresponded with many foreign naturalists including Linnaeus, Peter Simon Pallas and Thomas Pennant. He published his ''Entomologia'' in 1764. He then embarked on a long tour of Europe, spending time studying the fish of the Mediterranean Sea and publishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe. The eastern border of Anatolia has been held to be a line between the Gulf of Alexandretta and the Black Sea, bounded by the Armenian Highlands to the east and Mesopotamia to the southeast. By this definition Anatolia comprises approximately the western two-thirds of the Asian part of Turkey. Today, Anatolia is sometimes considered to be synonymou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rùm
Rùm (), a Scottish Gaelic name often anglicised to Rum (), is one of the Small Isles of the Inner Hebrides, in the district of Lochaber, Scotland. For much of the 20th century the name became Rhum, a spelling invented by the former owner, Sir George Bullough, because he did not relish the idea of having the title "Laird of Rum". It is the largest of the Small Isles, and the 15th largest Scottish island, but is inhabited by only about thirty or so people, all of whom live in the hamlet of Kinloch on the east coast. The island has been inhabited since the 8th millennium BC and provides some of the earliest known evidence of human occupation in Scotland. The early Celtic and Norse settlers left only a few written accounts and artefacts. From the 12th to 13th centuries on, the island was held by various clans including the MacLeans of Coll. The population grew to over 400 by the late 18th century but was cleared of its indigenous population between 1826 and 1828. The island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canna, Scotland
Canna (; gd, Canaigh; Eilean Chanaigh; sco, Canna) is the westernmost of the Small Isles archipelago, in the Scottish Inner Hebrides. It is linked to the neighbouring island of Sanday by a road and sandbanks at low tide. The island is long and wide. The isolated skerries of Hyskeir and Humla lie south-west of the island. The islands were left to the National Trust for Scotland (NTS) by their previous owners, the Gaelic folklorists and scholars John Lorne Campbell and Margaret Fay Shaw in 1981, and are run as a farm and conservation area. Canna House, one of two big houses on the island (the other being Tighard), contains John Campbell's important archives of Gaelic materials that were donated with the islands to the nation. Since then the NTS has engaged in new initiatives to attract new residents and visitors to Canna. However, these initiatives have enjoyed only limited success (see 'Call for families for Canna' below), and in December 2017 it was announced that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eigg
Eigg (; gd, Eige; sco, Eigg) is one of the Small Isles in the Scottish Inner Hebrides. It lies to the south of the Isle of Skye and to the north of the Ardnamurchan peninsula. Eigg is long from north to south, and east to west. With an area of , it is the second-largest of the Small Isles after Rùm. Eigg generates virtually all of its electricity using renewable energy. Eigg has been owned by the Isle of Eigg Heritage Trust since 1997, as a community ownership; another stakeholder, the Scottish Wildlife Trust, manages the island as a nature reserve. In April 2019, National Geographic discussed the island in an online article, estimating the population at 107 and the average number of annual visitors at 10,000. Geology The larger part of the island is formed from olivine-phyric basalt flows erupted during the Palaeocene epoch. Together with flows of hawaiite and mugearite, these form the Eigg Lava Formation. The Sgùrr is formed from porphyritic rhyolitic pitchstone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulva
Ulva (; gd, Ulbha) is a small island in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland, off the west coast of Mull. It is separated from Mull by a narrow strait, and connected to the neighbouring island of Gometra by a bridge. Much of the island is formed from Cenozoic basalt rocks, which are formed into columns in places. Ulva has been populated since the Mesolithic and there are various Neolithic remains on the island. The Norse occupation of the island in the Early Middle Ages has left few tangible artefacts but did bequeath the island its name, which is probably from ''Ulvoy'', meaning "wolf island". Celtic culture was a major influence during both Pictish and Dalriadan times as well as the post-Norse period when the islands became part of modern Scotland. This long period, when Gaelic became the dominant language, was ended by the 19th-century Clearances. At its height, Ulva had a population of over 800, but by May 2019, this had declined to 5; some increase in the number of resident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle Of Mull
The Isle of Mull ( gd, An t-Eilean Muileach ) or just Mull (; gd, Muile, links=no ) is the second-largest island of the Inner Hebrides (after Skye) and lies off the west coast of Scotland in the council area of Argyll and Bute. Covering , Mull is the fourth-largest island in Scotland and Great Britain. From 2001 to 2020, the population has gradually increased: during 2020 the populace was estimated to be 3,000, in the 2011 census it was approximately 2,800, and in 2001, it was measured at 2,667 people. It has the eighth largest Island population in Scotland. In the summer, these numbers are augmented by an influx of many tourists. Much of the year-round population lives in the colourful main settlement of Tobermory. There are two distilleries on the island: the Tobermory distillery, formerly named Ledaig, produces single malt Scotch whisky and another, opened in 2019 and located in the vicinity of Tiroran, which produces Whitetail Gin. Mull is host to numerous sport ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerrera
Kerrera (; gd, Cearara or ''Cearrara'') is an island in the Scotland, Scottish Inner Hebrides, close to the town of Oban. In 2016 it had a population of 45, divided into two communities in the north and south of the island. Geology The oldest bedrock of Kerrera is black slate ascribed to the Easdale Subgroup of the Dalradian Argyll Group. Overlying this across half of the island are conglomerate (geology), conglomeratic sandstones and basalt and augite-andesite lavas of early Devonian age, the former being the local representative of the Old Red Sandstone and the latter constituting part of the Lorne plateau lavas, Lorne Plateau Lavas. Ripple marks and mudcrack, sun cracks are preserved in shale strata on the south coast, belying the subaerial environment in which deposition of these sediments took place. There are thin limestones within both the Easdale Slate Formation and the younger sandstones. All of these strata are cut by NW-SE aligned igneous dike (geology), dykes for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lismore, Scotland
Lismore ( gd, Lios Mòr, possibly meaning "great enclosure" or "garden") is an island of some in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The climate is damp and mild, with over of rain recorded annually. This fertile, low-lying island was once a major centre of Celtic Christianity, with a 6th-century monastery associated with Saint Moluag, and later became the seat of the medieval Bishop of Argyll. There are numerous ruined structures including a broch and two 13th-century castles. During the 19th century various new industries were introduced, including lime quarrying. During the early decades of the 20th century the population exceeded 1,000; but this was followed by a lengthy decline. Although resident numbers are now less than 200, there was a small increase from 2001 to 2011. About a third of the population were recorded as Gaelic-speaking at the former date. The modern economy is largely based on farming, fishing and tourism and the largest settlement is Achnacroish. Variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
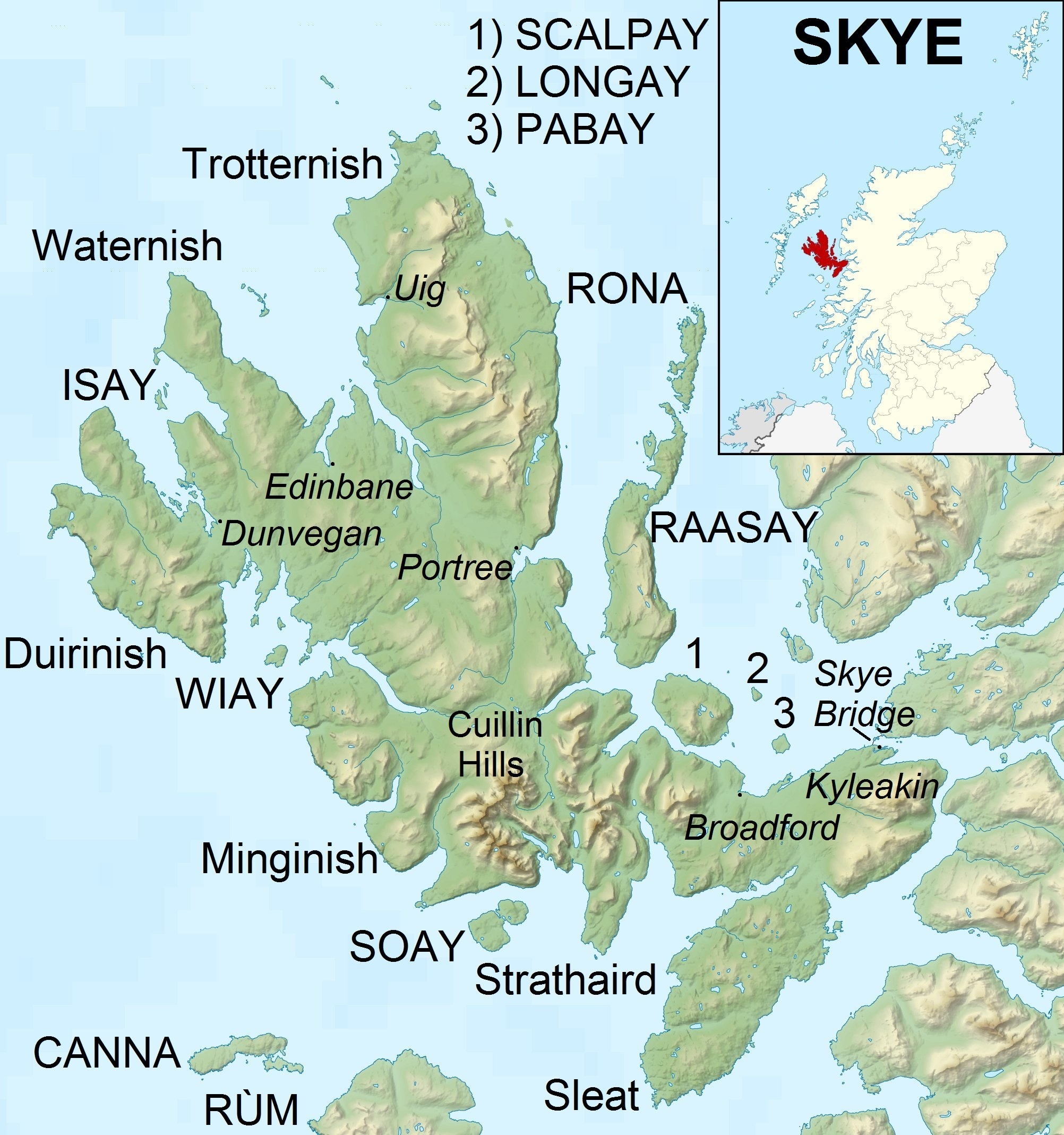
Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye (; gd, An t-Eilean Sgitheanach or ; sco, Isle o Skye), is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated by the Cuillin, the rocky slopes of which provide some of the most dramatic mountain scenery in the country. Slesser (1981) p. 19. Although has been suggested to describe a winged shape, no definitive agreement exists as to the name's origins. The island has been occupied since the Mesolithic period, and over its history has been occupied at various times by Celtic tribes including the Picts and the Gaels, Scandinavian Vikings, and most notably the powerful integrated Norse-Gaels clans of MacLeod and MacDonald. The island was considered to be under Norwegian suzerainty until the 1266 Treaty of Perth, which transferred control over to Scotland. The 18th-century Jacobite risings led to the breaking-up of the clan system and later c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrides
The Hebrides (; gd, Innse Gall, ; non, Suðreyjar, "southern isles") are an archipelago off the west coast of the Scottish mainland. The islands fall into two main groups, based on their proximity to the mainland: the Inner and Outer Hebrides. These islands have a long history of occupation (dating back to the Mesolithic period), and the culture of the inhabitants has been successively influenced by the cultures of Celtic-speaking, Norse-speaking, and English-speaking peoples. This diversity is reflected in the various names given to the islands, which are derived from the different languages that have been spoken there at various points in their history. The Hebrides are where much of Scottish Gaelic literature and Gaelic music has historically originated. Today, the economy of the islands is dependent on crofting, fishing, tourism, the oil industry, and renewable energy. The Hebrides have less biodiversity than mainland Scotland, but a significant number of seals a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altai Mountains
The Altai Mountains (), also spelled Altay Mountains, are a mountain range in Central and East Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia and Kazakhstan converge, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob have their headwaters. The massif merges with the Sayan Mountains in the northeast, and gradually becomes lower in the southeast, where it merges into the high plateau of the Gobi Desert. It spans from about 45° to 52° N and from about 84° to 99° E. The region is inhabited by a sparse but ethnically diverse population, including Russians, Kazakhs, Altais, Mongols and Volga Germans, though predominantly represented by indigenous ethnic minorities of semi-nomadic stock. The local economy is based on bovine, sheep, horse husbandry, hunting, agriculture, forestry, and mining. The Altaic language family takes its name from this mountain range. Etymology and modern names ''Altai'' is derived from underlying form *''altañ'' "gold, golden" (compare Old Turkic 𐰞𐱃𐰆𐰣 ''altun'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |