|
Tingmiatornis
''Tingmiatornis'' (meaning "bird that flies") is a genus of flighted and possibly diving ornithuran dinosaur from the High Arctic of Canada. The genus contains a single species, ''T. arctica'', described in 2016, which lived during the Turonian epoch of the Cretaceous. Description Given the small number of bones that are referrable to ''Tingmiatornis'', it is difficult to infer much about the animal. However, the thickness of the cortical bone (on average, ) and the relative length of the humerus suggest that it was apparently capable of flight and likely also diving, similar to the possible hesperornithine '' Pasquiaornis''. ''Tingmiatornis'' can be differentiated from the latter by numerous traits including larger size, a more globe-shaped dorsal condyle on the humerus, an olecranon process of the ulna that does not project outward as strongly, as well as a smaller bicipital tubercle of the ulna. ''Tingmiatornis'' also differs from ''Ichthyornis'' in the following ways: the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axel Heiberg Island
Axel Heiberg Island (, ) is an uninhabited island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. Located in the Arctic Ocean, it is the 32nd largest island in the world and Canada's seventh largest island. According to Statistics Canada, it has an area of . It is named after Axel Heiberg. One of the larger members of the Arctic Archipelago, it is also a member of the Sverdrup Islands and Queen Elizabeth Islands. It is known for its unusual fossil forests, which date from the Eocene period. Owing to the lack of mineralization in many of the forest specimens, the traditional characterization of "fossilisation" fails for these forests and "mummification" may be a more precise description. The fossil records provide strong evidence that the Axel Heiberg forest was a high-latitude wetland forest. A holotype of the ammonite '' Otoceras gracile'' was found in the Griesbachian (Early Triassic) deposits of this island. History Axel Heiberg Island has been inhabited in the past by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithurae
Ornithurae (meaning "bird tails" in Greek) is a natural group that includes modern birds and their very close relatives such as the ichthyornithines and the hesperornithines. This clade is defined in the ''PhyloCode'' by Juan Benito and colleagues in 2022 as "the smallest clade containing '' Ichthyornis dispar'', '' Hesperornis regalis'', and '' Vultur gryphus''". Classification Ernst Haeckel coined the name in 1866 and included in the group all "true birds" with the "characteristic tail morphology of all extant birds" (translation by Jacques Gauthier). This distinguishes the group from ''Archaeopteryx'', which Haeckel placed in another new group called Sauriurae. Said simply, modern birds have short, fused pygostyle tails, while ''Archaeopteryx'' retained the long tail characteristic of non-avian theropod dinosaurs.Haeckel, Ernst (1866). ''Generelle Morphologie der Organismen''. Berlin: Georg Reimer. Gauthier converted Ornithurae into a clade, giving it a branch-based defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turonian
The Turonian is, in the International Commission on Stratigraphy, ICS' geologic timescale, the second age (geology), age in the Late Cretaceous epoch (geology), Epoch, or a stage (stratigraphy), stage in the Upper Cretaceous series (stratigraphy), Series. It spans the time between 93.9 ± 0.8 annum, Ma and 89.8 ± 1 Ma (million years ago). The Turonian is preceded by the Cenomanian Stage and underlies the Coniacian Stage. At the beginning of the Turonian an anoxic event, oceanic anoxic event (OAE 2) took place, also referred to as the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary event or the "Bonarelli Event". Sea level fall took place in the latter part of the Turonian from the highstand at the beginning of the Turonian. Stratigraphic definition The Turonian (French: ''Turonien'') was defined by the France, French paleontologist Alcide d'Orbigny (1802–1857) in 1842. Orbigny named it after the French city of Tours in the region of Touraine (department Indre-et-Loire), which is the original Typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inuktitut
Inuktitut ( ; , Inuktitut syllabics, syllabics ), also known as Eastern Canadian Inuktitut, is one of the principal Inuit languages of Canada. It is spoken in all areas north of the North American tree line, including parts of the provinces of Newfoundland and Labrador, Quebec, to some extent in northeastern Manitoba as well as the Northwest Territories and Nunavut. It is one of the aboriginal languages written with Canadian Aboriginal syllabics. It is recognized as an official language in Nunavut alongside Inuinnaqtun and both languages are known collectively as ''Inuktut''. Further, it is recognized as one of eight official native tongues in the Northwest Territories. It also has legal recognition in Nunavik—a part of Quebec—thanks in part to the James Bay and Northern Quebec Agreement, and is recognized in the Charter of the French Language as the official language of instruction for Inuit school districts there. It also has some recognition in NunatuKavut and Nunatsiavu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanguk Formation
The Kanguk Formation is a geological formation in the Northwest Territories and Nunavut, Canada whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Late Cretaceous, North America)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. Pp. 574-588. . It was first described in the Kanguk Peninsula of the Axel Heiberg Island, along the shore of the Stand Fiord by Souther in 1963. The formation occurs throughout the Sverdrup Basin and the southern Queen Elizabeth Islands. Lithology The Kanguk Formation is composed of dark shale and siltstone with interbeds of sandstone, bentonite and tuff. Thicker sandstone and conglomerate beds occur in the western reaches in Eglinton Island. Fossil content The Kanguk Formation preserves an extensive record of shelf assembla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strand Fiord Formation
The Strand Fiord Formation is a Late Cretaceous volcanic component, located on northwestern and west-central Axel Heiberg Island, Nunavut, Canada. The formation contains flood basalts which are found on western Axel Heiberg Island at Dragon Cliff tall. The Strand Fiord Formation contains columnar jointing units that are usually in diameter. The formation is interpreted to represent the cratonward extension of the Alpha Ridge, a volcanic ridge that was active during the formation of the Amerasia Basin. Retrieved on 2007-08-15 The Strand Fiord Formation is also part of the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Museum Of Nature
The Canadian Museum of Nature (; CMN) is a national museums of Canada, national natural history museum based in Canada's National Capital Region (Canada), National Capital Region. The museum's exhibitions and public programs are housed in the Victoria Memorial Museum Building, a in Ottawa, Ontario. The museum's administrative offices and scientific centres are housed at a separate location, the Natural Heritage Campus, in Gatineau, Quebec. The museum originated from a museum established by the Geological Survey of Canada in 1856. Initially based in Montreal, the museum relocated to downtown Ottawa in 1881. In 1911, the museum relocated to the Victoria Memorial Museum Building. Initially, a natural history museum, the institution later expanded to include an anthropology and human history department; with the institution renamed the National Museum of Canada in 1927. The departments of the national museum were later split into separate national institutions, with the natural hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Rochester
The University of Rochester is a private university, private research university in Rochester, New York, United States. It was founded in 1850 and moved into its current campus, next to the Genesee River in 1930. With approximately 30,000 full-time employees, the university is the largest private employer in Upstate New York and the seventh-largest in all of New York (state), New York State. With over 12,000 students, the university offers 160 undergraduate and 30 graduate programs across seven schools spread throughout five campuses. The University of Rochester College of Arts Sciences and Engineering, College of Arts, Sciences, and Engineering is the largest school, and it includes the School of Engineering and Applied Sciences. The Eastman School of Music, founded by and named after George Eastman, is located in Downtown Rochester. The university is also home to Rochester's Laboratory for Laser Energetics, a national laboratory supported by the United States Department of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vidalamiinae
The Amiidae are a family of basal (phylogenetics), basal ray-finned fishes. The bowfin and the eyespot bowfin (''Amia ocellicauda'') are the only two species to survive today, although additional species in all four subfamilies of Amiidae are known from Jurassic, Cretaceous, and Eocene fossils. Bowfins are now found throughout eastern North America, typically in slow-moving backwaters, canals, and ox-bow lakes. When the oxygen level is low (as often happens in still waters), the bowfin can rise to the surface and gulp air into its swim bladder, which is lined with blood vessels and can serve as a primitive lung. Amiidae is a monophyletic group that has numerous synapomorphic characters. Amiidae were widespread and particularly rich in species during the Eocene era. During this era, they appeared to be confined almost exclusively to fresh water. Taxonomy The family is divided into five subfamilies, with 16 genera *Amiidae **Subfamily Amiinae (latest Cretaceous -Present) ***Genu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choristodera
Choristodera (from the Greek χωριστός ''chōristos'' + δέρη ''dérē'', 'separated neck') is an extinct order of semiaquatic diapsid reptiles that ranged from the Middle Jurassic, or possibly Triassic, to the Miocene (168 to 20 or possibly 11.6 million years ago). Choristoderes are morphologically diverse, with the best known members being the crocodile-like neochoristoderes such as '' Champsosaurus''. Other choristoderans had lizard-like or long necked morphologies. Choristoderes appear to have been confined to the Northern Hemisphere, having been found in North America, Asia, and Europe, and possibly also North Africa. Choristoderes are generally thought to be derived neodiapsids that are close relatives or members of Sauria. History of discovery Choristodera was erected in 1876, originally as a suborder of Rhynchocephalia by Edward Drinker Cope to contain '' Champsosaurus,'' which was described from Late Cretaceous strata of Montana by Cope in the same paper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
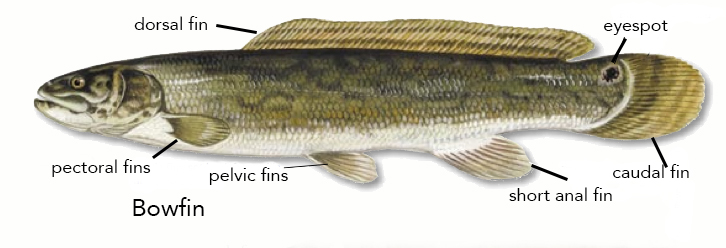
Bowfin
The ruddy bowfin (''Amia calva'') is a ray-finned fish native to North America. Common names include mudfish, mud pike, dogfish, grindle, grinnel, swamp trout, and choupique. It is regarded as a relict, being one of only two surviving species of the Halecomorphi, a group of fish that first appeared during the Early Triassic, around 250 million years ago. The bowfin is often considered a "living fossil" because they have retained some morphological characteristics of their early ancestors. It is one of two species in the genus ''Amia,'' along with '' Amia ocellicauda'', the eyespot bowfin. The closest living relatives of bowfins are gars, with the two groups being united in the clade Holostei. Bowfins are demersal freshwater piscivores, commonly found throughout much of the eastern United States, and in southern Ontario and Quebec. Fossil deposits indicate Amiiformes were once widespread in both freshwater and marine environments across North and South America, Europe, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |