|
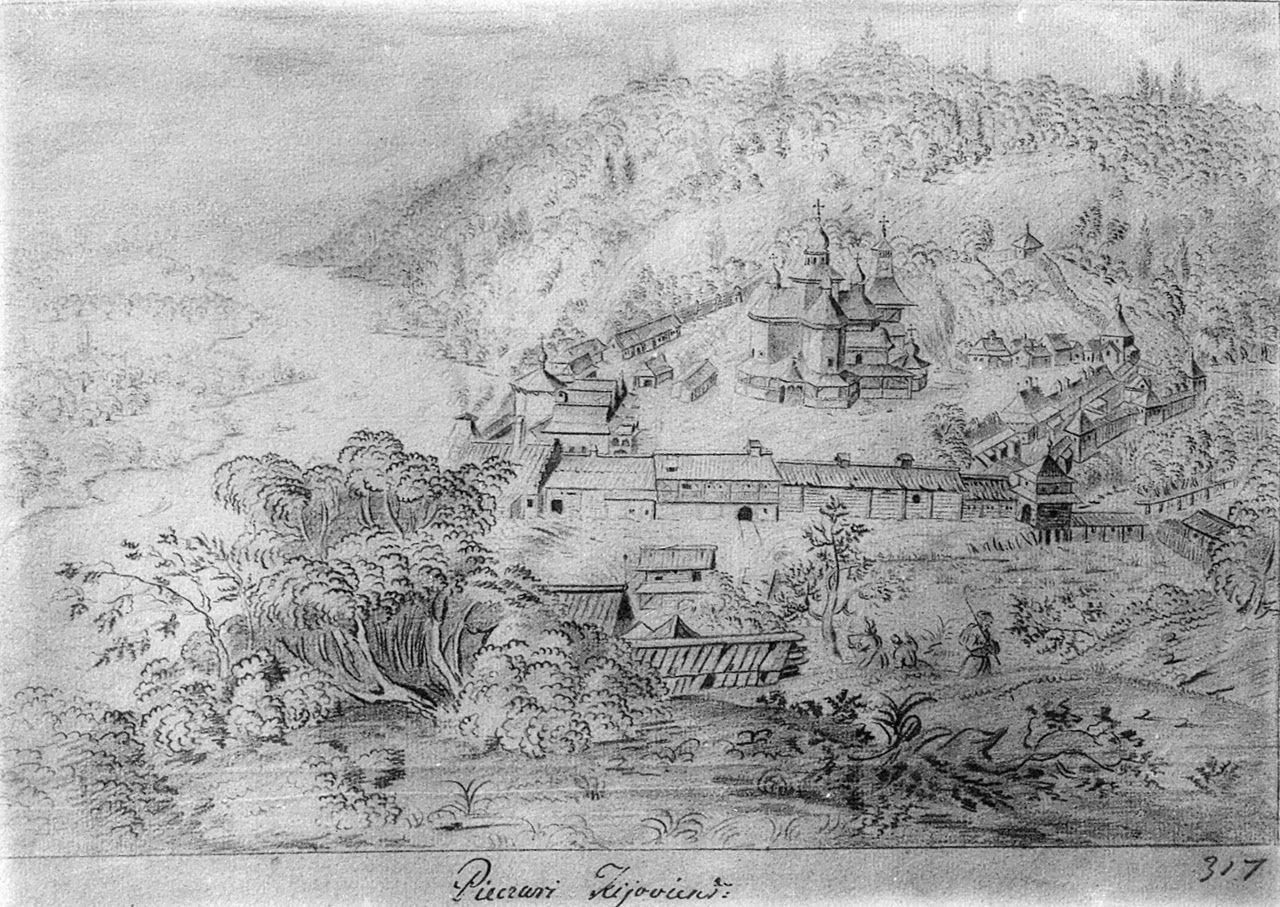
Trakhtemyrivskyi Monastery
The Trakhtemyriv Monastery ( uk, Трахтемирівський монастир) was a historic cossack monastery located near the settlements of Trakhtemyriv and Zarubnytsiv of modern-day Cherkasy Oblast (province). The area where the monastery was located, former village of Monastyrok, is now submerged under the Kaniv Reservoir due to the construction of the Kaniv Hydroelectric Station. The date of the monastery's foundation is unknown. The decree of Polish King Stephen Báthory dated 1578 made the monastery a place where sick and elderly Registered Cossacks could live at. In the 1660s, a Polish szlachta army destroyed the monastery; it was not reconstructed, and its position as the cossack monastery was replaced by the Mezhyhirskyi Monastery near Vyshhorod Vyshhorod ( uk, Ви́шгород) is a city in Kyiv Oblast (region) in central Ukraine, situated immediately north of Kyiv city, the national capital, and part of the Kyiv metropolitan area. It is on the right (wester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaporozhian Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack Army, Zaporozhian Host, (, or uk, Військо Запорізьке, translit=Viisko Zaporizke, translit-std=ungegn, label=none) or simply Zaporozhians ( uk, Запорожці, translit=Zaporozhtsi, translit-std=ungegn) were Cossacks who lived beyond (that is, downstream from) the Dnieper Rapids, the land also known historically as the Wild Fields in what is today central and eastern Ukraine. Much of this territory is now flooded by the waters of the Kakhovka Reservoir. The Zaporozhian Sich grew rapidly in the 15th century from serfs fleeing the more controlled parts of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It became established as a well-respected political entity with a parliamentary system of government. During the course of the 16th, 17th and well into the 18th century, the Zaporozhian Cossacks were a strong political and military force that challenged the authority of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Tsardom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherkasy Oblast
Cherkasy Oblast ( uk, Черка́ська о́бласть, Cherkaska oblast, ), also referred to as Cherkashchyna ( uk, Черка́щина, ) is an oblast (province) of central Ukraine located along the Dnieper River. The administrative center of the oblast is the city of Cherkasy. The current population of the oblast is Geography With 20,900 km², Cherkasy Oblast is the 18th largest oblast of Ukraine, comprising about 3.5% of the area of the country. The south flowing Dnieper River with the hilly western bank and the plain eastern bank divides the oblast into two unequal parts. The larger western part belongs to the Dnieper Upland. The low-lying eastern part of the oblast used to be subject to the frequent Dnieper flooding before the flow of the river became controlled by multiple dams of Hydroelectric Power Plants constructed along the river in the 20th century. The oblast extends for 245 km from south-west to north-east, and for 150 km from north to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oblast
An oblast (; ; Cyrillic (in most languages, including Russian and Ukrainian): , Bulgarian: ) is a type of administrative division of Belarus, Bulgaria, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Ukraine, as well as the Soviet Union and the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. Official terms in successor states of the Soviet Union differ, but some still use a cognate of the Russian term, e.g., ''vobłasć'' (''voblasts'', ''voblasts'', official orthography: , Taraškievica: , ) is used for regions of Belarus, ' (plural: ') for regions of Kazakhstan, and ''oblusu'' (') for regions of Kyrgyzstan. The term is often translated as "area", " zone", "province" or "region". The last translation may lead to confusion, because " raion" may be used for other kinds of administrative division, which may be translated as "region", "district" or "county" depending on the context. Unlike "province", translations as "area", "zone", and "region" may lead to confusion because they have very common meanings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaniv Reservoir
The Kaniv Reservoir ( uk, Канівське водосховище, ) is a water reservoir located on the Dnieper River in Ukraine. Named after the city of Kaniv, it covers a total area of 675 square kilometers within the Cherkasy and Kyiv Oblasts. It was created in 1972 following construction of the dams of the Kaniv Hydroelectric Power Plant on the Dnieper River. Along with the Kakhovka Reservoir The Kakhovka Reservoir (, ''Kakhovs′ke vodoskhovyshche'') is a water reservoir on the Dnieper River in Ukraine. It was created in 1956, when the Kakhovka Hydroelectric Power Plant was built. It is one of several reservoirs in the Dnieper rese ..., the Dnipro Reservoir, the Kamianske Reservoir, the Kremenchuk Reservoir, and the Kyiv Reservoir, it has created a deep-water route on the Dnieper, allowing ships to sail upstream as far as the Prypiat River. The reservoir is 162 km long, up to 5 km wide, and has an average depth of 5.5 meters. The total water volume i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaniv
Kaniv ( uk, Канів, ) city located in Cherkasy Raion, Cherkasy Oblast (province) in central Ukraine. The city rests on the Dnieper River, and is also one of the main inland river ports on the Dnieper. It hosts the administration of Kaniv urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Population: Kaniv is a historical town that was founded in the 11th century by Kievan Prince Yaroslav the Wise. This pleasant city is known today mostly for the burial site of Taras Shevchenko, the great Ukrainian poet and artist. Picturesque and ancient, Kaniv was once one of the largest cities of Kievan Rus'. At that time, it was an outpost used for diplomatic meetings between Ruthenian princes and ambassadors of militant tribes. Later, in the 18th century, it became a popular destination for elderly Cossacks, who wanted to live out their days on the banks of the great Dnieper River, and on the Chernecha Mountain, where, according to legend, a monastery stood in the past. The mountain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch in real union, who was both King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania. It was one of the largest and most populous countries of 16th- to 17th-century Europe. At its largest territorial extent, in the early 17th century, the Commonwealth covered almost and as of 1618 sustained a multi-ethnic population of almost 12 million. Polish and Latin were the two co-official languages. The Commonwealth was established by the Union of Lublin in July 1569, but the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania had been in a ''de facto'' personal union since 1386 with the marriage of the Polish queen Jadwiga (Hedwig) and Lithuania's Grand Duke Jogaila, who was crowned King '' jure uxoris'' Władys� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electable position in Europe (16th to 18th centuries). The first known Polish ruler is Duke Mieszko I, who adopted Christianity under the authority of Rome in the year 966. He was succeeded by his son, Bolesław I the Brave, who greatly expanded the boundaries of the Polish state and ruled as the first king in 1025. The following centuries gave rise to the mighty Piast dynasty, consisting of both kings such as Mieszko II Lambert, Przemysł II or Władysław I the Elbow-high and dukes like Bolesław III Wrymouth. The dynasty ceased to exist with the death of Casimir III the Great in 1370. In the same year, the Capetian House of Anjou became the ruling house with Louis I as king of both Poland and Hungary. His daughter, Jadwiga, later married Jogaila, the pagan Grand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Báthory Of Poland
Stephen or Steven is a common English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( grc-gre, Στέφανος ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the first martyr (or " protomartyr") of the Christian Church. In English, Stephen is most commonly pronounced as ' (). The name, in both the forms Stephen and Steven, is often shortened to Steve or Stevie. The spelling as Stephen can also be pronounced which is from the Greek original version, Stephanos. In English, the female version of the name is Stephanie. Many surnames are derived from the first name, including Stephens, Stevens, Stephenson, and Stevenson, all of which mean "Stephen's (son)". In modern times the name has sometimes been given with intentionally non-standard spelling, such as Stevan or Stevon. A common variant of the name used in English is Stephan ; related names that have found so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Registered Cossacks
Registered Cossacks (, , pl, Kozacy rejestrowi) comprised special Cossack units of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth army in the 16th and 17th centuries. Registered Cossacks became a military formation of the Commonwealth army beginning in 1572 soon after the Union of Lublin (1569), when most of the territory of modern Ukraine passed to the Crown of Poland. Registered Cossack formations were based on the Zaporozhian Cossacks who already lived on the lower reaches of the Dnieper River amidst the Pontic steppes as well as on self-defense formations within settlements in the region of modern Central and Southern Ukraine. History Origins The first recorded official plan for enlisting Cossack formations as a border service in Poland-Lithuania was brought to the State Council of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1524 by Semen Polozovic and Kristof Kmitic. However, due to a lack of funds, the idea was not realized. The starosta of Cherkasy, Ostap Dashkevych, revived the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szlachta
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian: šlėkta) were the noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth who, as a class, had the dominating position in the state, exercising extensive political rights and power. Szlachta as a class differed significantly from the feudal nobility of Western Europe. The estate was officially abolished in 1921 by the March Constitution."Szlachta. Szlachta w Polsce" ''Encyklopedia PWN'' The origins of the ''szlachta'' are obscure and the subject of several theories. Traditionally, its members owned land (allods), [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mezhyhirskyi Monastery
__NOTOC__ The Mezhyhirya Savior-Transfiguration Monastery). See: , group="nb" ( uk, Межигірський Спасо-Преображенський монастир, ''Mezhyhirskyi Spaso-Preobrazhenskyi Monastyr'') was an Eastern Orthodox female monastery that was located in the neighborhood of Mezhyhiria. The monastery served as a historic Princely residency of Rurik dynasty during the Medieval times located just to the north of Vyshhorod. Today, the territory is part of the Vyshhorod Raion, Kyiv Oblast (province) in northern Ukraine. The location is situated in the Mezhyhirya ravine, on the right bank of the Dnieper River in close proximity to the Kyiv Reservoir. Founded in 988 AD, the Mezhyhirya Monastery was one of the first monasteries established in the East Slavic state of Kievan Rus'. Throughout its existence, it was destroyed, and then restored numerous times, yet it was not spared destruction by Soviet authorities in 1935. At the time of its height, the Mezhyhir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vyshhorod
Vyshhorod ( uk, Ви́шгород) is a city in Kyiv Oblast (region) in central Ukraine, situated immediately north of Kyiv city, the national capital, and part of the Kyiv metropolitan area. It is on the right (western) bank of the Dnieper river and, as the location of the Kyiv Hydroelectric Power Plant, the northern part of the city is beside the Kyiv Reservoir. It is the administrative center of Vyshhorod Raion and hosts the administration of Vyshhorod urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. With a history dating back to the first millennium, Vyshhorod is now a notable industrial center and a growing commuter town for Kyiv. Its population is approximately Geography and climate Vyshhorod is located on a hilly right bank of the Dnieper river adjoining the dam of the Kyiv Reservoir. History The earliest historical mention of ''Vyshhorod'' (the name literally translates as " the town upstream") dates from as early as 946 when it was described as the favour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |