|
Tn10
Tn''10'' is a transposable element, which is a sequence of DNA that is capable of mediating its own movement from one position in the DNA of the host organism to another. There are a number of different transposition mechanisms in nature, but Tn''10'' uses the non-replicative cut-and-paste mechanism. The transposase protein recognizes the ends of the element and cuts it from the original locus. The protein-DNA complex then diffuses away from the donor site until random collisions brings it in contact with a new target site, where it is integrated. To accomplish this reaction the 50 kDa transposase protein must break four DNA strands to free the transposon from the donor site, and perform two strand exchange reactions to integrate the element at the target site. This leaves two strands unjoined at the target site, but the host DNA repair proteins take care of this. The target site selection is essentially random, but there is a preference for the sequence 5'-GCTNAGC-3'. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transposable Element
A transposable element (TE, transposon, or jumping gene) is a nucleic acid sequence in DNA that can change its position within a genome, sometimes creating or reversing mutations and altering the cell's genetic identity and genome size. Transposition often results in duplication of the same genetic material. Barbara McClintock's discovery of them earned her a Nobel Prize in 1983. Its importance in personalized medicine is becoming increasingly relevant, as well as gaining more attention in data analytics given the difficulty of analysis in very high dimensional spaces. Transposable elements make up a large fraction of the genome and are responsible for much of the mass of DNA in a eukaryotic cell. Although TEs are selfish genetic elements, many are important in genome function and evolution. Transposons are also very useful to researchers as a means to alter DNA inside a living organism. There are at least two classes of TEs: Class I TEs or retrotransposons generally f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an oral antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis. Common side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, rash, and loss of appetite. Other side effects include poor tooth development if used by children less than eight years of age, kidney problems, and sunburning easily. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby. It works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria. Tetracycline was patented in 1953 and came into commercial use in 1978. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Tetracycline is available as a generic medication. Tetracycline was originally made from bacteria of the genus ''Streptomyces''. Medical uses Spectrum of activity Tetracyclines have a broad spectrum of antibiotic action. Originally, they possessed some level of bacteriostatic activity against almost all medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, '' in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' ( la, in glass; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archetype
The concept of an archetype (; ) appears in areas relating to behavior, historical psychology, and literary analysis. An archetype can be any of the following: # a statement, pattern of behavior, prototype, "first" form, or a main model that other statements, patterns of behavior, and objects copy, emulate, or "merge" into. Informal synonyms frequently used for this definition include "standard example", "basic example", and the longer-form "archetypal example"; mathematical archetypes often appear as " canonical examples". # the Platonic concept of ''pure form'', believed to embody the fundamental characteristics of a thing. # a collectively-inherited unconscious idea, a pattern of thought, image, etc., that is universally present, in individual psyches, as in Jungian psychology # a constantly-recurring symbol or motif in literature, painting, or mythology. This definition refers to the recurrence of characters or ideas sharing similar traits throughout various, seemingly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar working in the 19th century in Brno, was the first to study genetics scientifically. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring over time. He observed that organisms (pea plants) inherit traits by way of discrete "units of inheritance". This term, still used today, is a somewhat ambiguous definition of what is referred to as a gene. Trait inheritance and molecular inheritance mechanisms of genes are still primary principles of genetics in the 21st century, but modern genetics has expanded to study the function and behavior of genes. Gene structure and function, variation, and distribution are studied within the context of the cell, the organism (e.g. dominance), and within the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanamycin
Kanamycin A, often referred to simply as kanamycin, is an antibiotic used to treat severe bacterial infections and tuberculosis. It is not a first line treatment. It is used by mouth, injection into a vein, or injection into a muscle. Kanamycin is recommended for short-term use only, usually from 7 to 10 days. As with most antibiotics, it is ineffective in viral infections. Common side effects include hearing and balance problems. Kidney problems may also occur. Kanamycin is not recommended during pregnancy as it may harm the baby. It is likely safe during breastfeeding. Kanamycin is in the aminoglycoside family of medications. It works by blocking the production of proteins that are required for bacterial survival. Kanamycin was first isolated in 1957 by Hamao Umezawa from the bacterium '' Streptomyces kanamyceticus''. It was removed from the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines in 2019. It is no longer marketed in the United States. Medical uses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances in the normal redox state of cells can cause toxic effects through the production of peroxides and free radicals that damage all components of the cell, including proteins, lipids, and DNA. Oxidative stress from oxidative metabolism causes base damage, as well as strand breaks in DNA. Base damage is mostly indirect and caused by the reactive oxygen species generated, e.g., O2− ( superoxide radical), OH ( hydroxyl radical) and H2O2 ( hydrogen peroxide). Further, some reactive oxidative species act as cellular messengers in redox signaling. Thus, oxidative stress can cause disruptions in normal mechanisms of cellular signaling. In humans, oxidative stress is thought to be involved in the development of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, cancer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Metal (chemistry)
upright=1.2, Crystals of lead.html" ;"title="osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead Heavy metals are generally defined as metals with relatively high density, densities, atomic weights, or atomic numbers. The criteria used, and whether metalloids are included, vary depending on the author and context. In metallurgy, for example, a heavy metal may be defined on the basis of density, whereas in physics the distinguishing criterion might be atomic number, while a chemist would likely be more concerned with chemical property, chemical behaviour. More specific definitions have been published, but none of these have been widely accepted. The definitions surveyed in this article encompass up to 96 out of the 118 known chemical elements; only mercury, lead and bismuth meet all of them. Despite this lack of agreement, the term (plural or singular) is widely used in science. A density of more than 5 g/cm3 is somet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
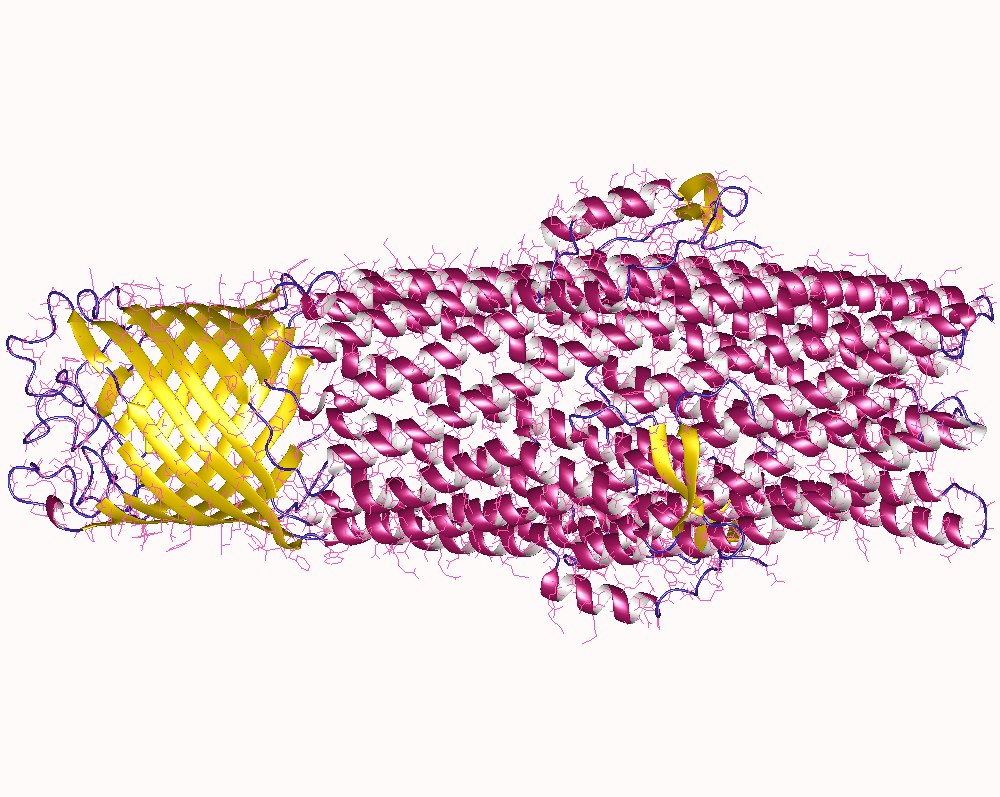
Efflux Pump
In microbiology, efflux is the moving of a variety of different compounds out of cells, such as antibiotics, heavy metals, organic pollutants, plant-produced compounds, quorum sensing signals, bacterial metabolites and neurotransmitters. All microorganisms, with a few exceptions, have highly conserved DNA sequences in their genome that are transcribed and translated to efflux pumps. Efflux pumps actively move substances out of a microorganism, in a process known as active efflux, which is a vital part of xenobiotic metabolism. This active efflux mechanism is responsible for various types of resistance to bacterial pathogens within bacterial species - the most concerning being antibiotic resistance because microorganisms can have adapted efflux pumps to divert toxins out of the cytoplasm and into extracellular media. Efflux systems function via an energy-dependent mechanism (active transport) to pump out unwanted toxic substances through specific efflux pumps. Some efflux systems a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorgani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transposition (horizontal Gene Transfer)
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between unicellular and/or multicellular organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the evolution of many organisms. HGT is influencing scientific understanding of higher order evolution while more significantly shifting perspectives on bacterial evolution. Horizontal gene transfer is the primary mechanism for the spread of antibiotic resistance in bacteria, and plays an important role in the evolution of bacteria that can degrade novel compounds such as human-created pesticides and in the evolution, maintenance, and transmission of virulence. It often involves temperate bacteriophages and plasmids. Genes responsible for antibiotic resistance in one species of bacteria can be transferred to another species of bacteria through various mechanisms of HGT such as transformation, transduction a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TetR
Tet Repressor proteins (otherwise known as TetR) are proteins playing an important role in conferring antibiotic resistance to large categories of bacterial species. Tetracycline (Tc) is a broad family of antibiotics to which bacteria have evolved resistance. Tc normally kills bacteria by binding to the bacterial ribosome and halting protein synthesis. The expression of Tc resistance genes is regulated by the repressor TetR. TetR represses the expression of TetA, a membrane protein that pumps out substances toxic to the bacteria like Tc, by binding the ''tetA'' operator. In Tc-resistant bacteria, TetA will pump out Tc before it can bind to the ribosome because the repressive action of TetR on TetA is halted by binding of Tc to TetR. Therefore, TetR may have an important role in helping scientists to better understand mechanisms of antibiotic resistance and how to treat antibiotic resistant bacteria. TetR is one of many proteins in the TetR protein family, which is so named becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)