|
Tolosa–Hunt Syndrome
Tolosa–Hunt syndrome is a rare disease, rare disorder characterized by severe and unilateral headaches with orbital pain, along with weakness and paralysis (ophthalmoplegia) of certain eye muscles (extraocular muscle paresis, extraocular palsies). In 2004, the International Headache Society defined the diagnostic criteria, which included granuloma. Signs and symptoms Symptoms are usually limited to one side of the head. In most cases, the individual affected will experience intense, sharp pain and paralysis of muscles around the eye. Symptoms may subside without medical intervention, yet recur without a noticeable pattern. Patients with this disorder describe it as almost like being stabbed in the head. The pain also comes from behind the eyes, forehead, and around the temple area. Not only is the disorder painful, but it is also severe. In addition, affected individuals may experience paralysis of various facial nerves and drooping of the upper eyelid (ptosis (eyelid), ptosis). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmoplegia
Ophthalmoparesis refers to weakness (-paresis) or paralysis (-plegia) of one or more extraocular muscles which are responsible for eye movements. It is a physical finding in certain neurologic, ophthalmologic, and endocrine disease. Internal ophthalmoplegia means involvement limited to the pupillary sphincter and ciliary muscle. External ophthalmoplegia refers to involvement of only the extraocular muscles. Complete ophthalmoplegia indicates involvement of both. Presentation Causes Ophthalmoparesis can result from disorders of various parts of the eye and nervous system: * Infection around the eye. Ophthalmoplegia is an important finding in orbital cellulitis. * The orbit of the eye, including mechanical restrictions of eye movement, as in Graves' disease. * The muscle, as in progressive external ophthalmoplegia or Kearns–Sayre syndrome. * The neuromuscular junction, as in myasthenia gravis. * The relevant cranial nerves (specifically the oculomotor, trochlear, and abdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatigue (medical)
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself. Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated with medical conditions including autoimmune disease, organ failure, chronic pain conditions, mood disorders, heart disease, infectious diseases, and post-infectious-disease states. However, fatigue is complex and in up to a third of primary care cases no medical or psychiatric diagnosis is found. Fatigue (in the general usage sense of normal tiredness) often follows prolonged physical or mental activity. Physical fatigue results from muscle fatigue brought about by intense physical activity. Mental fatigue results from prolonged periods of cognitive activity which impairs cognitive ability, can manifest as sleepiness, lethargy, or directed attention fatigue, and can also impair physical performance. Definition Fatigue in a medical context is used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antinuclear Antibody
Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs, also known as antinuclear factor or ANF) are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the cell nucleus. In normal individuals, the immune system produces antibodies to foreign proteins (antigens) but not to human proteins (autoantigens). In some cases, antibodies to human antigens are produced; these are known as autoantibodies. There are many subtypes of ANAs such as anti-Ro antibodies, anti-La antibodies, anti-Sm antibodies, anti-nRNP antibodies, anti-Scl-70 antibodies, anti-dsDNA antibodies, anti-histone antibodies, antibodies to nuclear pore complexes, anti-centromere antibodies and anti-sp100 antibodies. Each of these antibody subtypes binds to different proteins or protein complexes within the nucleus. They are found in many disorders including autoimmunity, cancer and infection, with different prevalences of antibodies depending on the condition. This allows the use of ANAs in the diagnosis of some autoimmune disorders, including system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (), or ACE, is a central component of the renin–angiotensin system (RAS), which controls blood pressure by regulating the volume of fluids in the body. It converts the hormone angiotensin I to the active vasoconstriction, vasoconstrictor angiotensin II. Therefore, ACE indirectly increases blood pressure by causing blood vessels to constrict. ACE inhibitors are widely used as pharmaceutical drugs for treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Other lesser known functions of ACE are degradation of bradykinin, substance P and amyloid beta, amyloid beta-protein. Nomenclature ACE is also known by the following names: * dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase I * peptidase P * dipeptide hydrolase * peptidyl dipeptidase * angiotensin converting enzyme * kininase II * angiotensin I-converting enzyme * carboxycathepsin * dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase * "hypertensin converting enzyme" peptidyl dipeptidase I * peptidyl-dipeptide hydrolase * peptidyldipeptide hydrolase * en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ventricles of the brain. CSF is mostly produced by specialized Ependyma, ependymal cells in the choroid plexuses of the ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations. It is also produced by ependymal cells in the lining of the ventricles. In humans, there is about 125 mL of CSF at any one time, and about 500 mL is generated every day. CSF acts as a shock absorber, cushion or buffer, providing basic mechanical and immune system, immunological protection to the brain inside the Human skull, skull. CSF also serves a vital function in the cerebral autoregulation of cerebral blood flow. CSF occupies the subarachnoid space (between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater) and the ventricular system around and inside t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serum Protein Electrophoresis
Serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP or SPE) is a laboratory test that examines specific proteins in the blood called globulins. The most common indications for a serum protein electrophoresis test are to diagnose or monitor multiple myeloma, a monoclonal gammopathy of uncertain significance (MGUS), or further investigate a discrepancy between a low albumin and a relatively high total protein. Unexplained bone pain, anemia, proteinuria, chronic kidney disease, and hypercalcemia are also signs of multiple myeloma, and indications for SPE. Blood must first be collected, usually into an airtight vial or syringe. Electrophoresis is a laboratory technique in which the blood serum (the fluid portion of the blood after the blood has clotted) is applied to either an acetate membrane soaked in a liquid buffer, or to a buffered agarose gel matrix, or into liquid in a capillary tube, and exposed to an electric current to separate the serum protein components into five major fract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the isthmus (: isthmi). Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis and growth and development in children. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regulated by thy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
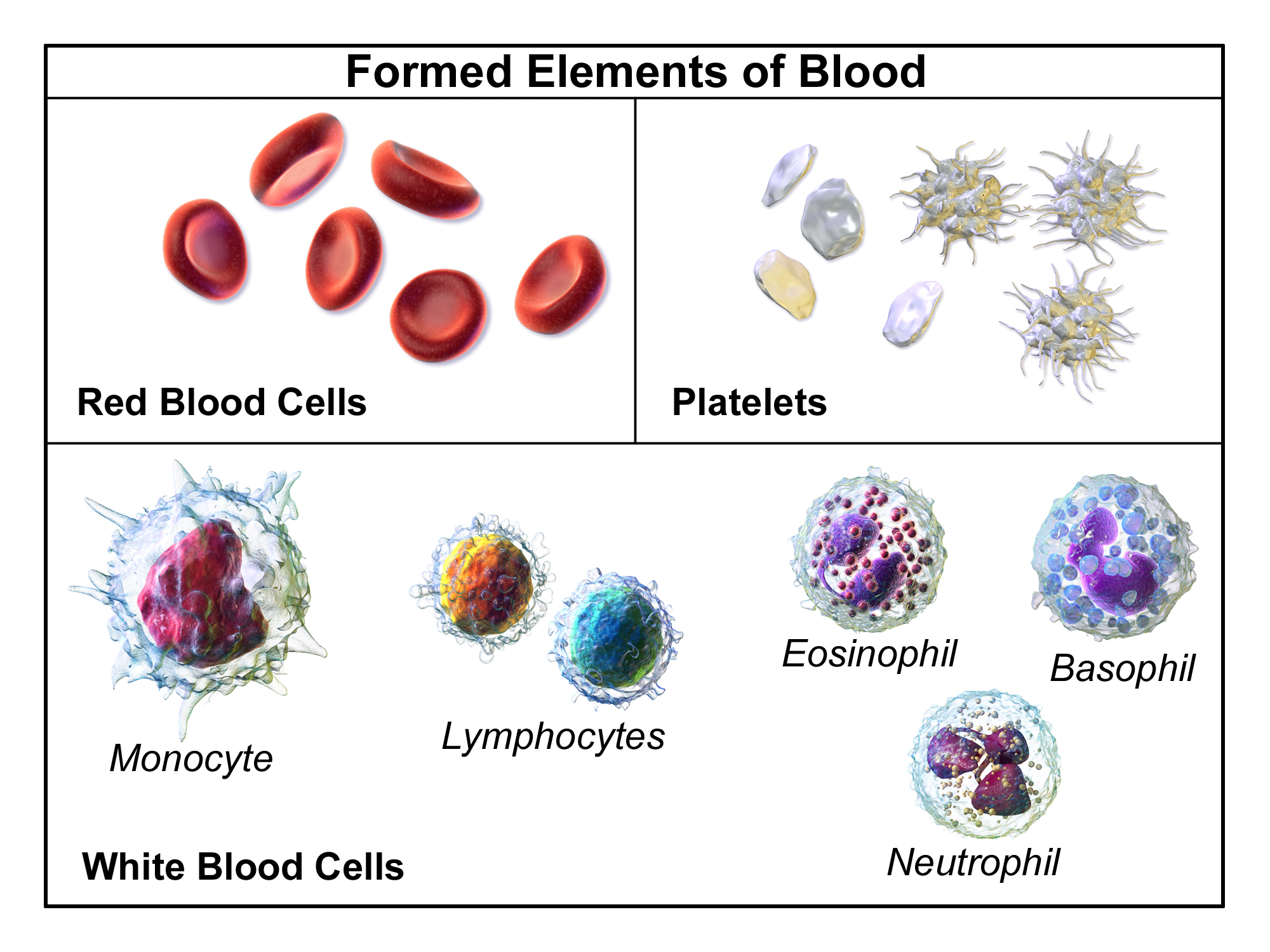
Complete Blood Count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC) or full haemogram (FHG), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide cytometry, information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets, the concentration of hemoglobin, and the hematocrit (the volume percentage of red blood cells). The red blood cell indices, which indicate the average size and hemoglobin content of red blood cells, are also reported, and a white blood cell differential, which counts the different types of white blood cells, may be included. The CBC is often carried out as part of a medical assessment and can be used to monitor health or diagnose diseases. The results are interpreted by comparing them to Reference ranges for blood tests, reference ranges, which vary with sex and age. Conditions like anemia and thrombocytopenia are defined by abnormal complete blood count results. The red blood cell indices can provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Classification Of Headache Disorders
The International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD) is a detailed hierarchical classification of all headache-related disorders published by the International Headache Society. It is considered the official classification of headaches by the World Health Organization, and, in 1992, was incorporated into the 10th edition of their ''International Classification of Diseases'' (ICD-10). Each class of headache contains explicit diagnostic criteria—meaning that the criteria include quantities rather than vague terms like ''several'' or ''usually''—that are based on clinical and laboratory observations. The ICHD was first published in 1988 (now known as the ICHD-1). A second version, the ICHD-2, was published in 2004. The most current version, ICHD-3, was published in 2018. Hierarchy Primary headaches ICHD 1, ICD10 G43: Migraine :Migraine without aura :Migraine with aura :Childhood periodic syndromes that are commonly precursors of migraine : Retinal migraine :Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Orbital Fissure
The superior orbital fissure is a foramen or cleft of the skull between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone. It gives passage to multiple structures, including the oculomotor nerve, trochlear nerve, ophthalmic nerve, abducens nerve, ophthalmic veins, and sympathetic fibres from the cavernous plexus. Structure The superior orbital fissure is usually 22 mm wide in adults, and is much larger medially. Its boundaries are formed by the (caudal surface of the) lesser wing of the sphenoid bone, and (medial border of the) greater wing of the sphenoid bone. Contents The superior orbital fissure is traversed by the following structures: * (superior and inferior divisions of the) oculomotor nerve (CN III) * trochlear nerve (CN IV) * lacrimal, frontal, and nasociliary branches of ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) * abducens nerve (CN VI) * superior ophthalmic vein and superior division of the inferior ophthalmic vein * sympathetic fibres from the cavernous nerve plex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavernous Sinus
The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica. Structure The cavernous sinus is one of the dural venous sinuses of the head. It is a network of veins that sit in a cavity. It sits on both sides of the sphenoidal bone and pituitary gland, approximately 1 × 2 cm in size in an adult. The carotid siphon of the internal carotid artery, and cranial nerves III, IV, V (branches V1 and V2) and VI all pass through this blood filled space. Both sides of cavernous sinus are connected to each other via intercavernous sinuses. The cavernous sinus lies in between the inner and outer layers of dura mater. Nearby structures * Above: optic tract, optic chiasma, internal carotid artery. * Inferiorly: foramen lacerum, and the junction of the body and greater wing of sphenoid bone. * Medially: p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granulomatous Nerve Inflammation
A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages (along with other cells) that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such substances include infectious organisms including bacteria and fungi, as well as other materials such as foreign objects, keratin, and suture fragments. Definition In pathology, a granuloma is an organized collection of macrophages. In medical practice, doctors occasionally use the term ''granuloma'' in its more literal meaning: "a small nodule". Since a small nodule can represent any tissue from a harmless nevus to a malignant tumor, this use of the term is not very specific. Examples of this use of the term ''granuloma'' are the lesions known as vocal cord granuloma (known as contact granuloma), pyogenic granuloma, and intubation granuloma, all of which are examples of granulation tissue, not granulomas. "Pulmonary hyalinizing granuloma" i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |