|
Toxin Complex A
''Photorhabdus luminescens'' (previously called ''Xenorhabdus luminescens'') is a Gammaproteobacterium of the family Morganellaceae, and is a lethal pathogen of insects. It lives in the Gut (zoology), gut of an entomopathogenic nematode of the family Heterorhabditidae. When the nematode infects an insect, ''P. luminescens'' is released into the blood stream and rapidly kills the insect Host (biology), host (within 48 hours) by producing toxins, such as the high molecular weight insecticidal protein complex Tca. ''P. luminescens'' also produces a proteic toxin through the expression of a single gene called ''makes caterpillars floppy'' (mcf). It also secretes enzymes which break down the body of the infected insect and bioconvert it into nutrients which can be used by both nematode and bacteria. In this way, both organisms gain enough nutrients to replicate (or reproduce in the case of the nematode) several times. The bacteria enter the nematode progeny (genetic descendant), proge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerard M
Gerard is a masculine forename of Proto-Germanic origin, variations of which exist in many Germanic and Romance languages. Like many other early Germanic names, it is dithematic, consisting of two meaningful constituents put together. In this case, those constituents are ''gari'' > ''ger-'' (meaning 'spear') and -''hard'' (meaning 'hard/strong/brave'). Common forms of the name are Gerard (English, Scottish, Irish, Dutch, Polish and Catalan); Gerrard (English, Scottish, Irish); (Italian, and Spanish); ( Portuguese); (Italian); (Northern Italian, now only a surname); (variant forms and , now only surnames, French); ( Irish); Gerhardt and Gerhart/Gerhard/Gerhardus (German, Dutch, and Afrikaans); ( Hungarian); ( Lithuanian) and / ( Latvian); (Greece). A few abbreviated forms are Gerry and Jerry (English); (German) and (Afrikaans and Dutch); (Afrikaans and Dutch); (Afrikaans); (Dutch) and ( Bulgarian). The introduction of the name 'Gerard' into the English langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Competition (biology)
Competition is an Biological interaction, interaction between organisms or species in which both require one or more Resource (biological), resources that are in Limiting factor, limited supply (such as food, water, or Territory (animal), territory). Competition lowers the Fitness (biology), fitness of both organisms involved since the presence of one of the organisms always reduces the amount of the resource available to the other. In the study of community ecology, competition within and between members of a species is an important biological interaction. Competition is one of many interacting Biotic component, biotic and Abiotic component, abiotic factors that affect Community (ecology), community structure, species diversity, and population dynamics (shifts in a population over time). There are three major Mechanism (biology), mechanisms of competition: interference, exploitation, and apparent competition (in order from most direct to least direct). Interference and exploitat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterobacterales
Enterobacterales is an order of Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, non-spore forming, Facultative anaerobic organism, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria with the class Gammaproteobacteria. The type genus of this order is ''Enterobacter.'' The name Enterobacterales is derived from the Latin term ''Enterobacter'', referring the type genus of the order and the suffix "-ales", an ending used to denote an order. Together, Enterobacterales refers to an order whose nomenclatural type is the genus ''Enterobacter''. Historical Identification and Systematics Enterobacterales was proposed in 2005 under the name "Enterobacteriales". However, the name "Enterobacteriales" was not validated according to the rules of the ''International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes,'' thus it lacked standing in nomenclature, so the name was written in parentheses. "Enterobacteriales" was a monotypic order, containing only the family ''Enterobacteriaceae'', and shared its type genus ''Esch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonas Protegens
''Pseudomonas protegens'' are widespread Gram-negative, plant-protecting bacteria. Some of the strains of this novel bacterial species (CHA0 and Pf-5, for example) previously belonged to '' P. fluorescens''. They were reclassified since they seem to cluster separately from other fluorescent ''Pseudomonas'' species. ''P. protegens'' is phylogenetically related to the ''Pseudomonas'' species complexes '' P. fluorescens'', '' P. chlororaphis'', and '' P. syringae''. The bacterial species characteristically produces the antimicrobial compounds pyoluteorin and 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol (DAPG) which are active against various plant pathogens. General characteristics Like '' P. fluorescens'', ''Pseudomonas protegens'' is a typical soil microorganism with an extremely versatile metabolism, and can be isolated from roots of various plant species. The microbe is strictly aerobe (no reduction of nitrate) and oxidase-positive. The bacterium grows at temperatures between 4 °C and 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioluminescence Imaging
Bioluminescence imaging (BLI) is a technology developed over the past decades (1990's and onward). that allows for the noninvasive study of ongoing biological processes Recently, bioluminescence tomography (BLT) has become possible and several systems have become commercially available. In 2011, PerkinElmer acquired one of the most popular lines of optical imaging systems with bioluminescence from Caliper Life Sciences. Background Bioluminescence is the process of light emission in living organisms. Bioluminescence imaging utilizes native light emission from one of several organisms which bioluminesce, also known as luciferase enzymes. The three main sources are the North American firefly, the sea pansy (and related marine organisms), and bacteria like '' Photorhabdus luminescens'' and '' Vibrio fischeri''. The DNA encoding the luminescent protein is incorporated into the laboratory animal either via a viral vector or by creating a transgenic animal. Rodent models of cancer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GcvB RNA
The gcvB RNA gene encodes a small non-coding RNA involved in the regulation of a number of amino acid transport systems as well as amino acid biosynthetic genes. The GcvB gene is found in enteric bacteria such as ''Escherichia coli''. GcvB regulates genes by acting as an antisense binding partner of the mRNAs for each regulated gene. This binding is dependent on binding to a protein called Hfq. Transcription of the GcvB RNA is activated by the adjacent GcvA gene and repressed by the GcvR gene. A deletion of GcvB RNA from ''Y. pestis'' changed colony shape as well as reducing growth. It has been shown by gene deletion that GcvB is a regulator of acid resistance in ''E. coli''. GcvB enhances the ability of the bacterium to survive low pH by upregulating the levels of the alternate sigma factor RpoS. A polymeric form of GcvB has recently been identified. Interaction of GcvB with small RNA SroC triggers the degradation of GcvB by RNase E, lifting the GcvB-mediated mRNA repression o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
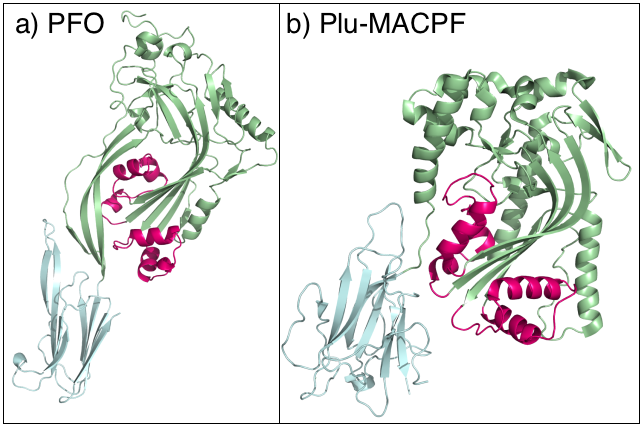
MACPF
The Membrane Attack Complex/Perforin (MACPF) superfamily, sometimes referred to as the MACPF/CDC superfamily, is named after a domain that is common to the membrane attack complex (MAC) proteins of the complement system (C6, C7, C8α, C8β and C9) and perforin (PF). Members of this protein family are pore-forming toxins (PFTs). In eukaryotes, MACPF proteins play a role in immunity and development. Archetypal members of the family are complement C9 and perforin, both of which function in human immunity. C9 functions by punching holes in the membranes of Gram-negative bacteria. Perforin is released by cytotoxic T cells and lyses virally infected and transformed cells. In addition, perforin permits delivery of cytotoxic proteases called granzymes that cause cell death. Deficiency of either protein can result in human disease. Structural studies reveal that MACPF domains are related to cholesterol-dependent cytolysins (CDCs), a family of pore forming toxins previously ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sequenced Bacterial Genomes
This list of sequenced eubacterial genomes contains most of the eubacteria known to have publicly available complete genome sequences. Most of these sequences have been placed in the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration, a public database which can be searched Search for details on specific genomes by organism name and strain. on the web. A few of the listed genomes may not be in the INSDC database, but in other public databases. Genomes listed as "Unpublished" are in a database, but not in the peer-reviewed scientific literature. For the genomes of archaea see list of sequenced archaeal genomes. Abditibacteriota Actinomycetota Aquificota Armatimonadota Bacteroidota/ Chlorobiota group Caldisericota Chlamydiota/ Verrucomicrobiota group Chloroflexota Chrysiogenota Cyanobacteria Deferribacterota Deinococcota Dictyoglomota Elusimicrobiota Fibrobacterota/Acidobacteriota group Bacillota Fusobacteriota Gemmatimonadota Nitr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mental Floss
''Mental Floss'' (stylized as ''mental_floss'') is an American online magazine and digital, print, and e-commerce media company focused on millennials. It is owned by Minute Media, an international digital media publisher based in London, England, with an associated research and development center in Tel Aviv, Israel. It is based in New York City, United States. mentalfloss.com, which presents facts, puzzles, and trivia with a humorous tone, draws 20.5 million unique users a month. Its YouTube channel produces three weekly series and has 1.3 million subscribers. In October 2015, ''Mental Floss'' teamed with the National Geographic Channel for its first televised special, ''Brain Surgery Live with'' mental_floss, the first brain surgery ever broadcast live. Launched in Birmingham, Alabama in 2001, the company has additional offices in Midtown Manhattan. The publication was included in ''Inc.'' magazine's list of the 5,000 fastest growing private companies. Before it became a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Scientist
''New Scientist'' is a popular science magazine covering all aspects of science and technology. Based in London, it publishes weekly English-language editions in the United Kingdom, the United States and Australia. An editorially separate organisation publishes a monthly Dutch-language edition. First published on 22 November 1956, ''New Scientist'' has been available in online form since 1996. Sold in retail outlets (paper edition) and on subscription (paper and/or online), the magazine covers news, features, reviews and commentary on science, technology and their implications. ''New Scientist'' also publishes speculative articles, ranging from the technical to the philosophical. ''New Scientist'' was acquired by Daily Mail and General Trust (DMGT) in March 2021. History Ownership The magazine was founded in 1956 by Tom Margerison, Max Raison and Nicholas Harrison as ''The New Scientist'', with Issue 1 on 22 November 1956, priced at one shilling (). An article in the magazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wound
A wound is any disruption of or damage to living tissue, such as skin, mucous membranes, or organs. Wounds can either be the sudden result of direct trauma (mechanical, thermal, chemical), or can develop slowly over time due to underlying disease processes such as diabetes mellitus, venous/arterial insufficiency, or immunologic disease. Wounds can vary greatly in their appearance depending on wound location, injury mechanism, depth of injury, timing of onset ( acute vs chronic), and wound sterility, among other factors. Treatment strategies for wounds will vary based on the classification of the wound, therefore it is essential that wounds be thoroughly evaluated by a healthcare professional for proper management. In normal physiology, all wounds will undergo a series of steps collectively known as the wound healing process, which include hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and tissue remodeling. Age, tissue oxygenation, stress, underlying medical conditions, and certain m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Shiloh
The Battle of Shiloh, also known as the Battle of Pittsburg Landing, was a major battle in the American Civil War fought on April 6–7, 1862. The fighting took place in southwestern Tennessee, which was part of the war's Western Theater of the American Civil War, Western Theater. The battlefield is located between a small, undistinguished church named Shiloh, Hardin County, Tennessee, Shiloh and Pittsburg Landing, Tennessee, Pittsburg Landing on the Tennessee River. Two Union Army, Union armies combined to defeat the Confederate States Army, Confederate Army of Mississippi. Major general (United States), Major General Ulysses S. Grant was the Union commander, while General officers in the Confederate States Army#General, General Albert Sidney Johnston was the Confederate commander until his battlefield death, when he was replaced by his second-in-command, General P. G. T. Beauregard. The Confederate army hoped to defeat Grant's Army of the Tennessee before it could be reinforce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |