|
Tor Stolpe
Tor Björn Stolpe (25 April 1927 – 10 December 2011) was a Finnish businessman and vuorineuvos. Stolpe was born in Hämeenlinna and completed his gymnasium in Kotka. He studied Master of Arts in University of Helsinki. After his graduation, he worked the following fourteen years in managerial positions for metal processor Oy Vuoksenniska Ab first as ore mine director and later in the head office. During 1968–1976 Stolpe worked as manager in Kymin Oy engineering industry division. Stolpe became division manager in Wärtsilä in 1976 and in 1978 he became the company director of operations. During period of dual leadership in 1978–1987 he managed Wärtsilä together with Tankmar Horn, after which he became managing director. Stolpe left his position in 1989 – in the same year when the company subsidiary Wärtsilä Marine fell in bankruptcy. Early years and studies Stolpe was born in Hämeenlinna, where his father Nils Stolpe served as military officer. He moved many ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vuorineuvos
Vuorineuvos ("mining counselor", literally Finnish for "mountain counselor"; sv, bergsråd) is a Finnish honorary title granted by the President of Finland to leading figures in industry and commerce. The title is honorary and has no responsibilities and no privileges. All Finnish titles are non-hereditary. The only title of equal rank is '' valtioneuvos''. Origin and history The vuorineuvos title originated in late 18th-century Sweden when mining played a major role in the economy, including in Swedish-held Finland. During that era five Finns were awarded the title. From 1809 to 1917 in the semi-autonomous, Russian-ruled Grand Duchy of Finland a further 19 titles were awarded. The first recipient of the vuorineuvos title in the modern Republic of Finland was Baron Fridolf Hisinger, on 17 July 1918. Awarding of the title has evolved to include not only giants of the mining industry but distinguished leaders in other industries and commerce. By 2010, the title had been gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Student Union Of The University Of Helsinki
The Student Union of the University of Helsinki ( fi, Helsingin yliopiston ylioppilaskunta, HYY, sv, Studentkåren vid Helsingfors universitet, HUS) was founded in 1868. It currently has 32,000 members and is one of the world's richest student organizations, with assets of several hundred million euro The euro (symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . ...s. Among other things, it owns a good deal of property in the city centre of Helsinki. The union has been at the centre of student politics from the 19th-century nationalist movements, through the actions of the New Left in the 1960s, up to the present. Its governing assembly consists of parties which are connected to faculty organisations, the Nations at Finnish universities#Student nations at Helsinki University, Student Nations, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Engine
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to mechanical compression; thus, the diesel engine is a so-called compression-ignition engine (CI engine). This contrasts with engines using spark plug-ignition of the air-fuel mixture, such as a petrol engine ( gasoline engine) or a gas engine (using a gaseous fuel like natural gas or liquefied petroleum gas). Diesel engines work by compressing only air, or air plus residual combustion gases from the exhaust (known as exhaust gas recirculation (EGR)). Air is inducted into the chamber during the intake stroke, and compressed during the compression stroke. This increases the air temperature inside the cylinder to such a high degree that atomised diesel fuel injected into the combustion chamber ignites. With the fuel being injected into the air just before combustion, the dispersion of the fuel is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siltasaari
Siltasaari ( Finnish), or Broholmen (Swedish), is a central neighborhood of Helsinki, Finland. Most of its area is unofficially known also as Hakaniemi Hakaniemi (; sv, Hagnäs) is an unofficial district of Helsinki, the Finnish capital. It covers most of the neighbourhood of Siltasaari in the district of Kallio. Hakaniemi is located at the sea shore and is separated from the city centre by the .... {{Helsinki Kallio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sörnäinen
Sörnäinen ( sv, Sörnäs; ''Sörkkä'' or ''Sörkka'' in Helsinki slang) is a neighbourhood in the city of Helsinki, Finland. Sörnäinen is located a little more than one kilometre north from the coastal centre of Helsinki, near the district of Hakaniemi. The east side of Sörnäinen borders the sea. Sörnäinen used to be primarily an industrial district with many shipping companies and warehouses, however, nowadays it is a thriving urban area divided into four districts: Vilhonvuori, Kalasatama, Sompasaari and Hanasaari. It also has two metro stations: Sörnäinen metro station and Kalasatama metro station in the Kalasatama quarter. The headquarters of Senate Properties (''Senaatti-kiinteistöt'') is located in Sörnäinen. Also the Helsinki Prison located there. Etymology The name "Sörnäinen" comes from the Swedish name "''Södernäs''" ("Southern cape") and was first mentioned in the foundation document for the New Helsinki in 1639, although the name is probabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1970s Energy Crisis
The 1970s energy crisis occurred when the Western world, particularly the United States, Canada, Western Europe, Australia, and New Zealand, faced substantial petroleum shortages as well as elevated prices. The two worst crises of this period were the 1973 oil crisis and the 1979 energy crisis, when, respectively, the Yom Kippur War and the Iranian Revolution triggered interruptions in Middle Eastern oil exports. The crisis began to unfold as petroleum production in the United States and some other parts of the world peaked in the late 1960s and early 1970s. World oil production per capita began a long-term decline after 1979. The oil crises prompted the first shift towards energy-saving (particular, fossil fuel-saving) technologies. The major industrial centers of the world were forced to contend with escalating issues related to petroleum supply. Western countries relied on the resources of countries in the Middle East and other parts of the world. The crisis led to stagnant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vehicle Industry
The automotive industry comprises a wide range of companies and organizations involved in the design, development, manufacturing, marketing, and selling of motor vehicles. It is one of the world's largest industries by revenue (from 16 % such as in France up to 40 % to countries like Slovakia). It is also the industry with the highest spending on research & development per firm. The word ''automotive'' comes from the Greek ''autos'' (self), and Latin ''motivus'' (of motion), referring to any form of self-powered vehicle. This term, as proposed by Elmer Sperry (1860-1930), first came into use with reference to automobiles in 1898. History The automotive industry began in the 1860s with hundreds of manufacturers that pioneered the horseless carriage. For many decades, the United States led the world in total automobile production. In 1929, before the Great Depression, the world had 32,028,500 automobiles in use, and the U.S. automobile industry produced over 90% of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathtub
A bathtub, also known simply as a bath or tub, is a container for holding water in which a person or animal may bathe. Most modern bathtubs are made of thermoformed acrylic, porcelain-enameled steel or cast iron, or fiberglass-reinforced polyester. A bathtub is usually placed in a bathroom, either as a stand-alone fixture or in conjunction with a shower. Modern bathtubs have overflow and waste drains and may have taps mounted on them. They are usually built-in, but may be free-standing or sometimes sunken. Until acrylic thermoforming technology permitted other shapes, virtually all bathtubs used to be roughly rectangular. Bathtubs are commonly white in color, although many other colors can be found. Two main styles are common: * Western style bathtubs in which the bather lies down. These baths are typically shallow and long. * Eastern style bathtubs in which the bather sits up. These are known as '' furo'' in Japan and are typically short and deep. History of bathtub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitreous Enamel
Vitreous enamel, also called porcelain enamel, is a material made by fusing powdered glass to a substrate by firing, usually between . The powder melts, flows, and then hardens to a smooth, durable vitreous coating. The word comes from the Latin , meaning "glass". Enamel can be used on metal, glass, ceramics, stone, or any material that will withstand the fusing temperature. In technical terms fired enamelware is an integrated layered composite of glass and another material (or more glass). The term "enamel" is most often restricted to work on metal, which is the subject of this article. Essentially the same technique used with other bases is known by different terms: on glass as '' enamelled glass'', or "painted glass", and on pottery it is called '' overglaze decoration'', "overglaze enamels" or "enamelling". The craft is called "enamelling", the artists "enamellers" and the objects produced can be called "enamels". Enamelling is an old and widely adopted technology, for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helsinki
Helsinki ( or ; ; sv, Helsingfors, ) is the Capital city, capital, primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Finland, most populous city of Finland. Located on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, it is the seat of the region of Uusimaa in southern Finland, and has a population of . The Helsinki urban area, city's urban area has a population of , making it by far the List of urban areas in Finland by population, most populous urban area in Finland as well as the country's most important center for politics, education, finance, culture, and research; while Tampere in the Pirkanmaa region, located to the north from Helsinki, is the second largest urban area in Finland. Helsinki is located north of Tallinn, Estonia, east of Stockholm, Sweden, and west of Saint Petersburg, Russia. It has History of Helsinki, close historical ties with these three cities. Together with the cities of Espoo, Vantaa, and Kauniainen (and surrounding commuter towns, including the eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
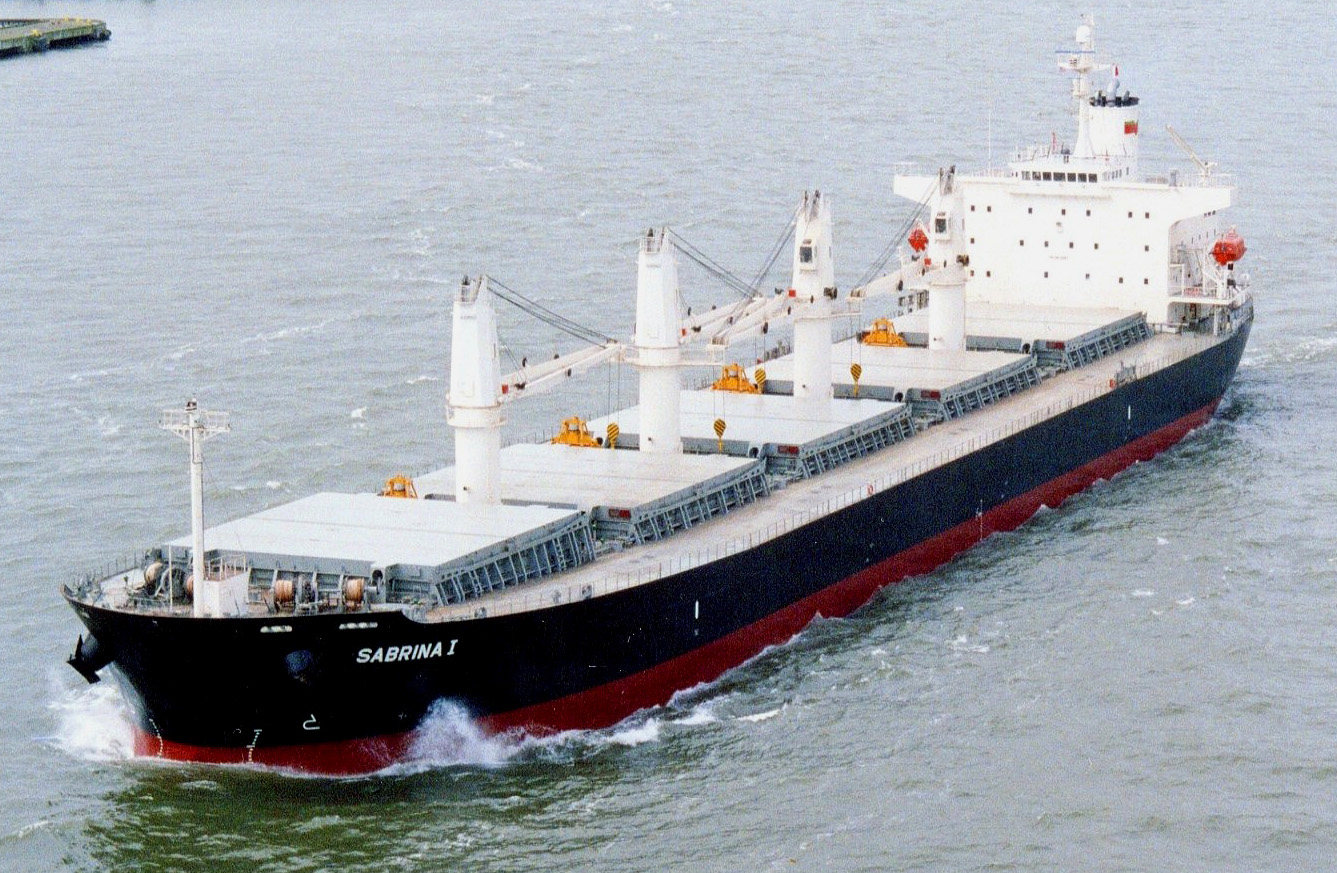
Bulk Carrier
A bulk carrier or bulker is a merchant ship specially designed to transport unpackaged bulk cargo — such as grains, coal, ore, steel coils, and cement — in its cargo holds. Since the first specialized bulk carrier was built in 1852, economic forces have led to continued development of these ships, resulting in increased size and sophistication. Today's bulk carriers are specially designed to maximize capacity, safety, efficiency, and durability. Today, bulk carriers make up 21 percent of the world's merchant fleets, and they range in size from single-hold mini-bulk carriers to mammoth ore ships able to carry 400,000 metric tons of deadweight (DWT). A number of specialized designs exist: some can unload their own cargo, some depend on port facilities for unloading, and some even package the cargo as it is loaded. Over half of all bulk carriers have Greek, Japanese, or Chinese owners, and more than a quarter are registered in Panama. South Korea is the largest sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekenäs, Finland
Ekenäs (; fi, Tammisaari ) is a town and former municipality in Finland that comprised the former municipalities of Snappertuna and Tenala together with the town of Ekenäs. It was merged with Pohja and Karis to form the new municipality of Raseborg on January 1, 2009. Ekenäs is in the province of Southern Finland, and is part of the Uusimaa ( sv, Nyland) region. The town had a population of 14,754 (as of 31 December 2008) and covered a land area of . The population density was . The town is bilingual, with the majority being Swedish speakers (81%), and the minority Finnish speakers (17%). History Ekenäs is Finland's seventh oldest town and the first of the non-medieval town. King Gustav Wasa granted town rights to Ekenäs in 1546, but even before that Ekenäs played a significant role in maritime transport. Today it is mostly noted for its archipelago, part of which is the Ekenäs Archipelago National Park. The old, mainly wooden town center is protected due to its cultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |