|
Tornquist Ocean
The Tornquist Sea or Tornquist Ocean was a sea located between the palaeocontinents Avalonia and Baltica about . The remains of the sea today form a suture stretching across northern Europe ( Tornquist Zone). Geologic evolution It probably formed at the same time (c. 600 Ma) as the Iapetus Ocean. Gondwana, including Avalonia until Early Ordovician, was separate from Baltica throughout the Cambrian. It probably closed during the Late Ordovician at the time of the Shelveian Orogeny of western England. There are faunal, palaeomagnetic, palaeogeographic, and apparent polar wander path evidence for the timing of closure for Eastern Avalonia (England, Wales and southern Ireland) and Baltica. The Baltica-Avalonia collision also resulted in that the Rheic Ocean ceased to expand south of Avalonia around 450 Ma, in huge magmatism in Avalonia, gigantic ash fall in Baltica, and metamorphism in present-day northern Germany. Present-day suture The suture resulting from cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avalonia
Avalonia was a microcontinent in the Paleozoic era. Crustal fragments of this former microcontinent are terranes in parts of the eastern coast of North America: Atlantic Canada, and parts of the East Coast of the United States, East Coast of the United States. In addition, terranes derived from Avalonia also make up portions of Northwestern Europe, being found in England, Wales and parts of Ireland. Avalonia developed as a volcanic arc on the northern margin of Gondwana. It eventually rifted off, becoming a drifting microcontinent. The Rheic Ocean formed behind it, and the Iapetus Ocean shrank in front. It collided with the continents Baltica, then Laurentia. The Armorican terrane, Armorican Terrane assemblage collided with the merged Baltica/Avalonia during the formation of Pangea. When Pangea broke up, Avalonia's remains were divided by the rift which became the Atlantic Ocean. Avalonia is named for the Avalon Peninsula in Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland. When the term "A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake District
The Lake District, also known as ''the Lakes'' or ''Lakeland'', is a mountainous region and National parks of the United Kingdom, national park in Cumbria, North West England. It is famous for its landscape, including its lakes, coast, and mountains, and for its literary associations with Beatrix Potter, John Ruskin, and the Lake Poets. The Lakeland fells, or mountains, include England's List of P600 mountains in the British Isles, highest: Scafell Pike (), Helvellyn () and Skiddaw (). The region also contains sixteen major lakes. They include Windermere, which with a length of and an area of is the longest and largest lake in England, and Wast Water, which at is the deepest lake in England. The Lake District National Park was established in 1951, and covers an area of , the bulk of the region. It was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2017. National Park The Lake District National Park includes all of the central Lake District, though the town of Kendal, some c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silurian Bodies Of Water
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of the Paleozoic Era, and the third of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out. One important event in this period was the initial establishment of terrestrial life in what is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution: vascular plants emerged from more primitive land plants, dikaryan fungi started expanding and diversifying along with glomeromycotan fungi, and three groups of arthropods ( myriapods, arachnids and hexapods) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordovician Paleogeography
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period Megaannum, Ma (million years ago) to the start of the Silurian Period Ma. The Ordovician, named after the Celtic Britons, Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same Rock (geology), rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed Stratum, strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Oceans
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categorize history as a social science, while others see it as part of the humanities or consider it a hybrid discipline. Similar debates surround the purpose of history—for example, whether its main aim is theoretical, to uncover the truth, or practical, to learn lessons from the past. In a more general sense, the term ''history'' refers not to an academic field but to the past itself, times in the past, or to individual texts about the past. Historical research relies on primary and secondary sources to reconstruct past events and validate interpretations. Source criticism is used to evaluate these sources, assessing their authenticity, content, and reliability. Historians strive to integrate the perspectives of several sources to develop a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
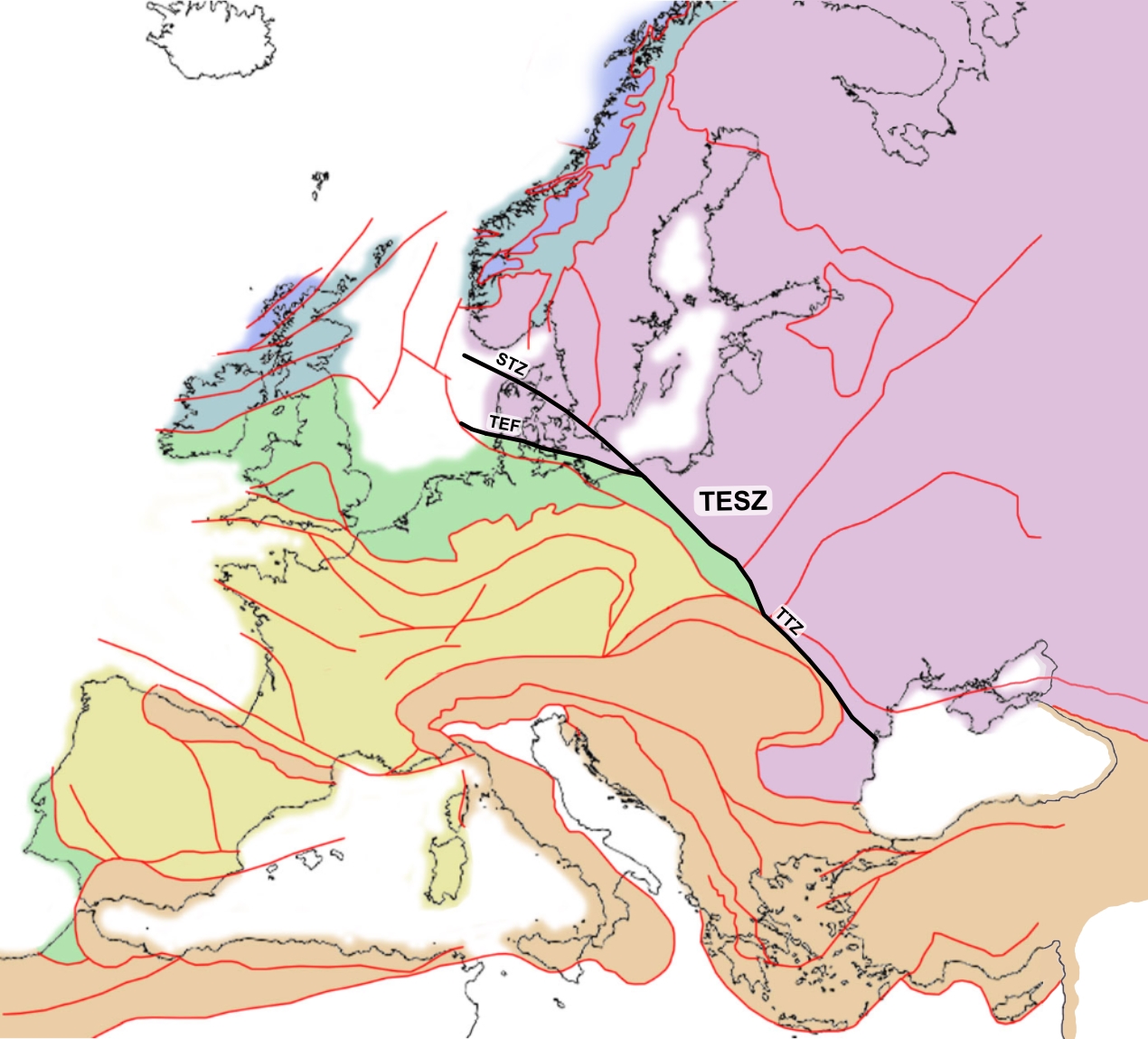
Trans-European Suture Zone
The Trans-European Suture Zone (TESZ), also known as the Tornquist Zone, is the crustal boundary between the Precambrian East European Craton and the Phanerozoic orogens of South-Western Europe. The zone runs from the North Sea to the Black Sea. The north-western part of the zone was created by the collision of Avalonia and Baltica/ East European Craton in the Late Ordovician. The south-eastern part of the zone, now largely concealed by deep sedimentary basins, developed through Variscan and Alpine orogenic events. Various branches of the TESZ go under different names: * The Teisseyre-Tornquist Zone (TTZ) in Ukraine and Poland. * The Sorgenfrei-Tornquist Zone (STZ) through Scania (Sweden), Kattegat, and North Jutland (Denmark). * The Trans-European Fault (TEF), Thor-Tornquist Suture or Thor Suture through southern Denmark. The latter two branches (STZ and TEF) span a triangular area of numerous faults, called the Tornquist Fan. Discovery In 1893 the Polish geologist Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Tornquist
Alexander Tornquist (18 June 1868 in Hamburg – 1 November 1944, Graz) was a German-Austrian geologist, who is known for his work on the northern part of the Trans European Suture Zone and on Mediterranean geology. Biography Alexander Tornquist was son of the merchant Alexander Heinrich Tornquist and Minna Mathilde Tornquist, née Fett. He studied at the universities of Freiburg, Munich and Göttingen. In 1892 he received a PhD in geology and paleontology at the university of Göttingen. In 1901 he obtained an associate professorship for geology and paleontology at Strasbourg, and in 1907 became a full professor at Königsberg. In Königsberg he also served as director of the famous Prussian amber collection and of the institute of seismology. He spent his later life in Graz, where he had a professorship at the Technische Hochschule from 1914 onward. From 1915 to 1918, he served as dean to the chemo-technical faculty. From 1924 to 1926, Tornquist was rector of the Technisch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wawrzyniec Teisseyre
Wawrzyniec Karol de Teisseyre (10 August 1860 – 2 May 1939) was a Polish geologist. He is known for his work on the southern part of the Trans European Suture Zone and Galician and Romanian geology. Wawrzyniec Teisseyre was born in Kraków, Austrian Empire of French ancestry. He studied at the University of Vienna and the Mining Academy in Leoben (Austria) and worked at the institutes of geology in Vienna and Bucharest. As part of his work on the Geological Atlas of Galicia, he mapped the southern part of the Trans European Suture Zone (Teisseyre-Tornquist Zone) and associated features of the Carpathian Mountains The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinav .... During his time in Bucharest he investigated oil deposits of Romania.R. Teisseyre and B. Teisseyre, ''Wawrzyniec Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suture (geology)
In structural geology, a suture is a joining along a major fault zone, of separate terranes, tectonic units that have different plate tectonic, metamorphic and paleogeographic histories. The suture is often represented on the surface by an orogen or mountain range. Overview In plate tectonics, sutures are the remains of subduction zones, and the terranes that are joined are interpreted as fragments of different palaeocontinents or tectonic plates. Outcrops of sutures can vary in width from a few hundred meters to a couple of kilometers. They can be networks of mylonitic shear zones or brittle fault zones, but are usually both. Sutures are usually associated with igneous intrusions and tectonic lenses with varying kinds of lithologies from plutonic rocks to ophiolitic fragments. An example from Great Britain is the Iapetus Suture which, though now concealed beneath younger rocks, has been determined by geophysical means to run along a line roughly parallel wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of the Paleozoic Era, and the third of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out. One important event in this period was the initial establishment of terrestrial life in what is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution: vascular plants emerged from more primitive land plants, dikaryan fungi started expanding and diversifying along with glomeromycotan fungi, and three groups of arthropods ( myriapods, arachnids and hexapods) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phyllite
Phyllite ( ) is a type of foliation (geology), foliated metamorphic rock formed from slate that is further metamorphosed so that very fine grained white mica achieves a preferred orientation.Stephen Marshak ''Essentials of Geology'', 3rd ed. It is primarily composed of quartz, sericite mica, and chlorite group, chlorite. Phyllite has fine-grained mica flakes, whereas slate has extremely fine mica flakes, and schist has large mica flakes, all mica flakes of which have achieved a preferred orientation. Among foliated metamorphic rocks, it represents a gradation in the degree of metamorphism between slate and schist. The minute crystals of graphite, sericite, or chlorite, or the translucent fine-grained white mica, impart a silky, sometimes golden sheen to the surfaces of cleavage (geology), cleavage, called "phyllitic luster". The word comes from the Greek ''phyllon'', meaning "leaf". The protolith (or parent rock) for phyllite is shale or pelite; or slate, which in turn came ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ardennes
The Ardennes ( ; ; ; ; ), also known as the Ardennes Forest or Forest of Ardennes, is a region of extensive forests, rough terrain, rolling hills and ridges primarily in Belgium and Luxembourg, extending into Germany and France. Geologically, the range is a western extension of the Eifel; both were raised during the Givetian age of the Devonian (382.7 to 387.7 million years ago), as were several other named ranges of the same greater range. The Ardennes proper stretches well into Germany and France (lending its name to the Ardennes department and the former Champagne-Ardenne region) and geologically into the Eifel (the eastern extension of the Ardennes Forest into Bitburg-Prüm, Germany); most of it is in the southeast of Wallonia, the southern and more rural part of Belgium (away from the coastal plain but encompassing more than half of the country's total area). The eastern part of the Ardennes forms the northernmost third of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, also called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |