|
Tobacco Etch Virus Protease
TEV protease (, ''Tobacco Etch Virus nuclear-inclusion-a endopeptidase'') is a highly sequence-specific cysteine protease from Tobacco Etch Virus (TEV). It is a member of the PA clan of chymotrypsin-like proteases. Due to its high sequence specificity, TEV protease is frequently used for the controlled cleavage of fusion proteins ''in vitro'' and ''in vivo''. The consensus sequence recognized by TEV protease is Glu-Asn-Leu-Tyr-Phe-Gln-, -Ser, where ", " denotes cleaved peptide bond. Origin The tobacco etch virus encodes its entire genome as a single massive polyprotein (350 kDa). This is cleaved into functional units by the three proteases: P1 protease (1 cleavage site), helper-component protease (1 cleavage site) and TEV protease (7 cleavage sites).UniProt: TEV polyprotein: The native TEV protease also contains an internal self-cleavage site. This site is slowly cleaved to inactivate the enzyme (the physiological reason for this is unknown). Structure and function Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine Protease
Cysteine proteases, also known as thiol proteases, are hydrolase enzymes that degrade proteins. These proteases share a common catalytic mechanism that involves a nucleophilic cysteine thiol in a catalytic triad or dyad. Discovered by Gopal Chunder Roy in 1873, the first cysteine protease to be isolated and characterized was papain, obtained from ''Carica papaya''. Cysteine proteases are commonly encountered in fruits including the papaya, pineapple, fig and kiwifruit. The proportion of protease tends to be higher when the fruit is unripe. In fact, the latex of dozens of different plant families are known to contain cysteine proteases. Cysteine proteases are used as an ingredient in meat tenderizers. Classification The MEROPS protease classification system counts 14 superfamilies plus several currently unassigned families (as of 2013) each containing many families. Each superfamily uses the catalytic triad or dyad in a different protein fold and so represent convergent evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MEROPS
MEROPS is an online database for peptidases (also known as proteases, proteinases and proteolytic enzymes) and their inhibitors. The classification scheme for peptidases was published by Rawlings & Barrett in 1993, and that for protein inhibitors by Rawlings ''et al.'' in 2004.Rawlings, N.D., Tolle, D.P. & Barrett, A.J. (2004) "Evolutionary families of peptidase inhibitors." ''Biochem J'' 378, 705-716. The most recent version, MEROPS 12.5, was released in September 2023. Overview The classification is based on similarities at the tertiary and primary structural levels. Comparisons are restricted to that part of the sequence directly involved in the reaction, which in the case of a peptidase must include the active site, and for a protein inhibitor the reactive site. The classification is hierarchical: sequences are assembled into families, and families are assembled into clans. Each peptidase, family, and clan has a unique identifier. Classification Family The families of pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maltose Binding Protein
Maltose-binding protein (MBP) is a part of the maltose/maltodextrin system of ''Escherichia coli'', which is responsible for the uptake and efficient catabolism of maltodextrins. It is a complex regulatory and transport system involving many proteins and protein complexes. MBP has an approximate molecular mass of 42.5 dalton (unit), kilodaltons. Structure and folding MBP is encoded by the ''malE'' gene of ''Escherichia coli''. The ''malE'' gene codes for a precursor polypeptide (396 amino acid residues) which yields the mature MBP (370 residues) upon cleavage of the N-terminus, NH2-terminal extension (26 residues). The precursor and mature forms of MBP do not contain any cysteine residues. MBP is a monomeric protein. Crystal structures have shown that MBP is divided into two distinct globular protein domain, domains that are connected by three short polypeptide segments. The two domains are separated by a deep groove that contains the maltose/maltodextrin binding site. Comparison ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
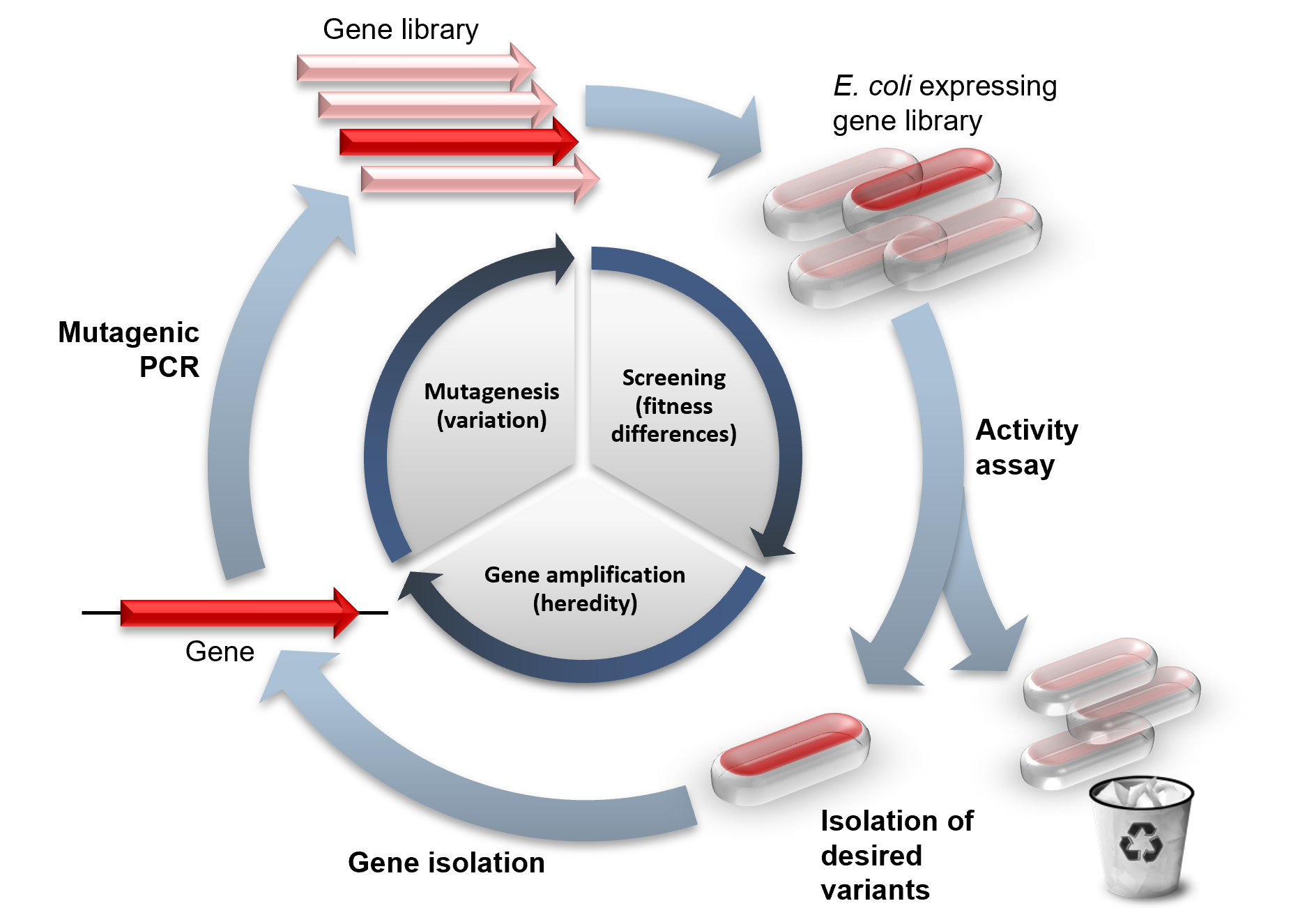
Directed Evolution
Directed evolution (DE) is a method used in protein engineering that mimics the process of natural selection to steer proteins or nucleic acids toward a user-defined goal. It consists of subjecting a gene to iterative rounds of mutagenesis (creating a library of variants), selection (expressing those variants and isolating members with the desired function) and amplification (generating a template for the next round). It can be performed ''in vivo'' (in living organisms), or ''in vitro'' (in cells or free in solution). Directed evolution is used both for protein engineering as an alternative to rationally designing modified proteins, as well as for experimental evolution studies of fundamental evolutionary principles in a controlled, laboratory environment. History Directed evolution has its origins in the 1960s with the evolution of RNA molecules in the "Spiegelman's Monster" experiment. The concept was extended to protein evolution via evolution of bacteria under selec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recombinant Fusion Protein
Fusion proteins or chimeric (kī-ˈmir-ik) proteins (literally, made of parts from different sources) are proteins created through the joining of two or more genes that originally coded for separate proteins. Translation of this ''fusion gene'' results in a single or multiple polypeptides with functional properties derived from each of the original proteins. ''Recombinant fusion proteins'' are created artificially by recombinant DNA technology for use in biological research or therapeutics. ''Chimera (genetics), Chimeric'' or ''chimera'' usually designate hybrid proteins made of polypeptides having different functions or physico-chemical patterns. ''Chimeric mutant proteins'' occur naturally when a complex mutation, such as a chromosomal translocation, tandem duplication, or retrotransposition creates a novel coding sequence containing parts of the coding sequences from two different genes. Naturally occurring fusion proteins are commonly found in cancer cells, where they may funct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affinity Tags
Protein tags are peptide sequences genetically grafted onto a recombinant protein. Tags are attached to proteins for various purposes. They can be added to either end of the target protein, so they are either C-terminus or N-terminus specific or are both C-terminus and N-terminus specific. Some tags are also inserted at sites within the protein of interest; they are known as internal tags. Affinity tags are appended to proteins so that they can be purified from their crude biological source using an affinity technique. Affinity tags include chitin binding protein (CBP), maltose binding protein (MBP), Strep-tag and glutathione-S-transferase (GST). The poly(His) tag is a widely used protein tag, which binds to matrices bearing immobilized metal ions. Solubilization tags are used, especially for recombinant proteins expressed in species such as ''E. coli'', to assist in the proper folding in proteins and keep them from aggregating in inclusion bodies. These tags include thioredo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binding Pocket
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate, the ''binding site'', and residues that catalyse a reaction of that substrate, the ''catalytic site''. Although the active site occupies only ~10–20% of the volume of an enzyme, it is the most important part as it directly catalyzes the chemical reaction. It usually consists of three to four amino acids, while other amino acids within the protein are required to maintain the tertiary structure of the enzymes. Each active site is evolved to be optimised to bind a particular substrate and catalyse a particular reaction, resulting in high specificity. This specificity is determined by the arrangement of amino acids within the active site and the structure of the substrates. Sometimes enzymes also need to bind with some cofactors to fulfil their function. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substrate Promiscuity
Enzyme promiscuity is the ability of an enzyme to catalyze an unexpected side reaction in addition to its main reaction. Although enzymes are remarkably specific catalysts, they can often perform side reactions in addition to their main, native catalytic activity. These wild activities are usually slow relative to the main activity and are under neutral selection. Despite ordinarily being physiologically irrelevant, under new selective pressures, these activities may confer a fitness benefit therefore prompting the evolution of the formerly promiscuous activity to become the new main activity. An example of this is the atrazine chlorohydrolase (''atzA'' encoded) from '' Pseudomonas sp.'' ADP evolved from melamine deaminase (''triA'' encoded), which has very small promiscuous activity toward atrazine, a man-made chemical. Introduction Enzymes are evolved to catalyze a particular reaction on a particular substrate with high catalytic efficiency (''kcat/KM'', ''cf''. Michaelis–Mente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
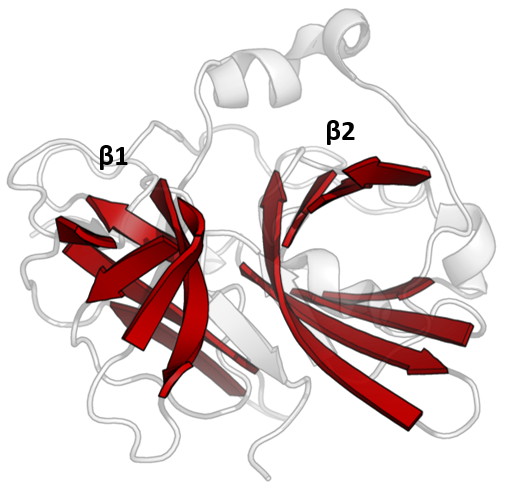
TEV Substrate Binding Tunnel
TEV may refer to: * Transient Earth voltage: a term for voltages appearing on the metal work of switchgear due to internal partial discharges * TeV, or teraelectronvolt or trillion electron volt, a measure of energy * Total enterprise value, a financial measure * Total economic value, an economic measure * Tracked Electric Vehicles, an open source electric vehicle system proposed by the TEV Project * Transparent Election Verification Software, open source software for auditing elections * Tobacco etch virus, a plant pathogenic virus of the family ''Potyviridae'' ** Tobacco etch virus protease, an enzyme commonly used in biochemistry * ''Today's English Version'', a former name for the ''Good News Bible'' * TEV, a ship prefix for Turbo-electric Vessel, usually with steam driven turbines. * Thermal expansion valve, a refrigeration system component * The IATA code designator for Teruel Airport Teruel Airport is an airport near Teruel in the Teruel Province of Spain. Known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic Triad
A catalytic triad is a set of three coordinated amino acid residues that can be found in the active site of some enzymes. Catalytic triads are most commonly found in hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, aminoacylase, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An acid-base (chemistry), base-nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the Substrate (chemistry), substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to release the Product (chemistry), product and regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine, but occasionally threonine or even selenocysteine. The Protein tertiary structure, 3D structure of the enzyme brings together the triad residues in a precise orientation, even though they may be far apart in the sequence (Protein primary structure, primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombin
Prothrombin (coagulation factor II) is encoded in the human by the F2-gene. It is proteolytically cleaved during the clotting process by the prothrombinase enzyme complex to form thrombin. Thrombin (Factor IIa) (, fibrose, thrombase, thrombofort, topical, thrombin-C, tropostasin, activated blood-coagulation factor II, E thrombin, beta-thrombin, gamma-thrombin) is a serine protease, that converts fibrinogen into strands of insoluble fibrin, as well as catalyzing many other coagulation-related reactions. History After the description of fibrinogen and fibrin, Alexander Schmidt hypothesised the existence of an enzyme that converts fibrinogen into fibrin in 1872. Prothrombin was discovered by Pekelharing in 1894. Physiology Synthesis Thrombin is produced by the enzymatic cleavage of two sites on prothrombin by activated Factor X (Xa). The activity of factor Xa is greatly enhanced by binding to activated Factor V (Va), termed the prothrombinase complex. Prothrombin is prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elastase
In molecular biology, elastase is an enzyme from the class of proteases (peptidases) that break down proteins, specifically one that can break down elastin. In other words, the name only refers to the substrate specificity (i.e. what proteins it can digest), not to any kind of evolutionary grouping. Forms and classification Eight human genes exist for elastase: The four "pancreatic elastases", chymotrypsin, and neutrophil elastase are serine proteases. The "macrophage elastase" is a matrix metallopeptidase. Chymotrypsin is weaker at digesting elastin than the architypical pancreatic elastase. Some bacteria (including ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'') also produce elastase; bacterial elestases work in many ways and include serine proteases, aspartic proteases, thiol proteases, and metalloenzymes. Function The fact that elastase can break down elastin in test tubes (while other proteases cannot) does not imply that there is a unifying function for all elastases in the living ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |