|
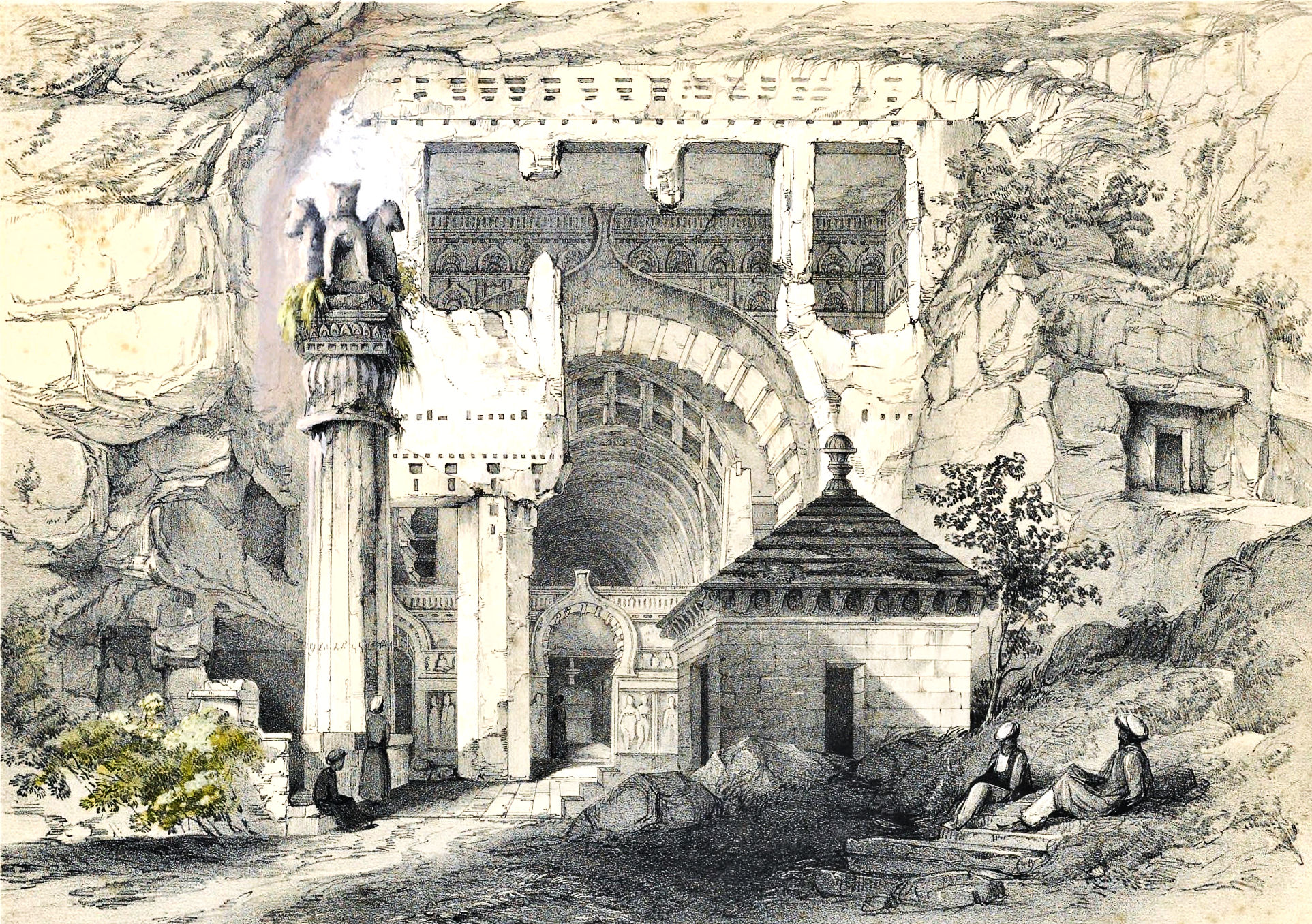
Tirmidh
Termez ( ) is the capital of Surxondaryo Region in southern Uzbekistan. Administratively, it is a district-level city. Its population is 182,800 (2021). It is notable as the site of Alexander the Great's city Alexandria on the Oxus, as a center of early Buddhism, as a site of Muslim pilgrimage, and as a base of Soviet Union military operations in Afghanistan, accessible via the nearby Hairatan border crossing. Etymology Some link the name of the city to the Greek word Θέρμος (''thermos''), meaning "hot", and date the toponym to the rule of Alexander the Great. Others suggest that it came from Sanskrit तर्मतो (''tarmato''), meaning "on the river bank". History Ancient times One of Central Asia's oldest towns, Old Termez, located a few kilometers west of the modern city along the Amu Darya river, was established sometime before the 3rd century BC. The city may have been known to the Achaemenids (the 10th century Shahnameh purports its existence during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan is divided into 12 regions (''viloyatlar'', singularwilayah, viloyat, ''viloyati'' in compound, e.g. Toshkent ''viloyati''), 1 autonomous republic (''respublika'', ''respublikasi'' in compound, e.g. Qaraqalpaqstan Avtonom ''Respublikasi''), and 1 independent city (''shahar'' or ''shahri'' in compounds, e.g. Toshkent ''shahri''). List Names are given below in the Uzbek language, although numerous variations of the transliterations of each name exist. The regions in turn are divided into districts of Uzbekistan, 175 districts (''tumanlar'', singular ''tuman''). Enclaves and exclaves There are four Uzbek enclave and exclave, exclaves, all of them surrounded by Kyrgyzstan, Kyrgyz territory in the Fergana Valley region where Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan meet. Two of them are the towns of Sokh District, Sokh, area of with a population of 42,800 in 1993 (with some estimates as high as 70,000, of which 99% are Tajiks and the remainder Uzbeks) and Shohimar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoroastrian
Zoroastrianism ( ), also called Mazdayasnā () or Beh-dīn (), is an Iranian religion centred on the Avesta and the teachings of Zarathushtra Spitama, who is more commonly referred to by the Greek translation, Zoroaster ( ). Among the world's oldest organized faiths, its adherents exalt an uncreated, benevolent, and all-wise deity known as Ahura Mazda (), who is hailed as the supreme being of the universe. Opposed to Ahura Mazda is Angra Mainyu (), who is personified as a destructive spirit and the adversary of all things that are good. As such, the Zoroastrian religion combines a dualistic cosmology of good and evil with an eschatological outlook predicting the ultimate triumph of Ahura Mazda over evil. Opinions vary among scholars as to whether Zoroastrianism is monotheistic, polytheistic, henotheistic, or a combination of all three. Zoroastrianism shaped Iranian culture and history, while scholars differ on whether it significantly influenced ancient Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, the length of the Sasanian dynasty's reign over ancient Iran was second only to the directly preceding Arsacid dynasty of Parthia. Founded by Ardashir I, whose rise coincided with the decline of Arsacid influence in the face of both internal and external strife, the House of Sasan was highly determined to restore the legacy of the Achaemenid Empire by expanding and consolidating the Iranian nation's dominions. Most notably, after defeating Artabanus IV of Parthia during the Battle of Hormozdgan in 224, it began competing far more zealously with the neighbouring Roman Empire than the Arsacids had, thus sparking a new phase of the Roman–Iranian Wars. This effort by Ardashir's dynasty ultimately re-established Iran as a major power of late an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century Before the Common Era, BCE. It is the Major religious groups, world's fourth-largest religion, with about 500 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise four percent of the global population. It arose in the eastern Gangetic plain as a movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia. Buddhism has subsequently played a major role in Asian culture and spirituality, eventually spreading to Western world, the West in the 20th century. According to tradition, the Buddha instructed his followers in a path of bhavana, development which leads to Enlightenment in Buddhism, awakening and moksha, full liberation from ''Duḥkha, dukkha'' (). He regarded this path as a Middle Way between extremes su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahāsāṃghika
The Mahāsāṃghika (Brahmi script, Brahmi: 𑀫𑀳𑀸𑀲𑀸𑀁𑀖𑀺𑀓, "of the Great Sangha (Buddhism), Sangha", ) was a major division (nikāya) of the early Buddhist schools in India. They were one of the two original communities that emerged from the first schism of the Pre-sectarian Buddhism, original pre-sectarian Buddhist tradition (the other being the Sthavira nikāya, Sthavira nikaya). This schism is traditionally held to have occurred after the Second Buddhist council, which occurred at some point during or after the reign of Kalashoka. The Mahāsāṃghika nikāya developed into numerous sects which spread throughout History of India, ancient India. Some scholars think that the Mahāsāṃghika Vinaya (Monasticism, monastic rule) represents the oldest Buddhist monastic source, although some other scholars think that it is not the case. While the Mahāsāṃghika tradition is no longer in existence, many scholars look to the Mahāsāṃghika tradition as an ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bactrian Language
Bactrian (, , meaning "Iranian") was an Eastern Iranian language formerly spoken in the Central Asian region of Bactria (present-day Afghanistan) and used as the official language of the Kushan and the Hephthalite empires. Name It was long thought that Avestan represented "Old Bactrian", but this notion had "rightly fallen into discredit by the end of the 19th century". Bactrian, which was written predominantly in an alphabet based on the Greek script, was known natively as (" Arya"; an endonym common amongst Indo-Iranian peoples). It has also been known by names such as Greco-Bactrian or Kushan or Kushano-Bactrian. Under Kushan rule, Bactria became known as ''Tukhara'' or ''Tokhara'', and later as '' Tokharistan''. When texts in two extinct and previously unknown Indo-European languages were discovered in the Tarim Basin of China, during the early 20th century, they were linked circumstantially to Tokharistan, and Bactrian was sometimes referred to as "Eteo-Tocharian" (i.e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire (– CE) was a Syncretism, syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Afghanistan, Eastern Iran, India, Pakistan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. Kushan territory in India went at least as far as Saketa and Sarnath, now near Varanasi district, Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh, where inscriptions have been found dating to the era of the Kushan emperor Kanishka the Great. The Kushans were most probably one of five branches of the Yuezhi confederation, an Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European nomadic people of possible Tocharians, Tocharian origin, who migrated from northwestern China (Xinjiang and Gansu) and settled in ancient Bactria. The founder of the dynasty, Kujula Kadphises, followed Iranian and Greek cultural ideas and iconography after the Greco-Bactrian tradition and was a follower of the Shaivism, Shaivite sect of Hinduism. Two later Kushan kings, Vima Kadphises and Vasudeva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is a historical name used by Islamic sources in the early Middle Ages to refer to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources. By the 6th century CE, Tokharistan came under rule of the First Turkic Khaganate, and in the 7th and 8th centuries, it was incorporated into the Tang dynasty, administered by the Protectorate General to Pacify the West. Today, Tokharistan is fragmented between Afghanistan, Uzbekistan and Tajikistan. Names Several languages have used variations of the word "Tokhara" to designate the region: * Tokharistan may appear in ancient Indian sources as the Kingdom of Tushara, to the northwest of the Indian subcontinent. "Tushara" is the Sanskrit word for "snowy" "frigid", and is known to have been used to designate the country of Tukhara. In Sanskrit, it became तुखार (Tukhāra). * In ancient Greek, the name was Tokharoi ( ) or Thaguroi. * Tocha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionian Greek
Ionic or Ionian Greek () was a subdialect of the Eastern or Attic Greek, Attic–Ionic Ancient Greek dialects, dialect group of Ancient Greek. The Ionic group traditionally comprises three dialectal varieties that were spoken in Euboea (West Ionic), the northern Cyclades (Central Ionic), and from BC onward in Ionia, Asiatic Ionia (East Ionic), where Ionians, Ionian Greek colonisation, colonists from Athens founded their cities. Ionic was the base of several literary language forms of the Archaic Greece, Archaic and Classical Greece, Classical periods, both in poetry and prose. The works of Homer and Hesiod are among the most popular Ancient Greek literature#Epic poetry, poetic works that were written in a literary form of the Ionic dialect, known as Epic or Homeric Greek. The oldest Ancient Greek literature#Historiography, Greek prose, including that of Heraclitus, Herodotus, Democritus, and Hippocrates, was also written in Ionic. By the end of the 5th century BC, Ionic was supplan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greco-Bactrian Kingdom
The Greco-Bactrian Kingdom () was a Ancient Greece, Greek state of the Hellenistic period located in Central Asia, Central-South Asia. The kingdom was founded by the Seleucid Empire, Seleucid satrap Diodotus I, Diodotus I Soter in about 256 BC, and continued to dominate Central Asia until its fall around 120 BC. At its peak the kingdom consisted of present-day Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan, and for a short time, small parts of Kazakhstan, Pakistan and Iran. An extension further east, with military campaigns and settlements, may have reached the borders of the Qin (state), Qin State in China by about 230 BC. Although a Greek population was already present in Bactria by the 5th century BC, Alexander the Great conquered the region by 327 BC and founded many cities, most of them named List of cities founded by Alexander the Great, Alexandria, and further settled with Ancient Macedonians, Macedonians and other Ancient Greece, Greeks. After the death of Alexande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great, and ruled by the Seleucid dynasty until its annexation by the Roman Republic under Pompey in 63 BC. After receiving the Mesopotamian regions of Babylonia and Assyria in 321 BC, Seleucus I began expanding his dominions to include the Near Eastern territories that encompass modern-day Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Syria, and Lebanon, all of which had been under Macedonian control after the fall of the former Achaemenid Empire. At the Seleucid Empire's height, it had consisted of territory that covered Anatolia, Persia, the Levant, Mesopotamia, and what are now modern Kuwait, Afghanistan, and parts of Turkmenistan. The Seleucid Empire was a major center of Hellenistic culture. Greek customs and language were privileged; the wide variety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |