|
Topra
Topra, combined name for the larger Topra Kalan and adjacent smaller Topra Khurd, is a Mauryan Empire-era village in Yamunanagar district of Haryana state in India. It lies 14 km west of Yamunanagar, 14 km from Radaur and 90 km from Chandigarh. Topra Ashokan Pillar Situated in ''Pong valley'' of is the original home of Delhi-Topra pillar (originally located at ), one of many pillars of Ashoka, that was moved from Topra to Feroz Shah Kotla in Delhi in 1356 CE by Firuz Shah Tughlaq (1309-1388 CE). The original inscription on the Delhi-Topra Ashokan obelisk is primarily in Brahmi script, but the language was Prakrit, with some Pali and Sanskrit added later. The inscription was successfully translated in 1837 by James Prinsep. This and other ancient ''lats'' (pillars, obelisk) have earned Feroz Shah Tughlaq and Delhi Sultanate fame for its architectural patronage. The Sultanate had wanted to break and reuse the Ashokan pillar for a minaret. Feroz Shah Tuh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
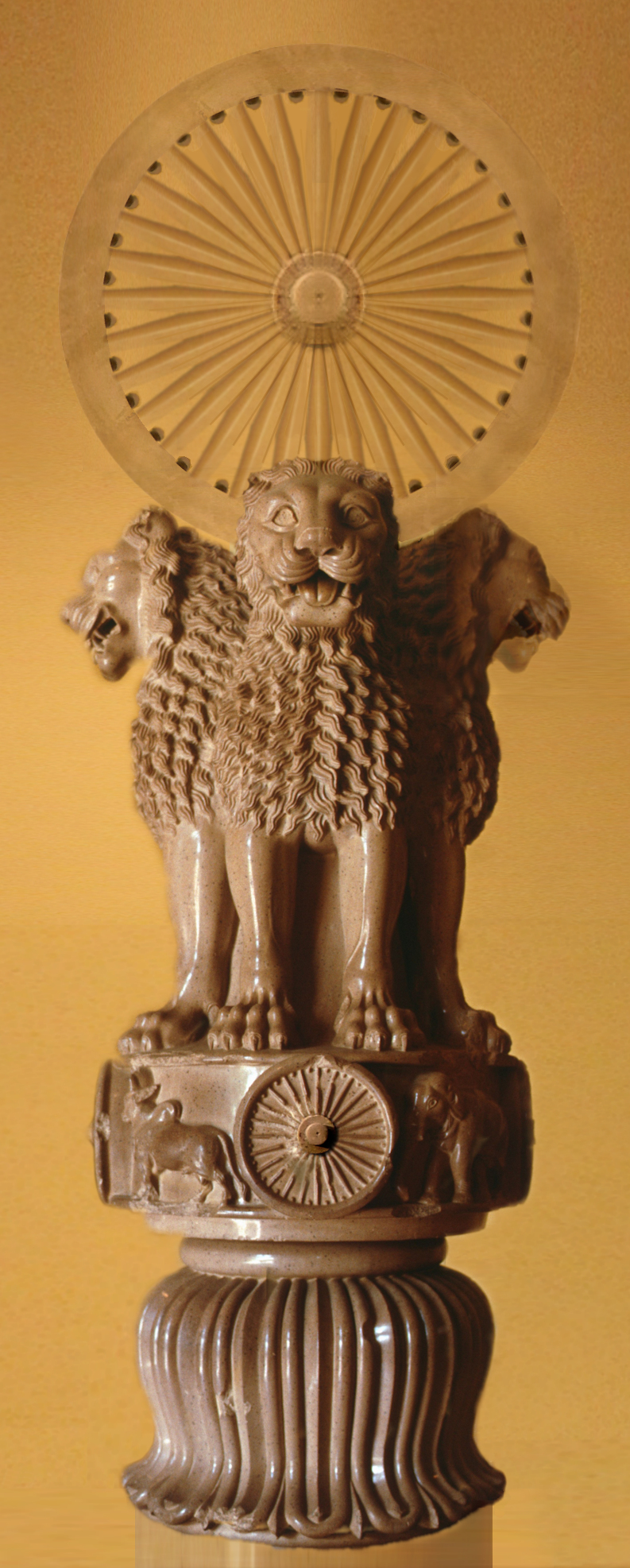
Delhi-Topra Pillar
The Delhi-Topra pillar is one of the pillars of Ashoka, inscribed with the moral edicts promulgated by Ashoka, the Mauryan Emperor who ruled in the Indian subcontinent during the 3rd century BCE. The Edicts of Ashoka were either carved on in-situ rocks or engraved on pillars erected throughout the empire. The pillar, originally erected in Topra Kalan, was transferred to Delhi in the 14th century by Feroz Shah Tughlaq.Bhandarkar pp. 206–207 Pillar edicts in Delhi All of the Ashokan pillar or column edicts were made out of Chunar sandstone quarried from Chunar in the Mirzapur District of Uttar Pradesh. They were chiseled at the quarry and then transported to various places in the country. They were chiseled from massive rock blocks of square and long, which were extracted from the quarry. They were chiseled as monolith pillars of size between and in length with an average diameter of .Bhandarkar p.206 The pillars were cut, dressed, finely polished into circular columns, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pillars Of Ashoka
The pillars of Ashoka are a series of Monolith, monolithic columns dispersed throughout the Indian subcontinent, erected—or at least inscribed with Edicts of Ashoka, edicts—by the 3rd Mauryan Emperor Ashoka the Great, who reigned from to 232 BC. Ashoka used the expression ''Dhaṃma thaṃbhā'' (Dharma stambha), i.e. "pillars of the Dharma" to describe his own pillars. These pillars constitute important monuments of the architecture of India, most of them exhibiting the characteristic Mauryan polish. Twenty of the pillars erected by Ashoka still survive, including those with inscriptions of his edicts. Only a few with animal capitals survive of which seven complete specimens are known. Two pillars were relocated by Firuz Shah Tughlaq to Delhi Sultanate, Delhi. Several pillars were relocated later by Mughal Empire rulers, the animal capitals being removed.Krishnaswamy, 697-698 Averaging between in height, and weighing up to 50 tons each, the pillars were dragged, sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feroz Shah Kotla
The Feroz Shah Kotla or Kotla ("fortress", "citadel") was a fortress built circa 1354 by Feroz Shah Tughlaq to house his version of Delhi called Firozabad. A pristine polished sandstone Topra Ashokan pillar from the 3rd century BC rises from the palace's crumbling remains, one of many pillars of Ashoka left by the Mauryan emperor; it was moved from Topra Kalan in Pong Ghati of Yamunanagar district in Haryana to Delhi under orders of Firoz Shah Tughlaq of Delhi Sultanate, and re-erected in its present location in 1356. The original inscription on the obelisk is primarily in Brahmi script but language was Prakrit, with some Pali and Sanskrit added later. The inscription was successfully translated to English in 1837 by James Prinsep. This and other ancient ''lats'' (pillars, obelisk) have earned Firoz Shah Tughlaq and Delhi Sultanate fame for its architectural patronage. Other than the Ashokan Pillar, the Fort complex also houses the Jami Masjid (Mosque), a ''Baoli'' and a la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmi Script
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO 15919, ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' or 'Lat', 'Southern Aśokan', 'Indian Pali', 'Mauryan', and so on. The application to it of the name Brahmi [''sc. lipi''], which stands at the head of the Buddhist and Jaina script lists, was first suggested by T[errien] de Lacouperie, who noted that in the Chinese Buddhist encyclopedia ''Fa yiian chu lin'' the scripts whose names corresponded to the Brahmi and Kharosthi of the ''Lalitavistara'' are described as written from left to right and from right to left, respectively. He therefore suggested that the name Brahmi should refer to the left-to-right 'Indo-Pali' script of the Aśokan pillar inscriptions, and Kharosthi to the right-to-left 'Bactro-Pali' script of the rock inscriptions from the northwest." that appeared as a fully ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
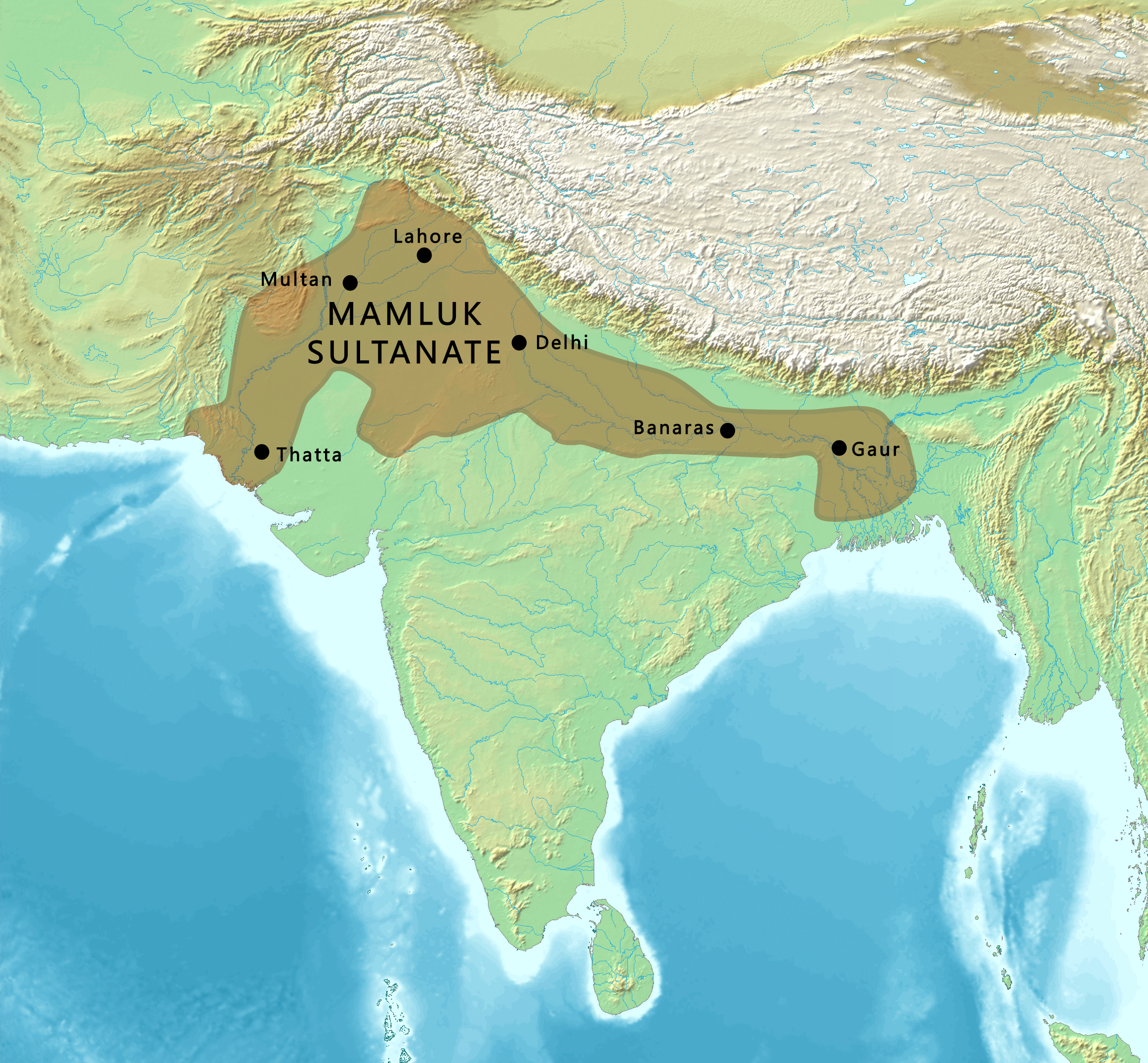
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries.Delhi Sultanate Encyclopædia Britannica The sultanate was established around in the former Ghurid Empire, Ghurid territories in India. The sultanate's history is generally divided into five periods: Mamluk dynasty (Delhi), Mamluk (1206–1290), Khalji dynasty, Khalji (1290–1320), Tughlaq dynasty, Tughlaq (1320–1414), Sayyid dynasty, Sayyid (1414–1451), and Lodi dynasty, Lodi (1451–1526). It covered large swaths of territory in modern-day India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, as well as some parts of southern Nepal. The foundation of the Sultanate was established by the Ghurid conqueror Muhammad of Ghor, Muhammad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firuz Shah Tughlaq
Firuz Shah Tughlaq (1309 – 20 September 1388), also known as Firuz III, was Sultan of Delhi from 1351 until his death in 1388. He succeeded his cousin Muhammad bin Tughlaq following the latter's death at Thatta, Sindh. His father was Sipahsalar Malik Rajab, the brother of Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq, the founder of the dynasty, whilst his mother was a princess a princess originating from Abohar, Punjab of the Indian subcontinent. Firuz Shah has been accredited with the construction of numerous cities and irrigation projects and has been regarded as a great builder with the creation of Firozpur, Hisar and Fatehabad in the Punjab and Haryana regions. Firuz Shah's reign was met with numerous conquests such as the Raja's of Bengal, Sindh and Kangra later in his reign, whilst upon receiving the throne, it has been noted that he successfully repelled a Mongol attack. Background The Tarikh-i-Firuz Shahi is one of the main sources of information regarding the Sultan's bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamunanagar District
Yamunanagar district is one of the 22 districts of the Indian state of Haryana. The district came into existence on 1November 1989 and occupies an area of . Yamunanagar town is the district headquarters. Yamunanagar's average rainfall in Monsoon is 892 mm, which is much higher than the state average of 462 mm. The district is bounded by Himachal Pradesh state in the north, by Uttar Pradesh state in the east, by Karnal district in the south, by Kurukshetra district in the southwest and Ambala district in the west. Divisions The district is divided into 3 sub divisions: Jagadhri, Radaur and Bilaspur. There are 4 tehsils: Jagadhri, Chhachhrauli, Radaur and Bilaspur. These are further divided into 7 development blocks: Bilaspur, Sadhaura, Radaur, Jagadhri, Chhachhrauli, Saraswati Nagar and Partap Nagar. There are 4 Vidhan Sabha constituencies in the district: Sadhaura, Jagadhri, Yamuna Nagar and Radaur. While Sadhaura, Jagadhri and Yamuna Nagar are part of Ambala Lok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radaur
Radaur is a town and municipal committee in Yamunanagar district in the Indian state of Haryana. It approx. 17 km from Yamunanagar, the district headquarters. Demographics As of 2011 Indian Census, Radaur had a total population of 13,690, of which 7,250 were males and 6,440 were females. Population within the age group of 0 to 6 years was 1,467. The total number of literates in Radaur was 10,380, which constituted 75.8% of the population with male literacy of 78.9% and female literacy of 72.4%. The effective literacy rate of 7+ population of Radaur was 84.9%, of which male literacy rate was 89.5% and female literacy rate was 79.9%. The Scheduled Castes population was 2,410. Radaur had 2794 households in 2011. India census, Radaur had a population of 11,737, of which 6,164 were males and 5,573 were females. Population in the age range of 0 to 6 years was 1,397. Radaur had an average literacy rate of 71.5%, male literacy was 75.8%, and female literacy was 66.8%. Education * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village
A village is a human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Although villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a church.-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... ''village'', from Latin ''villāticus'', ultimately from Latin ''villa'' (English ''vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dharma
Dharma (; , ) is a key concept in various Indian religions. The term ''dharma'' does not have a single, clear Untranslatability, translation and conveys a multifaceted idea. Etymologically, it comes from the Sanskrit ''dhr-'', meaning ''to hold'' or ''to support'', thus referring to law that sustains things—from one's life to society, and to the Universe at large. In its most commonly used sense, dharma refers to an individual's moral responsibilities or duties; the dharma of a farmer differs from the dharma of a soldier, thus making the concept of dharma a varying dynamic. As with the other components of the Puruṣārtha, the concept of ''dharma'' is pan-Indian. The antonym of dharma is ''adharma''. In Hinduism, ''dharma'' denotes behaviour that is considered to be in accord with ''Ṛta''—the "order and custom" that makes life and universe possible. This includes duties, rights, laws, conduct, virtues and "right way of living" according to the stage of life or social posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolt Of 1857
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising in India in 1857–58 against the rule of the British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the British Crown. The rebellion began on 10 May 1857 in the form of a mutiny of sepoys of the company's army in the garrison town of Meerut, northeast of Delhi. It then erupted into other mutinies and civilian rebellions chiefly in the upper Gangetic plain and central India, though incidents of revolt also occurred farther north and east. The rebellion posed a military threat to British power in that region, and was contained only with the rebels' defeat in Gwalior on 20 June 1858., , and On 1 November 1858, the British granted amnesty to all rebels not involved in murder, though they did not declare the hostilities to have formally ended until 8 July 1859. The name of the revolt is contested, and it is variously described as the Sepoy Mutiny, the Indian Mutiny, the Great Rebellion, the Revolt of 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raja Hindu Rao
Raja Hindu Rao was a Maratha nobleman, the brother-in-law of Maharaja Daulat Rao Scindia of Gwalior, and the brother of Baiza Bai, the regent of the Indian princely state of Gwalior. Following the Revolt of 1857, he shifted to Delhi where he was on friendly terms with the British Resident. According to Emily Eden, sister of the then Governor General of India, Lord Auckland: "On a revolution at Gwaliar, he retired to Delhi, where he now principally resides, and where he is well known in European society, with which he is fond of Mixing. Hindoo Rao is a very constant attendant on the person of the Governor-General wherever he may be in the neighbourhood of Delhi; making a point, generally, of joining his suite and riding with him on his morning marches." His residence was a scene of a major battle in Delhi during the Revolt of 1857Michael Edwardes ''Red Year:The Indian Rebellion of 1857'', London, 1975 ed, p.53 and has long since been converted into the Hindu Rao Hospit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |