|
Transition Metal Hydride
Transition metal hydrides are chemical compounds containing a transition metal bonded to hydrogen. Most transition metals form hydride complexes and some are significant in various catalytic and synthetic reactions. The term "hydride" is used loosely: some of them are acidic (e.g., H2Fe(CO)4), whereas some others are hydridic, having H−-like character (e.g., ZnH2). Classes of metal hydrides Binary metal hydrides Many transition metals form compounds with hydrogen. These materials are called binary hydrides, because they contain only two elements. The hydrogenic ligand is assumed to have hydridic (H−-like) character. These compounds are invariably insoluble in all solvents, reflecting their polymeric structures. They often exhibit metal-like electrical conductivity. Many are nonstoichiometric compounds. Electropositive metals ( Ti, Zr, Hf, Zn) and some other metals form hydrides with the stoichiometry MH or sometimes MH2 (M = Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Zn). The best studied are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken or new bonds formed or both. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
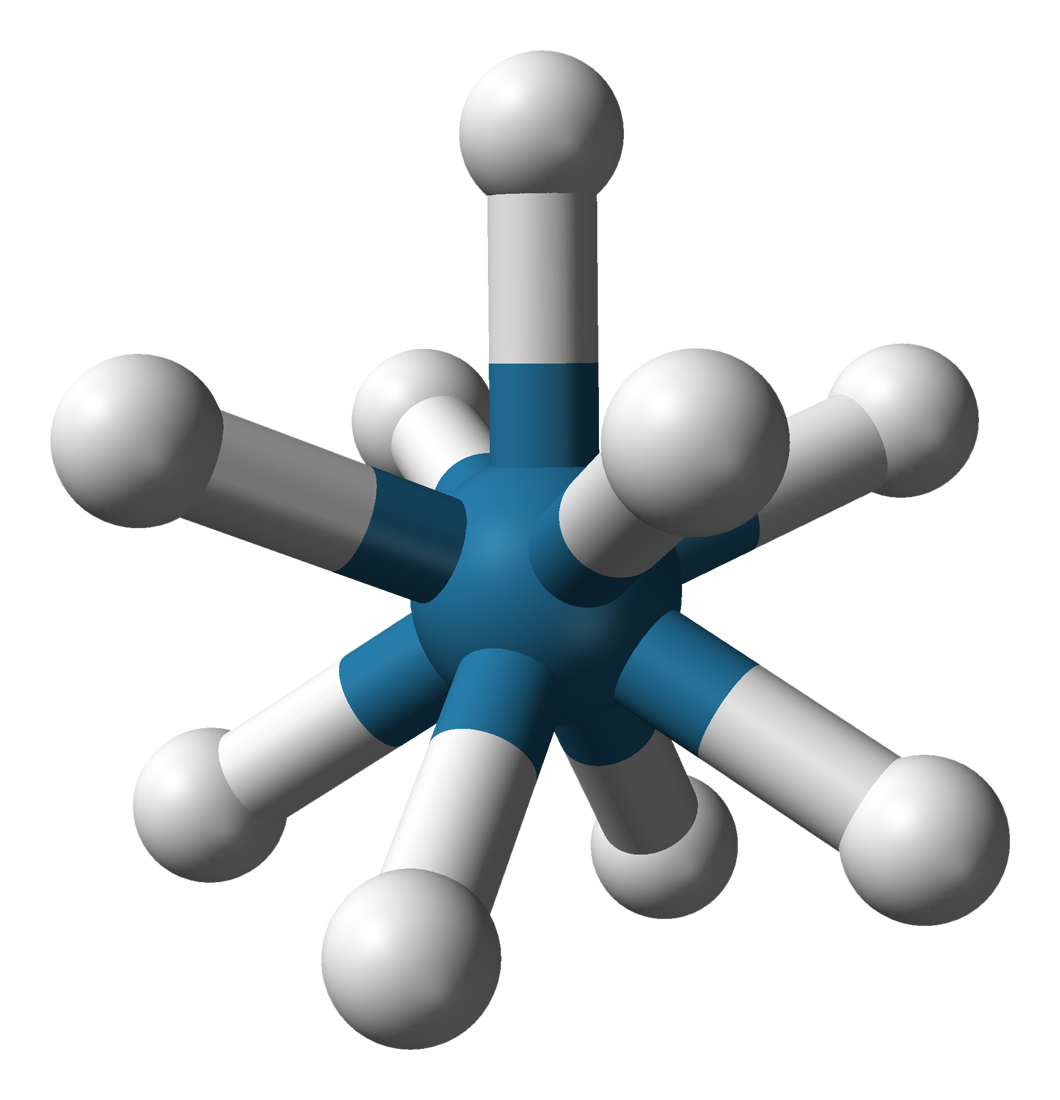
Potassium Nonahydridorhenate
Potassium nonahydridorhenate(VII) is an inorganic compound having the formula . This colourless salt is soluble in water but only poorly soluble in most alcohols. This salt contains the nonahydridorhenate(VII) anion, , which is a rare example of a coordination complex bearing only hydride ligands. History The study of rhenium hydrides can be traced to the 1950s and included reports of the "rhenide" anion, supposedly . These reports led to a series of investigations by A. P. Ginsberg and coworkers on the products from the reduction of perrhenate. The ''rhenide'' anion, , was based on the product of the reduction of perrhenate salts, such as the reduction of potassium perrhenate () by potassium metal. "Potassium rhenide" was shown to exist as a tetrahydrated complex, with the postulated chemical formula (potassium rhenide tetrahydrate). This compound exhibits strongly reducing properties, and slowly yields hydrogen gas when dissolved in water. The lithium and thallous salts were a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobalt Tetracarbonyl Hydride
Cobalt tetracarbonyl hydride is an organometallic compound with the formula H Co(CO)4. It is a volatile, yellow liquid that forms a colorless vapor and has an intolerable odor. The compound readily decomposes upon melt and ''in absentia'' of high CO partial pressures forms Co2(CO)8. Despite operational challenges associated with its handling, the compound has received considerable attention for its ability to function as a catalyst in hydroformylation. In this respect, HCo(CO)4 and related derivatives have received significant academic interest for their ability to mediate a variety of carbonylation (introduction of CO into inorganic compounds) reactions. Structure and properties HCo(CO)4 adopts trigonal bipyramidal structure, with the hydride ligand occupying one of the axial positions, giving an overall symmetry of ''C''3''v''. The three equatorial CO ligands are slightly bent out of the equatorial plane. The Co–CO and Co–H bond distances were determined by gas-phase electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Hieber
Walter Hieber (18 December 1895 – 29 November 1976) was an inorganic chemist, known as the father of metal carbonyl chemistry. He was born 18 December 1895 and died 29 November 1976. Hieber's father was Johannes Hieber, an influential evangelical minister and politician. Hieber was educated at Tübingen, Würzburg, and Heidelberg. In 1935 he was appointed Director of the Inorganic Chemical Institute at the Technical University in Münich. Among his numerous research findings, Hieber prepared the first metal carbonyl hydrides such as H2Fe(CO)4 and HMn(CO)5. He discovered that metal carbonyls undergo nucleophilic attack by hydroxide, the “Hieber base reaction.” He and his students discovered several metal carbonyl compounds such as Re2(CO)10 and Os3(CO)12 He pioneered the development of metal carbonyl sulfides.Hieber, W. and Scharfenberg, C., "Einwirkung organischer Schwefelverbindungen auf die Carbonyls des Eisens", Chemische Berichte, 1940, volume 73, pages 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwartz's Reagent
Schwartz's reagent is the common name for the organozirconium compound with the formula (C5H5)2ZrHCl, sometimes called zirconocene hydrochloride or zirconocene chloride hydride, and is named after Jeffrey Schwartz, a chemistry professor at Princeton University. This metallocene is used in organic synthesis for various transformations of alkenes and alkynes. Preparation The complex was first prepared by Wailes and Weigold. It can be purchased or readily prepared by reduction of zirconocene dichloride with lithium aluminium hydride: : (C5H5)2ZrCl2 + LiAlH4 → (C5H5)2ZrHCl + LiAlCl4 This reaction also affords (C5H5)2ZrH2, which is treated with methylene chloride to give Schwartz's reagent An alternative procedure that generated Schwartz's reagent from dihydride has also been reported. Moreover, it's possible to perform an ''in situ'' preparation of (C5H5)2ZrHCl from zirconocene dichloride by using LiH. This method can also be used to synthesize isotope-labeled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroformylation
In organic chemistry, hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an industrial process for the production of aldehydes () from alkenes (). This chemical reaction entails the net addition of a formyl group () and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention: production capacity reached 6.6 tons in 1995. It is important because aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resultant aldehydes are hydrogenated to Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols that are converted to detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in speciality chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and pharmaceuticals. The development of hydroformylation is one of the premier achievements of 20th-century Chemical industry, industrial chemistry. The process entails treatment of an alkene typically with high pressures (between 10 and 100 Atmosphere (unit), atmospheres) of carbon monoxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalyst
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. The rate increase occurs because the catalyst allows the reaction to occur by an alternative mechanism which may be much faster than the noncatalyzed mechanism. However the noncatalyzed mechanism does remain possible, so that the total rate (catalyzed plus noncatalyzed) can only increase in the presence of the catalyst and never decrease. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium Carbonyl Hydride
Carbonyl hydrido tris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I) arbonyl(hydrido)tris(triphenylphosphane)rhodium(I)is an organorhodium compound with the formula hH(CO)(PPh3)3(Ph = C6H5). It is a yellow, benzene-soluble solid, which is used industrially for hydroformylation. Preparation hH(CO)(PPh3)3was first prepared by the reduction of hCl(CO)(PPh3)2 e.g. with sodium tetrahydroborate, or triethylamine and hydrogen, in ethanol in the presence of excess triphenylphosphine: : hCl(CO)(PPh3)2 + NaBH4 + PPh3 → hH(CO)(PPh3)3 + NaCl + BH3 It can also be prepared from an aldehyde, rhodium trichloride and triphenylphosphine in basic alcoholic media. Structure The complex adopts a trigonal bipyramidal geometry with trans CO and hydrido ligands, resulting in ''pseudo'' -C3v symmetry. The Rh-P, Rh-C, and Rh-H distances are 2.32, 1.83, and 1.60 Å, respectively. This complex is one of a small number of stable pentacoordinate rhodium hydrides. Use in hydroformylation This precatalyst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury Hydride
Mercury hydride may refer to: * Mercury(I) hydride (HgH or Hg2H2), an extremely unstable gas *Mercury(II) hydride Mercury(II) hydride (systematically named mercurane(2) and dihydridomercury) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula (also written as ). It is both thermodynamically and kinetically unstable at ambient temperature, and as such, little ... (HgH2), a volatile but relatively stable white solid {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadmium Hydride
Cadmium is a chemical element; it has symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Like zinc, it demonstrates oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds, and like mercury, it has a lower melting point than the transition metals in groups 3 through 11. Cadmium and its congeners in group 12 are often not considered transition metals, in that they do not have partly filled ''d'' or ''f'' electron shells in the elemental or common oxidation states. The average concentration of cadmium in Earth's crust is between 0.1 and 0.5 parts per million (ppm). It was discovered in 1817 simultaneously by Stromeyer and Hermann, both in Germany, as an impurity in zinc carbonate. Cadmium occurs as a minor component in most zinc ores and is a byproduct of zinc production. It was used for a long time in the 1900s as a corrosion-resistant plating on steel, and cadmium compounds are used as red, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Complex
A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the periodic table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |