|
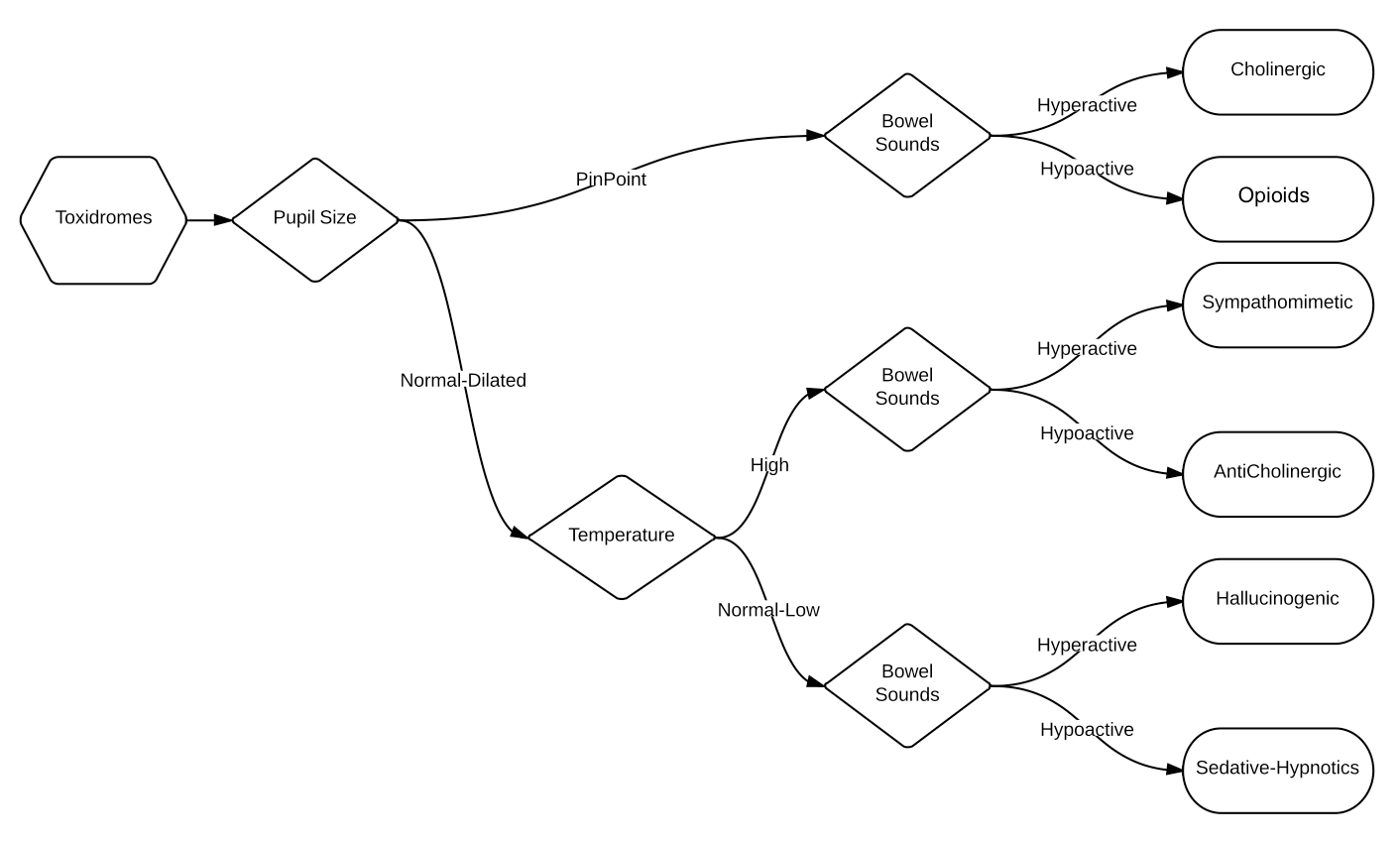
Toxidrome
A toxidrome (a portmanteau of ''toxic'' and ''syndrome'', coined in 1970 by Mofenson and Greensher) is a syndrome caused by a dangerous level of toxins in the body. It is often the consequence of a drug overdose. Common symptoms include dizziness, disorientation, nausea, vomiting and oscillopsia. It may indicate a medical emergency requiring treatment at a poison control center. Aside from poisoning, a systemic infection may also lead to one. Classic toxidromes may be variable or obscured by co-ingestion of multiple drugs. A common tool for assessing for the presence of toxidrome in the United Kingdom is the CRESS tool. Anticholinergic The symptoms of an anticholinergic toxidrome include blurred vision, coma, decreased bowel sounds, delirium, dry skin, fever, Flushing (physiology), flushing, hallucinations, ileus, memory loss, mydriasis (dilated pupils), myoclonus, psychosis, seizures and urinary retention. Complication (medicine), Complications include hypertension, hypertherm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overdose
A drug overdose (overdose or OD) is the ingestion or application of a drug or other substance in quantities much greater than are recommended. Retrieved on September 20, 2014."Stairway to Recovery: Glossary of Terms" . Retrieved on March 19, 2021 Typically the term is applied for cases when a risk to health is a potential result. An overdose may result in a toxicity, toxic state or death. Classification The word "overdose" implies that there is a common safe dosage and usage for the drug; therefore, the term is commonly applied only to drugs, not poisons, even though many poisons as well are harmless at a low enough dosage. Drug overdose is sometimes used as a means to commit suicide, as the result of intentional or unintentional misuse of medi ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndrome
A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms which are correlated with each other and often associated with a particular disease or disorder. The word derives from the Greek language, Greek σύνδρομον, meaning "concurrence". When a syndrome is paired with a definite cause this becomes a disease. In some instances, a syndrome is so closely linked with a pathogenesis or cause that disease#Terminology, the words ''syndrome'', ''disease'', and ''disorder'' end up being used interchangeably for them. This substitution of terminology often confuses the reality and meaning of medical diagnoses. This is especially true of heredity, inherited syndromes. About one third of all phenotypes that are listed in Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM are described as dysmorphic, which usually refers to the facial gestalt. For example, Down syndrome, Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome, and Andersen–Tawil syndrome are disorders with known pathogeneses, so each is more than just a set of sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in a brachial artery, where it is most commonly measured. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure (maximum pressure during one Cardiac cycle, heartbeat) over diastolic pressure (minimum pressure between two heartbeats) in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in Millimetre of mercury, millimetres of mercury (mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure, or in Pascal (unit), kilopascals (kPa). The difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures is known as pulse pressure, while the average pressure during a cardiac cycle is known as mean arterial pressure. Blood pressure is one of the vital signs—together with respiratory rate, heart rate, Oxygen saturation (me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to Nociception, respond normally to Pain, painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal Circadian rhythm, sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. The person may experience respiratory and circulatory problems due to the body's inability to maintain normal bodily functions. People in a coma often require extensive medical care to maintain their health and prevent complications such as pneumonia or blood clots. Coma patients exhibit a complete absence of wakefulness and are unable to consciously feel, speak or move. Comas can be the result of natural causes, or can be Induced coma, medically induced, for example, during General anaesthesia, general anesthesia. Clinically, a coma can be defined as the consistent inability to follow a one-step command. For a patient to maintain consciousness, the components of ''wakefulness'' and ''awareness'' must be maintained. Wak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atropine
Atropine is a tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically given intravenously or by injection into a muscle. Eye drops are also available which are used to treat uveitis and early amblyopia. The intravenous solution usually begins working within a minute and lasts half an hour to an hour. Large doses may be required to treat some poisonings. Common side effects include dry mouth, abnormally large pupils, urinary retention, constipation, and a fast heart rate. It should generally not be used in people with closed-angle glaucoma. While there is no evidence that its use during pregnancy causes birth defects, this has not been well studied so sound clinical judgment should be used. It is likely safe during breastfeeding. It is an antimuscarinic (a type of anticholinergic) that works by inhibit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an Disease#Terminology, illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune systems. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an Innate immune system, innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an Adaptive immune system, adaptive response. Treatment for infections depends on the type of pathogen involved. Common medications include: * Antibiotics for bacterial infections. * Antivirals for viral infections. * Antifungals for fungal infections. * Antiprotozoals for protozoan infections. * Antihelminthics for infections caused by parasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poison
A poison is any chemical substance that is harmful or lethal to living organisms. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figuratively, with a broad sense. Whether something is considered a poison or not may depend on the amount, the circumstances, and what living things are present. Poisoning could be accidental or deliberate, and if the cause can be identified there may be ways to neutralise the effects or minimise the symptoms. In biology, a poison is a chemical substance causing death, injury or harm to organisms or their parts. In medicine, poisons are a kind of toxin that are delivered passively, not actively. In industry the term may be negative, something to be removed to make a thing safe, or positive, an agent to limit unwanted pests. In ecological terms, poisons introduced into the environment can later cause unwanted effects elsewhere, or in other pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poison Control Center
A poison control center is a medical service that is able to provide immediate, free, and expert treatment advice and assistance over the telephone in case of exposure to poisonous or hazardous substances. Poison control centers answer questions about potential poisons in addition to providing treatment management advice about household products, medicines, pesticides, plants, bites and stings, food poisoning, and fumes. In the US, more than 72% of poison exposure cases are managed by phone, greatly reducing the need for costly emergency department and doctor visits. History After World War II there was a proliferation of new drugs and chemicals in the marketplace, and consequently suicide and childhood poisonings from these agents drastically increased. Around this time up to half of all accidents in children were poisonings with a substantial number of fatalities. These factors led to the medical community developing a response to both unintentional and intentional pois ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Emergency
A medical emergency is an acute injury or illness that poses an immediate risk to a person's life or long-term health, sometimes referred to as a situation risking "life or limb". These emergencies may require assistance from another, qualified person, as some of these emergencies, such as cardiovascular (heart), respiratory, and gastrointestinal cannot be dealt with by the victim themselves.AAOS 10th Edition Orange Book Dependent on the severity of the emergency, and the quality of any treatment given, it may require the involvement of multiple levels of care, from first aiders through emergency medical technicians, paramedics, emergency physicians and anesthesiologists. Any response to an emergency medical situation will depend strongly on the situation, the patient involved, and availability of resources to help them. It will also vary depending on whether the emergency occurs whilst in hospital under medical care, or outside medical care (for instance, in the street or alon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscillopsia
Oscillopsia is a visual disturbance in which objects in the visual field appear to oscillate. The severity of the effect may range from a mild blurring to rapid and periodic jumping. Oscillopsia is an incapacitating condition experienced by many patients with neurological disorders. It may be the result of ocular instability occurring after the oculomotor system is affected, no longer holding images steady on the retina. A change in the magnitude of the vestibulo-ocular reflex due to vestibular disease can also lead to oscillopsia during rapid head movements. Oscillopsia may also be caused by involuntary eye movements such as nystagmus, or impaired coordination in the visual cortex (especially due to toxins) and is one of the symptoms of superior canal dehiscence syndrome. Those affected may experience dizziness and nausea. Oscillopsia can also be used as a quantitative test to document aminoglycoside toxicity. Permanent oscillopsia can arise from an impairment of the ocular syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose. Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pregnancy, motion sickness, or hangover; or it can be an after effect of diseases such as brain tumors, elevated intracranial pressure, or overexposure to ionizing radiation. The feeling that one is about to vomit is called nausea; it often precedes, but does not always lead to vomiting. Impairment due to alcohol or anesthesia can cause inhalation of vomit. In severe cases, where dehydration develops, intravenous fluid may be required. Antiemetics are sometimes necessary to suppress nausea and vomiting. Self-induced vomiting can be a component of an eating disorder such as bulimia nervosa, and is itself now classified as an eating disorder on its own, purging disorder. Complications Aspiration Vomiting is dangerous if gastric content e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |