|
Tiong Bahru
Tiong Bahru is a housing estate and subzone region located within Bukit Merah planning area, in the Central Region, Singapore, Central Region of Singapore. Tiong Bahru was constructed in the 1920s by the Singapore Improvement Trust, the predecessor to the Housing Development Board (HDB) and an entity of the British colonial authority providing mass public housing in Singapore and is the oldest housing estate in Singapore. According to Urban Redevelopment Authority, URA's definition, the area known as 'Tiong Bahru' is represented by three contiguous subzones of Bukit Merah, namely Tiong Bahru, Tiong Bahru Station and Kampong Tiong Bahru. The namesake subzone refers to the main estate which consists of 54 Walk-up flats with over 900 housing units built by SIT, as well as modern HDB flats and private condominiums along Boon Tiong Road, Kim Tian Road and Chay Yan Street. Tiong Bahru Station subzone refers to the locality that encompasses Tiong Bahru MRT station, Tiong Bahru Plaza and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiong Bahru Plaza
Tiong Bahru Plaza (Simplified Chinese: 中峇鲁广场) is a shopping mall located in Tiong Bahru Estate, in Bukit Merah, Singapore, near Tiong Bahru Road, Jalan Membina and Bukit Ho Swee Crescent, which is where the entrance to the mall is located. It consists of a 20-storey office tower block (Central Plaza), and a 6-storey shopping and entertainment complex, with 3 basement carparks. The mall is also directly linked to Tiong Bahru MRT station of the East West MRT line, which is accessible from Exit B of the station. The suburban mall has a total of 167 shops spread across 6 floors. History Developed by UOL Limited, Tiong Bahru Plaza and the adjacent 20-storey office tower, Central Plaza, were completed in late 1994 as the first shopping mall in Tiong Bahru and Bukit Merah. Like a typical suburban mall at that time, it had a cinema, a department store, a supermarket, a food court, and more than 100 specialty shops. In 2003, the mall was sold to ARMF Pte Ltd. The mall comme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bukit Merah
Bukit Merah, also known as Redhill, is a Planning Areas of Singapore, planning area and New towns of Singapore, new town situated in the southernmost part of the Central Region, Singapore, Central Region of Singapore. The planning area borders Tanglin to the north, Queenstown, Singapore, Queenstown to the west and the Downtown Core, Outram, Singapore, Outram and Singapore River planning areas of the Central Area, Singapore, Central Area to the east. It also shares a maritime boundary with the Southern Islands planning area to the south. Bukit Merah is linked to Sentosa Island via Sentosa Gateway, Sentosa Broadwalk, Sentosa Express and the Singapore Cable Car, Cable Car. Bukit Merah planning area also includes two offshore islands which are linked to the mainland by road, namely Pulau Brani and Keppel Island, Singapore, Keppel Island. It is the most populated planning area in the Central Region, and the 12th most populated planning area in the country overall, being home to more t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban Redevelopment Authority
The Urban Redevelopment Authority (URA) is the national urban planning authority of Singapore, and a Statutory boards of the Singapore Government, statutory board under the Ministry of National Development (Singapore), Ministry of National Development of the Government of Singapore. Mission The authority was established on 1 April 1974, and is of critical importance to the city-state. Singapore is an extremely dense country where land usage is required to be efficient and maximized. The city state is trying to reduce land wastage in the face of land shortage in the area. Responsibilities Land use planning URA's main responsibility is land-use planning. URA planners devise both long-term strategic plans, along with medium-term plans, which are reviewed every five to ten years. These plans designate the land use and urban density for the entirety of Singapore. These designations are divided by URA into 55 Planning Areas of Singapore, planning areas. Development control It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great World Amusement Park
The Great World Amusement Park () also known locally as "Tua Seh Kai" (Pe̍h-ōe-jī: tōa sè-kài) in Hokkien, was the second of three former amusement parks in Singapore, along with New World (established 1923) and Gay World (established 1936). It was established in 1929 and closed down in 1978. It provided entertainment and leisure to people, catering especially to the middle and lower income groups of citizens in the past. History The amusement park was situated between Zion Road, River Valley Road and Kim Seng Road in the central part of Singapore. In the 1920s, the site was originally a Chinese cemetery. Taking reference to a map of Singapore in 1909, the place was covered with swampy marshes back then and a small canal run across the site, eventually meeting with the Singapore River thereafter. The landowner, Lee Geok Kun (brother of philanthropist Lee Kong Chian), redeveloped the site into an amusement park in the 1930s. Business within Great World did not fulfil the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
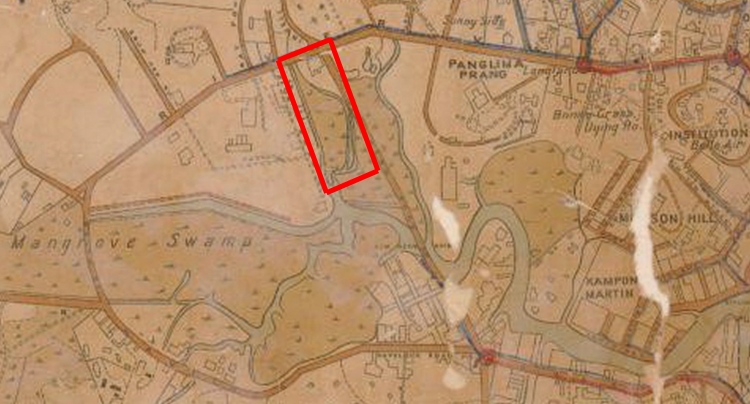
Mangrove Swamp
Mangrove forests, also called mangrove swamps, mangrove thickets or mangals, are productive wetlands that occur in coastal intertidal zones. Mangrove forests grow mainly at tropical and subtropical latitudes because mangrove trees cannot withstand freezing temperatures. There are about 80 different species of mangroves, all of which grow in areas with low-oxygen soil, where slow-moving waters allow fine sediments to accumulate.What is a mangrove forest? National Ocean Service, NOAA. Updated: 25 March 2021. Retrieved: 4 October 2021. Many mangrove forests can be recognised by their dense tangle of prop roots that make the trees appear to be standing on stilts above the water. This tangle of roots allows the trees to handle the daily rise and fall of tides, as most mangroves get flooded at least twice per day. The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lim Nee Soon
Lim Nee Soon (; 12 November 1879 – 20 March 1936) was a Singaporean banker and businessman who promoted social and community matters, and was a respected community leader in Singapore. Lim was of Peranakan descent, with ancestry from Chenghai District, Shantou in Guangdong, China. He was a rubber magnate and was nicknamed the "pineapple king" for being the leading pineapple planter in the region. He was also a banker, contractor and general commission agent. He was the first general manager of the Bukit Sembawang Rubber Company Limited, formed in 1908. Nee Soon and Company was formed in 1911. As a Chinese Peranakan, known as "Baba" locally, he was affectionately known as Bah Soon Pah (). Bah Soon Pah Road was named after him. Early life Lim Nee Soon was born in Kampong Glam, Singapore. His family was from Shantou, Guangdong, China. His father died when he was eight and his maternal grandfather, a merchant, took care of him. Lim was educated in English at the St. Joseph's I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tan Chay Yan
Tan Chay Yan (; 1871 - 6 March 1916) was a rubber plantation merchant and philanthropist. A Peranakan, Tan is the grandson of philanthropist Tan Tock Seng by his father, Tan Teck Guan. Tan was noted in Malayan history as the first man to plant rubber on a commercial basis, after he was introduced to rubber planting by Henry Nicholas Ridley. Subsequently, Tan started a rubber estate at Bukit Lintang. He then ventured his rubber plantation business into Sri Lanka. According to his family, Tan's rubber plantation still belonged to the family. As a philanthropist, Tan also gave $15,000 towards the setting up of a medical college in Singapore. The donation went towards the construction of the Tan Teck Guan Building, which Tan named in memory of his late father. Tan was also appointed as a Justice of the Peace at age 24, and served on the Malacca Municipal Commission. He also served as a Trustee of the Cheng Hoon Teng Temple. Tan died of malaria at the age of 46. A relative beli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typology (urban Planning And Architecture)
Typology is the study and classification of object types. In urban planning and architecture, typology refers to the task of identifying and grouping buildings and urban spaces according to the similarity of their essential characteristics. Common examples of essential characteristics include intensity of development (from rural to suburban to urban) and building use (church, hospital, school, apartment, house, etc.) Non-essential characteristics are those which, if modified, would not change the building type. Color, for example, would rarely be considered an essential characteristic of building type. Material, however, may or may not be considered essential depending on how integral the material is to the structure (engineering) and construction (assembly) of the building. Building types may be further divided into subtypes. For example, among religious structures there are churches and mosques, etc.; among churches there are cathedrals and chapels, etc.; among cathedrals the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squatting
Squatting is the action of occupying an abandoned or unoccupied area of land or a building (usually residential) that the squatter does not own, rent or otherwise have lawful permission to use. The United Nations estimated in 2003 that there were one billion slum residents and squatters globally. Squatting is practiced worldwide, typically when people find empty buildings or land to occupy for housing. In developing countries and least developed countries, shanty towns often begin as squatted settlements. In African cities such as Lagos, much of the population lives in slums. There are pavement dwellers in India and in Hong Kong as well as rooftop slums. Informal settlements in Latin America are known by names such as villa miseria (Argentina), pueblos jóvenes (Peru) and asentamientos irregulares (Guatemala, Uruguay). In Brazil, there are favelas in the major cities and rural land-based movements. In industrialized countries, there are often residential squats and also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coolie
Coolie (also spelled koelie, kouli, khuli, khulie, kuli, cooli, cooly, or quli) is a pejorative term used for low-wage labourers, typically those of Indian people, Indian or Chinese descent. The word ''coolie'' was first used in the 16th century by European traders across Asia. In the 18th century, the term more commonly referred to migrant Indian indenture system, Indian indentured labourers. In the 19th century, during the Colonial India, British colonial era, the term was adopted for the transportation and employment of Asian labourers via employment contracts on Sugar plantations in the Caribbean, sugar plantations formerly worked by enslaved Africans. The word has had a variety of negative implications. In modern-day English, it is usually regarded as offensive. In the 21st century, ''coolie'' is generally considered a racial slur for Asians in Oceania, Africa, Southeast Asia, and the Americas (particularly in the Caribbean). The word originated in the 17th-century India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singapore General Hospital
Singapore General Hospital (SGH) is an academic health science centre and tertiary referral hospital in Singapore. It is located next to the Bukit Merah and Chinatown districts of the Central Region, close to the Outram Community Hospital (OCH), which functions as a supplementary community and rehabilitation hospital to SGH for newly discharged patients. There is also the Outram Polyclinic to complement outpatient care. All of these institutions are operated by SingHealth, which comes under the purview of the Ministry of Health (MOH). It is the largest and oldest hospital in Singapore and functions as the country's national hospital. The foundation of its first building was laid in 1821, before its first major expansion in 1926. Subsequent expansions as well as renovations were also made in the following decades. SGH is the flagship hospital of SingHealth, the country's largest group of public healthcare institutions and the principal teaching hospital for the Duke–NUS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hokkien
Hokkien ( , ) is a Varieties of Chinese, variety of the Southern Min group of Chinese language, Chinese languages. Native to and originating from the Minnan region in the southeastern part of Fujian in southeastern China, it is also referred to as Quanzhang ( zh, c=泉漳, poj=Choân-chiang, links=no), from the first characters of the urban centers of Quanzhou and Zhangzhou. Taiwanese Hokkien is one of the national languages in Taiwan. Hokkien is also widely spoken within the overseas Chinese diaspora in Singapore, Malaysia, the Philippines, Indonesia, Cambodia, Myanmar, Hong Kong, Thailand, Brunei, Vietnam, and elsewhere across the world. Mutual intelligibility between Hokkien dialects varies, but they are still held together by ethnolinguistic identity. In maritime Southeast Asia, Hokkien historically served as the lingua franca amongst overseas Chinese communities of Han Chinese subgroups, all dialects and subgroups, and it remains today as the most spoken Varieties of Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |