|
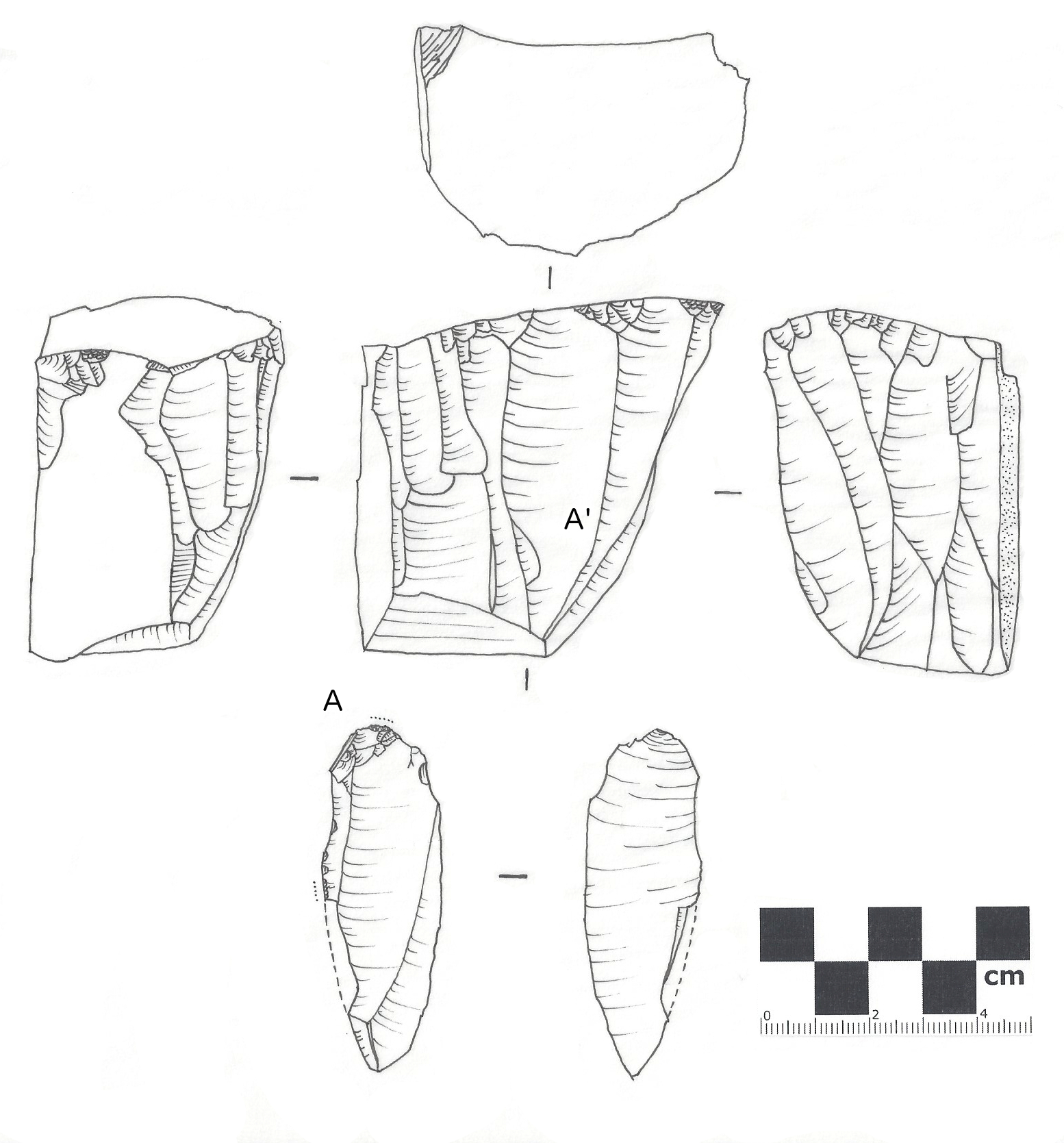
Tranchet Axehead (FindID 631102)
In archaeology, a tranchet flake is a characteristic type of Lithic flake, flake removed by a flintknapper during lithic reduction. Known as one of the major categories in core-trimming flakes, the making of a tranchet flake involves removing a flake parallel to the final intended cutting edge of the tool which creates a single straight edge as wide as the tool itself. A large flint artifact with a chisel-end, the tranchet flake has a cutting edge that is sharp and straight. The cutting edge is unmodified in most cases; sometimes, it is polished for increased durability and/or sharpness. To make a tranchet flake, a flintknapper can hold the core from which the tranchet flake is to be removed in two ways: freehand or with it supported against the leg. Knapping freehand allows for greater control while supporting the core against the leg makes the work easier. The technique used to make the tranchet flake was used in the making of other tools as well, including Tranchet axe, tranchet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Mesolithic Tranchet Flake (FindID 433078)
Late or LATE may refer to: Everyday usage * Tardy, or late, not being on time * Late (or the late) may refer to a person who is dead Music * ''Late'' (The 77s album), 2000 * Late (Alvin Batiste album), 1993 * Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Grohl on his ''Pocketwatch'' album * Late (rapper), an underground rapper from Wolverhampton * "Late", a song by Kanye West from ''Late Registration'' Other uses * Late (Tonga), an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavau in the kingdom of Tonga * "Late" (''The Handmaid's Tale''), a television episode * LaTe, Oy Laivateollisuus Ab, a defunct shipbuilding company * Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia * Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law * Local average treatment effect, a concept in econometrics * Late, a synonym for ''cooler'' in stellar classification See also * * * ''Lates'', a genus of fish in the lates perch family * Later (other) Later may refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves Survey (archaeology), surveying, Archaeological excavation, excavation, and eventually Post excavation, analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithic Flake
In archaeology, a lithic flake is a "portion of rock (geology), rock removed from an objective piece by percussion or pressure,"Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press and may also be referred to as simply a ''flake'', or collectively as debitage. The objective piece, or the rock being reduced by the removal of flakes, is known as a lithic core, core.Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press Once the proper tool stone has been selected, a percussor or pressure flaker (e.g., an antler Tine (structural), tine) is used to direct a sharp blow, or apply sufficient force, respectively, to the surface of the stone, often on the edge of the piece. The energy of this blow propagates through the material, often (termination type, but not always) producing a Hertzian cone of force which causes the rock to fracture in a controllable fashion. Since c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flintknapper
Knapper is a village in Nord-Odal Municipality in Innlandet county, Norway. The village is located about north of the village of Mo. The village had a population (2009) of 212 and a population density of . Since 2009, the population and area data for this village area has not been separately tracked by Statistics Norway Statistics Norway (, abbreviated to ''SSB'') is the Norwegian statistics bureau. It was established in 1876. Relying on a staff of about 1,000, Statistics Norway publish about 1,000 new statistical releases every year on its web site. All rele .... References Nord-Odal Villages in Innlandet {{Innlandet-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithic Reduction
In archaeology, in particular of the Stone Age, lithic reduction is the process of fashioning stones or rocks from their natural state into tools or weapons by removing some parts. It has been intensely studied and many archaeological industries are identified almost entirely by the lithic analysis of the precise style of their tools and the chaîne opératoire of the reduction techniques they used. Normally the starting point is the selection of a piece of tool stone that has been detached by natural geological processes, and is an appropriate size and shape. In some cases solid rock or larger boulders may be quarried and broken into suitable smaller pieces, and in others the starting point may be a piece of the debitage, a flake removed from a previous operation to make a larger tool. The selected piece is called the lithic core (also known as the "objective piece"). A basic distinction is that between flaked or knapped stone, the main subject here, and ground stone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tranchet Axe
A tranchet axe is a Stone tool, lithic tool made by removing a lithic flake, flake, known as a tranchet flake. The flake is removed parallel to the final intended cutting edge of the tool which creates a single straight and sharp cutting edge as wide as the tool itself. The blade can be easily resharpened by detaching a new tranchet flake.This stone working technique represents an important step in the evolution of lithic technology, as it bridged the gap between the more rudimentary Paleolithic tools and the relatively polished tools of the Neolithic. At certain European excavation sites, the discovery of tranchet axeheads is regarded as an early Mesolithic marker. Archeologists have unearthed these axes from various time periods in excavation sites on many continents. They have been found in some Acheulean Assemblage (archaeology), assemblages as well as in Mesolithic flaked stone industries. Archeologists have also excavated tranchet axes from Central American sites, including t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Paleolithic
The Lower Paleolithic (or Lower Palaeolithic) is the earliest subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. It spans the time from around 3.3 million years ago when the first evidence for stone tool production and use by hominins appears in the current archaeological record, until around 300,000 years ago, spanning the Oldowan ("mode 1") and Acheulean ("mode 2") lithics industries. In African archaeology, the time period roughly corresponds to the Early Stone Age, the earliest finds dating back to 3.3 million years ago, with Lomekwian stone tool technology, spanning Mode 1 stone tool technology, which begins roughly 2.6 million years ago and ends between 400,000 and 250,000 years ago, with Mode 2 technology. The Middle Paleolithic followed the Lower Paleolithic and recorded the appearance of the more advanced prepared-core tool-making technologies such as the Mousterian. Whether the earliest control of fire by hominins dates to the Lower or to the Middle Paleolithic rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |