|
Tlacateccatl
In the Aztec military, tlacateccatl () was a title roughly equivalent to general. The tlacateccatl was in charge of the ''tlacatecco'', a military quarter in the center of the Aztec capital, Tenochtitlan. In wartime he was second-in-command to the ''tlatoani ''Tlahtoāni'' ( , "ruler, sovereign"; plural ' ) is a historical title used by the dynastic rulers of (singular ''āltepētl'', often translated into English as "city-state"), autonomous political entities formed by many pre-Columbian Nahuatl- ...'' ("ruler", "king") and the '' tlacochcalcatl'' ("high general"). The tlacateccatl was always a member of the military order of the '' Cuachicqueh'', "the shorn ones". References *{{cite book , author=Hassig, Ross , year=1988 , title=Aztec Warfare: Imperial Expansion and Political Control , publisher=University of Oklahoma Press , location=Norman , isbn=0-8061-2121-1 Aztec warfare Aztec society Nahuatl words and phrases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tlacochcalcatl
Tlacochcalcatl ( "The man from the house of darts") was an Aztec military title or rank; roughly equivalent to the modern title of field marshal. In Aztec warfare the ''tlacochcalcatl'' was second in command only to the ''tlatoani'' and he usually led the Aztec army into battle when the ruler was otherwise occupied. Together with the '' tlacateccatl'' (general), he was in charge of the Aztec army and undertook all military decisions and planning once the ''tlatoani'' had decided to undertake a campaign. The ''tlacochcalcatl'' was also in charge of the ''tlacochcalco. Tlacochcalco'' ("in the house of darts") was the name of four armories placed at the four entries to the ceremonial precinct of the Aztec capital Tenochtitlan. These mains armories were stocked with new weapons every year (during the festival of Quecholli), and one account by the Spanish ''conquistador'' Andrés de Tapia estimates the number of weapons found in each of the four armories to be "500 cartloads". Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Warfare
Aztec warfare concerns the aspects associated with the military conventions, forces, weaponry and strategic expansions conducted by the Mesoamerican chronology, Late Postclassic Aztec civilizations of Mesoamerica, including particularly the military history of the Aztec Triple Alliance involving the city-states of Tenochtitlan, Texcoco (Aztec site), Texcoco, Tlacopan and other allied polity, polities of the central Mexican region. This united the Mexica, Apulteca, and Chichimeca people through marriages. The Aztec armed forces were typically made up of a large number of commoners (''yāōquīzqueh'' , "those who have gone to war") who possessed extensive military training, and a smaller but still considerable number of highly professional warriors belonging to the nobility (''Pipiltin, pīpiltin'' ) and who were organized into warrior societies and ranked according to their achievements. The Aztec state's primary purpose was political expansion and dominance of and exaction of tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General
A general officer is an Officer (armed forces), officer of high rank in the army, armies, and in some nations' air force, air and space forces, marines or naval infantry. In some usages, the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. March 2021. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/77489?rskey=dCKrg4&result=1 (accessed May 11, 2021) The adjective ''general'' had been affixed to officer designations since the late medieval period to indicate relative superiority or an extended jurisdiction. French Revolutionary system Arab system Other variations Other nomenclatures for general officers include the titles and ranks: * Adjutant general * Commandant-General, Commandant-general * Inspector general * General-in-chief * General of the Air Force (USAF only) * General of the Armies, General of the Armies of the United States (of America), a title created for General John J. Pershing, and subsequently grante ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
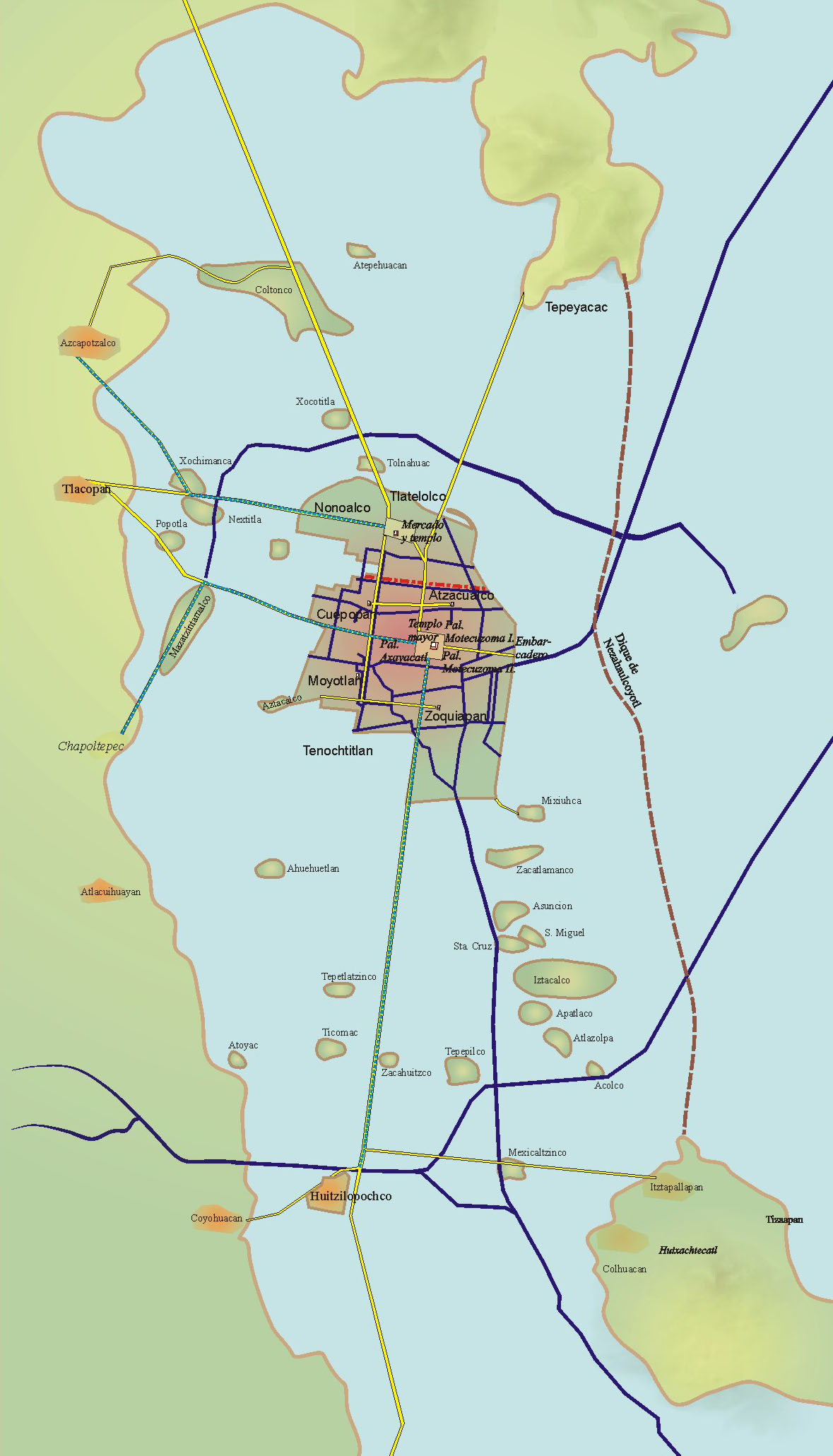
Tenochtitlan
, also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear, but the date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th anniversary of the city. The city was built on an island in what was then Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. The city was the capital of the expanding Aztec Empire in the 15th century until it was Fall of Tenochtitlan, captured by the Tlaxcaltec and the Spanish in 1521. At its peak, it was the largest city-state, city in the pre-Columbian Americas. It subsequently became a ''Municipalities of Mexico, cabecera'' of the Viceroyalty of New Spain. Today, the ruins of are in the historic center of the Mexican capital. The World Heritage Site of contains what remains of the geography (water, boats, Chinampa, floating gardens) of the Mexica capital. was one of two Mexica (city-states or Polity, polities) on the island, the other being . Etymol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tlatoani
''Tlahtoāni'' ( , "ruler, sovereign"; plural ' ) is a historical title used by the dynastic rulers of (singular ''āltepētl'', often translated into English as "city-state"), autonomous political entities formed by many pre-Columbian Nahuatl-speaking peoples in the Valley of Mexico during the Postclassic Period. The title of ' (, "great ruler, emperor") was used by the rulers of the Aztec Empire, an alliance between the ''āltepēmeh'' of Tenochtitlan, Tetzcoco, and Tlacopan. Each ''āltepētl'' had its own ''tlahtoāni'' who would concurrently function as its ruler, high priest and commander-in-chief. The ''tlahtoāni'' wielded ultimate authority over all land within the ''āltepētl'', overseeing tribute collection, market activities, temple affairs, and the resolution of judicial disputes. Typically a dynastic ruler hailing from the royal lineage, the ''tlahtoāni'' served for life. However, in certain instances, a council of nobles, elders, and priests could elect a ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
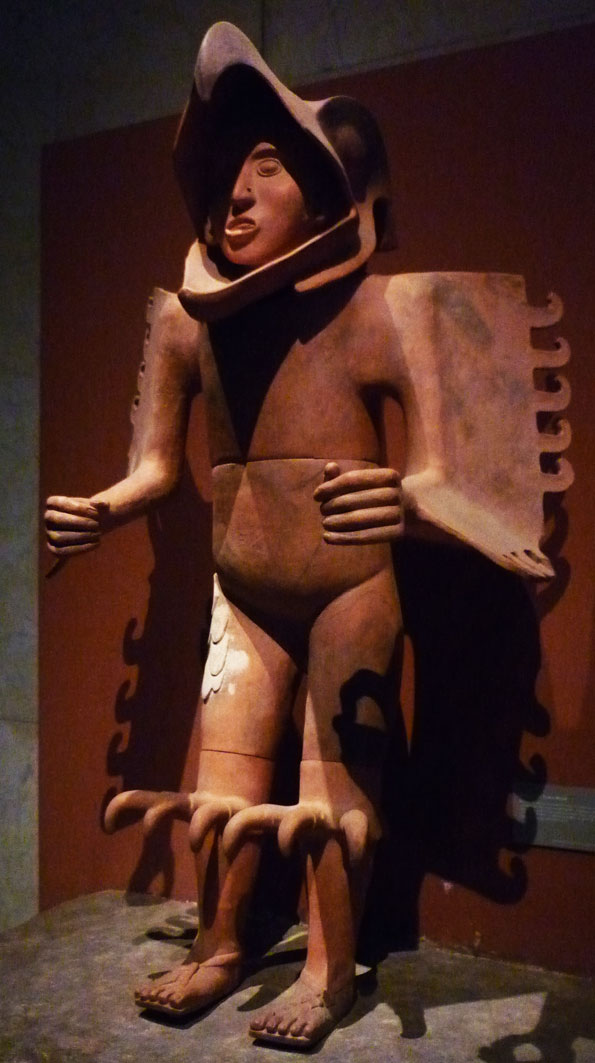
Aztec Military Orders
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the Post-Classic stage, post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl, Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica from the 14th to the 16th centuries. Aztec culture was organized into city-states (''altepetl''), some of which joined to form alliances, political confederations, or empires. The Aztec Empire was a confederation of three city-states established in 1427: Tenochtitlan, the capital city of the Mexica or Tenochca, Tetzcoco (altepetl), Tetzcoco, and Tlacopan, previously part of the Tepanec empire, whose dominant power was Azcapotzalco (altepetl), Azcapotzalco. Although the term Aztecs is often narrowly restricted to the Mexica of Tenochtitlan, it is also broadly used to refer to Nahuas, Nahua polities or peoples of central Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codex Mendoza Fol
The codex (: codices ) was the historical ancestor format of the modern book. Technically, the vast majority of modern books use the codex format of a stack of pages bound at one edge, along the side of the text. But the term ''codex'' is now reserved for older manuscript books, which mostly used sheets of vellum, parchment, or papyrus, rather than paper. By convention, the term is also used for any Aztec codex (although the earlier examples do not actually use the codex format), Maya codices and other pre-Columbian manuscripts. Library practices have led to many European manuscripts having "codex" as part of their usual name, as with the Codex Gigas, while most do not. Modern books are divided into paperback (or softback) and those bound with stiff boards, called hardbacks. Elaborate historical bindings are called treasure bindings. At least in the Western world, the main alternative to the paged codex format for a long document was the continuous scroll, which was the dominan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Society
Aztec society was a highly complex and stratified society that developed among the Aztecs of central Mexico in the centuries prior to the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, and which was built on the cultural foundations of the larger region of Mesoamerica. Politically, the society was organized into independent city-states, called altepetls, composed of smaller divisions ( calpulli), which were again usually composed of one or more extended kinship groups. Socially, the society depended on a rather strict division between nobles and free commoners, both of which were themselves divided into elaborate hierarchies of social status, responsibilities, and power. Economically the society was dependent on agriculture, and also to a large extent on warfare. Other economically important factors were commerce, long-distance and local, and a high degree of trade specialization. Overview Aztec society can trace its roots to Mesoamerican Origins. Their language, lifestyle, and technolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |