|
Trace (matrix)
In linear algebra, the trace of a square matrix , denoted , is the sum of the elements on its main diagonal, a_ + a_ + \dots + a_. It is only defined for a square matrix (). The trace of a matrix is the sum of its eigenvalues (counted with multiplicities). Also, for any matrices and of the same size. Thus, similar matrices have the same trace. As a consequence, one can define the trace of a linear operator mapping a finite-dimensional vector space into itself, since all matrices describing such an operator with respect to a basis are similar. The trace is related to the derivative of the determinant (see Jacobi's formula). Definition The trace of an square matrix is defined as \operatorname(\mathbf) = \sum_^n a_ = a_ + a_ + \dots + a_ where denotes the entry on the row and column of . The entries of can be real numbers, complex numbers, or more generally elements of a field . The trace is not defined for non-square matrices. Example Let be a matrix, with \mathb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Algebra
Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning linear equations such as :a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n=b, linear maps such as :(x_1, \ldots, x_n) \mapsto a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n, and their representations in vector spaces and through matrix (mathematics), matrices. Linear algebra is central to almost all areas of mathematics. For instance, linear algebra is fundamental in modern presentations of geometry, including for defining basic objects such as line (geometry), lines, plane (geometry), planes and rotation (mathematics), rotations. Also, functional analysis, a branch of mathematical analysis, may be viewed as the application of linear algebra to Space of functions, function spaces. Linear algebra is also used in most sciences and fields of engineering because it allows mathematical model, modeling many natural phenomena, and computing efficiently with such models. For nonlinear systems, which cannot be modeled with linear algebra, it is often used for dealing with first-order a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vectorization (mathematics)
In mathematics, especially in linear algebra and matrix theory, the vectorization of a matrix is a linear transformation which converts the matrix into a vector. Specifically, the vectorization of a matrix ''A'', denoted vec(''A''), is the column vector obtained by stacking the columns of the matrix ''A'' on top of one another: \operatorname(A) = _, \ldots, a_, a_, \ldots, a_, \ldots, a_, \ldots, a_\mathrm Here, a_ represents the element in the ''i''-th row and ''j''-th column of ''A'', and the superscript ^\mathrm denotes the transpose. Vectorization expresses, through coordinates, the isomorphism \mathbf^ := \mathbf^m \otimes \mathbf^n \cong \mathbf^ between these (i.e., of matrices and vectors) as vector spaces. For example, for the 2×2 matrix A = \begin a & b \\ c & d \end, the vectorization is \operatorname(A) = \begin a \\ c \\ b \\ d \end. The connection between the vectorization of ''A'' and the vectorization of its transpose is given by the commutation matrix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Similarity Invariance
In linear algebra, similarity invariance is a property exhibited by a function whose value is unchanged under similarities of its domain. That is, f is invariant under similarities if f(A) = f(B^AB) where B^AB is a matrix similar to ''A''. Examples of such functions include the trace, determinant, characteristic polynomial, and the minimal polynomial. A more colloquial phrase that means the same thing as similarity invariance is "basis independence", since a matrix can be regarded as a linear operator, written in a certain basis, and the same operator in a new basis is related to one in the old basis by the conjugation B^AB, where B is the transformation matrix to the new basis. See also * Invariant (mathematics) In mathematics, an invariant is a property of a mathematical object (or a class of mathematical objects) which remains unchanged after operations or transformations of a certain type are applied to the objects. The particular class of objec ... * Gauge inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix Product
In mathematics, specifically in linear algebra, matrix multiplication is a binary operation that produces a matrix from two matrices. For matrix multiplication, the number of columns in the first matrix must be equal to the number of rows in the second matrix. The resulting matrix, known as the matrix product, has the number of rows of the first and the number of columns of the second matrix. The product of matrices and is denoted as . Matrix multiplication was first described by the French mathematician Jacques Philippe Marie Binet in 1812, to represent the composition of linear maps that are represented by matrices. Matrix multiplication is thus a basic tool of linear algebra, and as such has numerous applications in many areas of mathematics, as well as in applied mathematics, statistics, physics, economics, and engineering. Computing matrix products is a central operation in all computational applications of linear algebra. Notation This article will use the following notat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Conjugate
In mathematics, the complex conjugate of a complex number is the number with an equal real part and an imaginary part equal in magnitude but opposite in sign. That is, if a and b are real numbers, then the complex conjugate of a + bi is a - bi. The complex conjugate of z is often denoted as \overline or z^*. In polar form, if r and \varphi are real numbers then the conjugate of r e^ is r e^. This can be shown using Euler's formula. The product of a complex number and its conjugate is a real number: a^2 + b^2 (or r^2 in polar coordinates). If a root of a univariate polynomial with real coefficients is complex, then its complex conjugate is also a root. Notation The complex conjugate of a complex number z is written as \overline z or z^*. The first notation, a vinculum, avoids confusion with the notation for the conjugate transpose of a matrix, which can be thought of as a generalization of the complex conjugate. The second is preferred in physics, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Vector Space
In mathematics and physics, a vector space (also called a linear space) is a set whose elements, often called ''vectors'', can be added together and multiplied ("scaled") by numbers called ''scalars''. The operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication must satisfy certain requirements, called ''vector axioms''. Real vector spaces and complex vector spaces are kinds of vector spaces based on different kinds of scalars: real numbers and complex numbers. Scalars can also be, more generally, elements of any field. Vector spaces generalize Euclidean vectors, which allow modeling of physical quantities (such as forces and velocity) that have not only a magnitude, but also a direction. The concept of vector spaces is fundamental for linear algebra, together with the concept of matrices, which allows computing in vector spaces. This provides a concise and synthetic way for manipulating and studying systems of linear equations. Vector spaces are characterized by their dim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
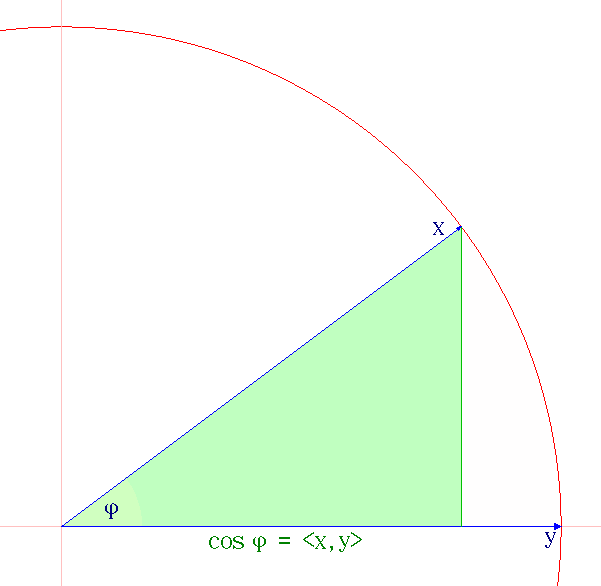
Hermitian Inner Product
In mathematics, an inner product space (or, rarely, a Hausdorff pre-Hilbert space) is a real vector space or a complex vector space with an operation called an inner product. The inner product of two vectors in the space is a scalar, often denoted with angle brackets such as in \langle a, b \rangle. Inner products allow formal definitions of intuitive geometric notions, such as lengths, angles, and orthogonality (zero inner product) of vectors. Inner product spaces generalize Euclidean vector spaces, in which the inner product is the dot product or ''scalar product'' of Cartesian coordinates. Inner product spaces of infinite dimension are widely used in functional analysis. Inner product spaces over the field of complex numbers are sometimes referred to as unitary spaces. The first usage of the concept of a vector space with an inner product is due to Giuseppe Peano, in 1898. An inner product naturally induces an associated norm, (denoted , x, and , y, in the picture); so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of statistical survey, surveys and experimental design, experiments. When census data (comprising every member of the target population) cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey sample (statistics), samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix Calculus
In mathematics, matrix calculus is a specialized notation for doing multivariable calculus, especially over spaces of matrix (mathematics), matrices. It collects the various partial derivatives of a single Function (mathematics), function with respect to many Variable (mathematics), variables, and/or of a multivariate function with respect to a single variable, into Vector (mathematics and physics), vectors and matrices that can be treated as single entities. This greatly simplifies operations such as finding the maximum or minimum of a multivariate function and solving systems of differential equations. The notation used here is commonly used in statistics and engineering, while the tensor index notation is preferred in physics. Two competing notational conventions split the field of matrix calculus into two separate groups. The two groups can be distinguished by whether they write the derivative of a Scalar (mathematics), scalar with respect to a vector as a Row and column ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cauchy–Schwarz Inequality
The Cauchy–Schwarz inequality (also called Cauchy–Bunyakovsky–Schwarz inequality) is an upper bound on the absolute value of the inner product between two vectors in an inner product space in terms of the product of the vector norms. It is considered one of the most important and widely used inequalities in mathematics. Inner products of vectors can describe finite sums (via finite-dimensional vector spaces), infinite series (via vectors in sequence spaces), and integrals (via vectors in Hilbert spaces). The inequality for sums was published by . The corresponding inequality for integrals was published by and . Schwarz gave the modern proof of the integral version. Statement of the inequality The Cauchy–Schwarz inequality states that for all vectors \mathbf and \mathbf of an inner product space where \langle \cdot, \cdot \rangle is the inner product. Examples of inner products include the real and complex dot product; see the examples in inner product. Every ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frobenius Norm
In the field of mathematics, norms are defined for elements within a vector space. Specifically, when the vector space comprises matrices, such norms are referred to as matrix norms. Matrix norms differ from vector norms in that they must also interact with matrix multiplication. Preliminaries Given a field \ K\ of either real or complex numbers (or any complete subset thereof), let \ K^\ be the -vector space of matrices with m rows and n columns and entries in the field \ K ~. A matrix norm is a norm on \ K^~. Norms are often expressed with double vertical bars (like so: \ \, A\, \ ). Thus, the matrix norm is a function \ \, \cdot\, : K^ \to \R^\ that must satisfy the following properties: For all scalars \ \alpha \in K\ and matrices \ A, B \in K^\ , * \, A\, \ge 0\ (''positive-valued'') * \, A\, = 0 \iff A=0_ (''definite'') * \left\, \alpha\ A \right\, = \left, \alpha \\ \left\, A\right\, \ (''absolutely homogeneous'') * \, A + B \, \le \, A \, + \, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norm (mathematics)
In mathematics, a norm is a function (mathematics), function from a real or complex vector space to the non-negative real numbers that behaves in certain ways like the distance from the Origin (mathematics), origin: it Equivariant map, commutes with scaling, obeys a form of the triangle inequality, and zero is only at the origin. In particular, the Euclidean distance in a Euclidean space is defined by a norm on the associated Euclidean vector space, called the #Euclidean norm, Euclidean norm, the #p-norm, 2-norm, or, sometimes, the magnitude or length of the vector. This norm can be defined as the square root of the inner product of a vector with itself. A seminorm satisfies the first two properties of a norm but may be zero for vectors other than the origin. A vector space with a specified norm is called a normed vector space. In a similar manner, a vector space with a seminorm is called a ''seminormed vector space''. The term pseudonorm has been used for several related meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |