|
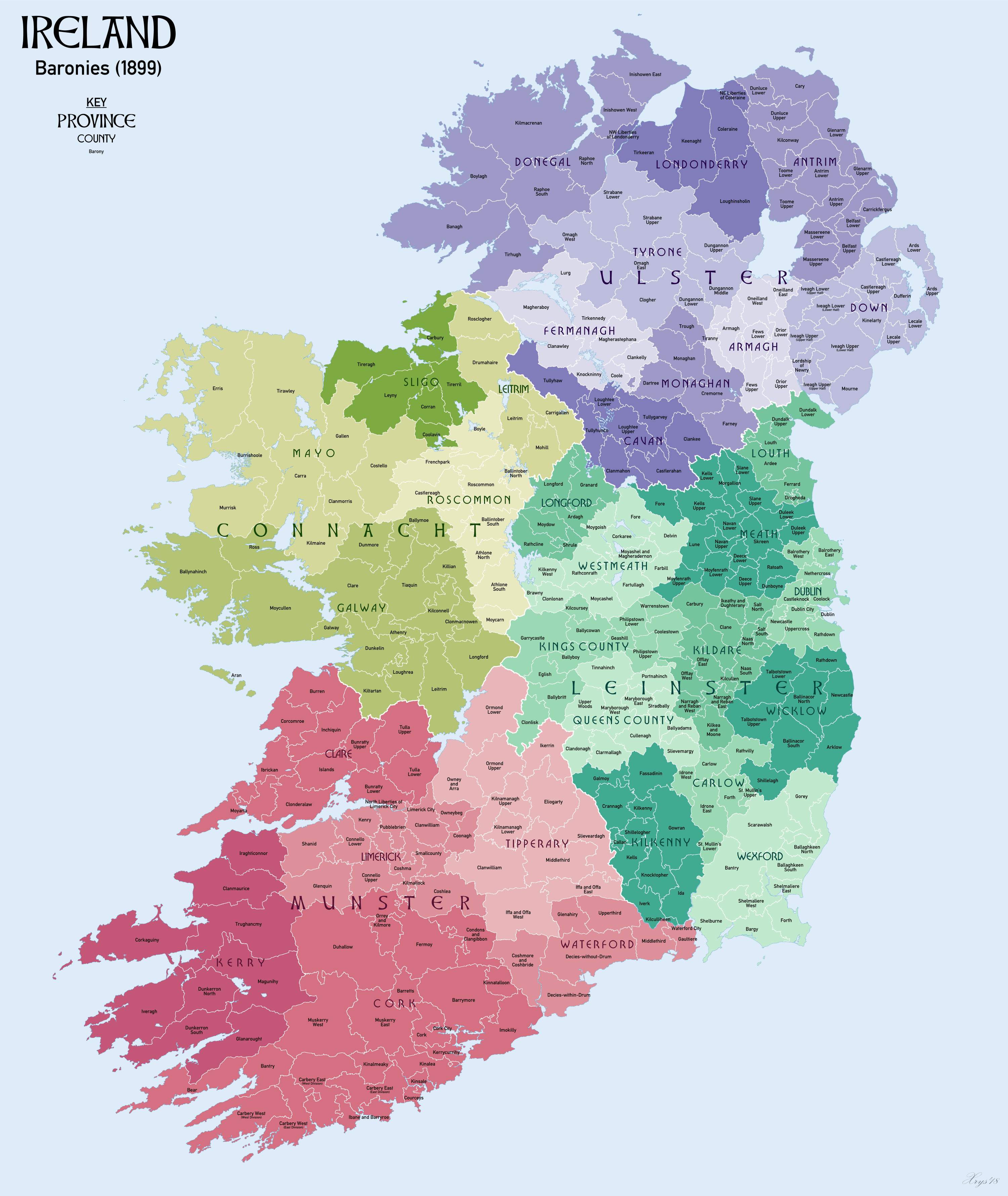
Tinnahinch (barony)
Tinnahinch () is a barony in County Laois (formerly called ''Queen's County'' or ''County Leix''), in Ireland. History The southern part of Tinnahinch was called ''Gailine'', and it is mentioned in the topographical poem ''Tuilleadh feasa ar Éirinn óigh'' (Giolla na Naomh Ó hUidhrín, d. 1420): List of settlements Settlements in Tinnahinch barony: *Clonaghadoo *Clonaslee *Mountmellick Mountmellick or Mountmellic () is a town in the north of County Laois, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is on the N80 road (Ireland), N80 road, 6 km north of Portlaoise. The town is within Mountmellick (parish), Mountmellick Roman Catholic p ... * Rosenallis References {{County Laois Baronies of County Laois ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Language
Irish (Standard Irish: ), also known as Irish Gaelic or simply Gaelic ( ), is a Celtic language of the Indo-European language family. It is a member of the Goidelic languages of the Insular Celtic sub branch of the family and is indigenous language, indigenous to the island of Ireland. It was the majority of the population's first language until the 19th century, when English (language), English gradually became dominant, particularly in the last decades of the century, in what is sometimes characterised as a result of linguistic imperialism. Today, Irish is still commonly spoken as a first language in Ireland's Gaeltacht regions, in which 2% of Ireland's population lived in 2022. The total number of people (aged 3 and over) in Ireland who declared they could speak Irish in April 2022 was 1,873,997, representing 40% of respondents, but of these, 472,887 said they never spoke it and a further 551,993 said they only spoke it within the education system. Linguistic analyses o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Modern Irish
Early Modern Irish () represented a transition between Middle Irish and Modern Irish. Its literary form, Classical Gaelic, was used in Ireland and Scotland from the 13th to the 18th century. Classical Gaelic Classical Gaelic or Classical Irish () was a shared literary form of Gaelic that was in use by poets in Scotland and Ireland from the 13th century to the 18th century. Although the first written signs of Scottish Gaelic having diverged from Irish appear as far back as the 12th century annotations of the Book of Deer, Scottish Gaelic did not have a separate standardised form and did not appear in print on a significant scale until the 1767 translation of the New Testament into Scottish Gaelic;Thomson (ed.), ''The Companion to Gaelic Scotland'' however, in the 16th century, John Carswell's ', an adaptation of John Knox's ''Book of Common Order'', was the first book printed in either Scottish or Irish Gaelic. Before that time, the vernacular dialects of Ireland and Scotland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountmellick
Mountmellick or Mountmellic () is a town in the north of County Laois, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is on the N80 road (Ireland), N80 road, 6 km north of Portlaoise. The town is within Mountmellick (parish), Mountmellick Roman Catholic parish. Name ''Mountmellick'', sometimes spelt ''Montmellick'' or ''Montmellic'', is an anglicisation of the Irish language, Irish name ''Móinteach Mílic'', which means "(the) bog of/by (the) land bordering a river". Older anglicisations include ''Mointaghmeelick, Montaghmelick, Montiaghmeelick'' and ''Monteaghmilick''.Placenames Database of Ireland (see archival records) History Mountmellick was a 15th-century settlement on the narrow Owenass River ('River of the Falls' in Irish) with an encampment on its banks at Irishtown. Overlooking this valley with its trees an ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clonaslee
Clonaslee () is a village in north County Laois, Ireland, situated in the foothills of the Slieve Bloom Mountains on the R422 Mountmellick to Birr road. Clonaslee is approximately 100 km west of Dublin, and is close to the towns of Portlaoise and Tullamore. As of the 2022 census, the village had a recorded population of 608. Name The primary spelling of the name, Clonaslee, is associated by several sources to the Irish ''Cluain na Slí'' (translated as "pasture of the way" or "roadside meadow" or similar) and related to the village's location on ancient cross-country route. Though this is the commonly and officially accepted version, an alternative spelling of the name, Cloneslieu, is associated by some sources to the Irish ''Cluain na Sléibhe'' (translated as "the mountain meadow"). The original name of the parish, Kilmanman, from the Irish ''Cill na mBanbhán'' or ''Cill Mheanman'' (translated as "the church of Manman"), is associated with Saint Manman who founde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clonaghadoo
Clonaghadoo is a village in County Laois, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, located north of Mountmellick just off the N80 road (Ireland), N80 national secondary road. The Slieve Bloom Mountains lie southwest of the village. The village is part of the Mountmellick (parish), Roman Catholic parish Mountmellick. Amenities There is a Catholic church, school and a community hall. The hall was originally a Clonaghadoo National School, opened in 1912. The name Clonaghadoo comes from Cluanacha Dubha, or the Black Meadows. In the grounds of the church, there is a labyrinth of low hedges and gravel paths. Sport Kilcavan GAA is the village's club for Gaelic football, while other nearby Gaelic games clubs are The Rock GAA and Mountmellick GAA. See also * List of towns and villages in the Republic of Ireland, List of towns and villages in Ireland External linksSt Marys church Clonaghadooh1> References Towns and villages in County Laois Townlands of County Laois {{Laois-geo-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rout
A rout is a Panic, panicked, disorderly and Military discipline, undisciplined withdrawal (military), retreat of troops from a battlefield, following a collapse in a given unit's discipline, command authority, unit cohesion and combat morale (''esprit de corps''). History Historically, lightly equipped soldiers such as light cavalry, auxiliaries, partisan (military), partisans or militia were important when pursuing a fast-moving, defeated enemy force and could often keep up the pursuit into the following day, causing the routed army heavy casualties or total dissolution. The slower-moving heavy forces could then either seize objectives or pursue at leisure. However, with the advent of armoured warfare and ''blitzkrieg'' style operations, an enemy army could be kept more or less in a routed or disorganized state for days or weeks on end. In modern times, a routed formation will often cause a complete breakdown in the entire front, enabling the organized foe to attain a quick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taoiseach
The Taoiseach (, ) is the head of government or prime minister of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The office is appointed by the President of Ireland upon nomination by Dáil Éireann (the lower house of the Oireachtas, Ireland's national legislature) and the office-holder must retain the support of a majority in the Dáil to remain in office. The Irish language, Irish word ''Wiktionary:taoiseach, taoiseach'' means "chief" or "leader", and was adopted in the 1937 Constitution of Ireland as the title of the "head of the Government or Prime Minister". It is the official title of the head of government in both English and Irish, and is not used for the prime ministers of other countries, who are instead referred to in Irish by the generic term . The phrase ''an Taoiseach'' is sometimes used in an otherwise English-language context, and means the same as "the Taoiseach". The incumbent Taoiseach is Micheál Martin, Teachta Dála, TD, leader of Fianna Fáil, who took office on 23 Janu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ó Duinn
Ó, ó (o-acute accent, acute) is a letter in the Czech language, Czech, Dobrujan Tatar, Emilian-Romagnol language, Emilian-Romagnol, Faroese language, Faroese, Hungarian language, Hungarian, Icelandic language, Icelandic, Kashubian language, Kashubian, Polish language, Polish, Slovak language, Slovak, Karakalpak language, Karakalpak, and Sorbian languages. The symbol also appears in the Afrikaans language, Afrikaans, Catalan language, Catalan, Dutch language, Dutch, Irish language, Irish, Norwegian language, Nynorsk, Norwegian language, Bokmål, Occitan language, Occitan, Portuguese language, Portuguese, Spanish language, Spanish, Italian language, Italian and Galician language, Galician languages as a variant of the letter "o". It usually represents a vowel sound longer than or slightly different from that represented by plain "o", although in some cases its sound is notably different (as in modern Polish, where it is pronounced the same as "u"). In some cases it represents the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giolla Na Naomh Ó HUidhrín
Giolla na Naomh O hUidhrin, Irish historian and poet, died 1420. O hUidhrin is known as the author of '' Tuilleadh feasa ar Éirinn óigh'', a topographical poem of a kind with Seán Mór Ó Dubhagáin's '' Triallam timcheall na Fodla'', of which it is a supplement. Although his obit is noted in all the main Irish annals A number of Irish annals, of which the earliest was the Chronicle of Ireland, were compiled up to and shortly after the end of the 17th century. Annals were originally a means by which monks determined the yearly chronology of feast days. Over ti ..., indicating he was regarded as a noteworthy man, nothing further is known of him. References * ''O hUidhrin, Giolla-na-naomh'', Aidan Breen, in ''Dictionary of Irish Biography'', p. 574, Cambridge, 2009. 15th-century Irish historians 15th-century Irish poets 1420 deaths Year of birth unknown Irish male poets Irish-language writers {{Ireland-historian-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barony (Ireland)
In Ireland, a barony (, plural ) is a historical subdivision of a counties of Ireland, county, analogous to the hundred (county subdivision), hundreds into which the counties of England were divided. Baronies were created during the Tudor reconquest of Ireland, replacing the earlier cantreds formed after the original Norman invasion of Ireland, Norman invasion.Mac Cotter 2005, pp.327–330 Some early baronies were later subdivided into half baronies with the same standing as full baronies. Baronies were mainly cadastre, cadastral rather than administrative units. They acquired modest local taxation and spending functions in the 19th century before being superseded by the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898. Subsequent adjustments of county boundaries mean that some baronies now straddle two counties. The final catalogue of baronies numbered 331, with an average area of ; each county was divided, on average, into 10 or 11 baronies. Creation The island of Ireland was "shired" i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuilleadh Feasa Ar Éirinn óigh
Tuilleadh feasa ar Éirinn óigh ("More knowledge on the entirety of Ireland") is a medieval Gaelic- Irish topographical text, composed by Giolla na Naomh Ó hUidhrín (died 1420). Overview ''Tuilleadh feasa ...'' is both a supplement and a continuation of Seán Mór Ó Dubhagáin's '' Triallam timcheall na Fodla''. Of the two, James Carney wrote: * "These two poems together constitute a compendium of the topography of pre-Norman Ireland, as seen, however, by poets who lived two centuries after the invasion. ''Triallam timcheall na Fodla'' ... is an account of the territories of the northern half of Ireland and Leinster, indicating the ruling family or families of each district. ''Tuilleadh feasa ar Éirinn óigh'' ... treats in similar fashion of the southern half of Ireland, including Leinster, of which we have therefore two independent accounts. The introductory stanzas of Ó hUidhrín's poem, in which he defines the scope of his work and its relation to that of his predeces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |