|
Tindi People
The Tindi are an indigenous people of Dagestan, North Caucasus living in five villages in the center area around the Andi-Koisu river and the surrounding mountains in the northwestern part of southern Dagestan. They have their own language, Tindi, and primarily follow Sunni Islam Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagre ..., which reached the Tindi people around the 8th or 9th century. The only time that the Tindis were counted as a distinct ethnic group in the Russian Census was in 1926, when 3,812 reported to be ethnic Tindis. In 1967, there were about 5,000 ethnic Tindis (T. Gudava). They are culturally similar to the Avars. The basis of the Tindis' ethnic identity is their language, but its use is limited to domestic settings and is decreasing. Therefore, the Tindis a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tindi Language
Tindi is a Northeast Caucasian language spoken in the Russian republic of Dagestan. Tindis call their language ''Idarab mitstsi'' meaning 'the language of the Idar village'. It is only an oral language; Avar or Russian are used in written communication instead. Tindi vocabulary contains many loanword A loanword (also loan word or loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language. This is in contrast to cognates, which are words in two or more languages that are similar because th ...s from Avar, Turkish, Arabic, and Russian. It has approximately 2,150 speakers. References External links The peoples of the Red Book: Tindis Northeast Caucasian languages Andic languages Dagestan Languages of Russia Endangered Caucasian languages {{NEC-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word ''Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagreement over the succession to Muhammad and subsequently acquired broader political significance, as well as theological and juridical dimensions. According to Sunni traditions, Muhammad left no successor and the participants of the Saqifah event appointed Abu Bakr as the next-in-line (the first caliph). This contrasts with the Shia view, which holds that Muhammad appointed his son-in-law and cousin Ali ibn Abi Talib as his successor. The adherents of Sunni Islam are referred to in Arabic as ("the people of the Sunnah and the community") or for short. In English, its doctrines and practices are sometimes called ''Sunnism'', while adherents are known as Sunni Muslims, Sunnis, Sunnites and Ahlus Sunnah. Sunni Islam is sometimes referr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeast Caucasian Languages
The Northeast Caucasian languages, also called East Caucasian, Nakh-Daghestani or ''Vainakh-Daghestani'', is a family of languages spoken in the Russian republics of Dagestan, Chechnya and Ingushetia and in Northern Azerbaijan as well as in diaspora populations in Western Europe and the Middle East. They are occasionally called ''Caspian'', as opposed to ''Pontic'' for the Northwest Caucasian languages. Name of the family Several names have been in use for this family. The most common term, ''Northeast Caucasian'', contrasts the three established families of the Caucasian languages: ''Northeast Caucasian'', ''Northwest Caucasian'' (Abkhaz–Adyghean) and ''South Caucasian'' (Kartvelian). This may be shortened to ''East Caucasian''. The term ''Nakh(o)-Dagestanian'' can be taken to reflect a primary division of the family into Nakh and Dagestanian branches, a view which is no longer widely accepted, or ''Dagestanian'' can subsume the entire family. The rare term ''North Cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
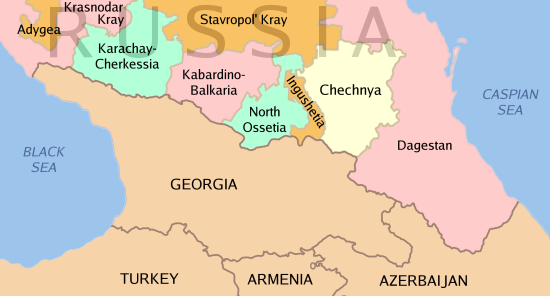
Dagestan
Dagestan ( ; rus, Дагеста́н, , dəɡʲɪˈstan, links=yes), officially the Republic of Dagestan (russian: Респу́блика Дагеста́н, Respúblika Dagestán, links=no), is a republic of Russia situated in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe, along the Caspian Sea. It is located north of the Greater Caucasus, and is a part of the North Caucasian Federal District. The republic is the southernmost tip of Russia, sharing land borders with the countries of Azerbaijan and Georgia to the south and southwest, the Russian republics of Chechnya and Kalmykia to the west and north, and with Stavropol Krai to the northwest. Makhachkala is the republic's capital and largest city; other major cities are Derbent, Kizlyar, Izberbash, Kaspiysk and Buynaksk. Dagestan covers an area of , with a population of over 3.1 million, consisting of over 30 ethnic groups and 81 nationalities. With 14 official languages, and 12 ethnic groups each constituting more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Caucasus
The North Caucasus, ( ady, Темыр Къафкъас, Temır Qafqas; kbd, Ишхъэрэ Къаукъаз, İṩxhərə Qauqaz; ce, Къилбаседа Кавказ, Q̇ilbaseda Kavkaz; , os, Цӕгат Кавказ, Cægat Kavkaz, inh, Даькъасте, Däq̇aste, krc, Шимал Кавказ, Şimal Kavkaz, russian: Северный Кавказ, r=Severnyy Kavkaz, p=ˈsʲevʲɪrnɨj kɐfˈkas) or Ciscaucasia (russian: Предкавказье, Predkavkazye), is a subregion of Eastern Europe in the Eurasian continent. It is the northern part of the wider Caucasus region, and is entirely a part of Russia, sandwiched between the Sea of Azov and Black Sea to the west, and the Caspian Sea to the east. The region shares land borders with Georgia and Azerbaijan to the south. Krasnodar is the largest city within the North Caucasus. Politically, the North Caucasus is made up of Russian republics and krais. It lies north of the Main Caucasian Range, which separates it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avar People (Caucasus)
The Avars, also known as ''Maharuls'' (Avar language, Avar: , , "mountaineers") are a Northeast Caucasian languages, Northeast Caucasian ethnic group. The Avars are the largest of several ethnic groups living in the Russian republic of Dagestan. The Avars reside in the North Caucasus between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea. Alongside other ethnic groups in the North Caucasus region, the Avars live in ancient villages located approximately 2,000 m above sea level. The Avar language spoken by the Caucasian Avars belongs to the family of Northeast Caucasian languages. Sunni Islam has been the prevailing religion of the Avars since the 13th century. Ethnonyms According to 19th-century Russian historians, the Avars' neighbors usually referred to them as Tavlins (''tavlintsy''). This is an exonym. Vasily Potto wrote that those to the south usually knew them as Tavlins (''tavlintsy''). Potto wrote, "The words in different languages have the same meaning... [of] mountain dwellers [or] ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avar Language
Avar (, , "language of the mountains" or , , "Avar language"), also known as Avaric, is a Northeast Caucasian language of the Avar–Andic subgroup that is spoken by Avars, primarily in Dagestan. In 2010, there were approximately 1 million speakers in Dagestan and elsewhere in Russia. Geographic distribution It is spoken mainly in the western and southern parts of the Russian Caucasus republic of Dagestan, and the Balaken, Zaqatala regions of north-western Azerbaijan. Some Avars live in other regions of Russia. There are also small communities of speakers living in the Russian republics of Chechnya and Kalmykia; in Georgia, Kazakhstan, Ukraine, Jordan, and the Marmara Sea region of Turkey. It is spoken by about 762,000 people worldwide. UNESCO classifies Avar as vulnerable to extinction. Status It is one of six literary languages of Dagestan, where it is spoken not only by the Avar, but also serves as the language of communication between different ethnic groups ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamalal People
The Chamalals are an indigenous people of Dagestan, North Caucasia living in a few villages in the Tsumadinsky District on the left bank of the Andi-Koisu river. They have their own language, Chamalal, and primarily follow Sunni Islam, which reached the Chamalal people around the 8th or 9th century. There are about 5,000 ethnic Chamalals (1999, Kubrik). They are culturally similar to the Avars. Neighboring peoples are the Godoberi, Avars, Bagvalals, and Tindis The Tindi are an indigenous people of Dagestan, North Caucasus living in five villages in the center area around the Andi-Koisu river and the surrounding mountains in the northwestern part of southern Dagestan. They have their own language, Ti .... References The peoples of the Red Book: Chamalals Ethnic groups in Dagestan Muslim communities of Russia Peoples of the Caucasus {{caucasus-ethno-group-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avars (Caucasus)
The Avars, also known as ''Maharuls'' ( Avar: , , "mountaineers") are a Northeast Caucasian ethnic group. The Avars are the largest of several ethnic groups living in the Russian republic of Dagestan. The Avars reside in the North Caucasus between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea. Alongside other ethnic groups in the North Caucasus region, the Avars live in ancient villages located approximately 2,000 m above sea level. The Avar language spoken by the Caucasian Avars belongs to the family of Northeast Caucasian languages. Sunni Islam has been the prevailing religion of the Avars since the 13th century. Ethnonyms According to 19th-century Russian historians, the Avars' neighbors usually referred to them as Tavlins (''tavlintsy''). This is an exonym. Vasily Potto wrote that those to the south usually knew them as Tavlins (''tavlintsy''). Potto wrote, "The words in different languages have the same meaning... fmountain dwellers rhighlanders."''В. А. Потто.'Кавка ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagvalal People
The Bagvalal (also called Bagulal, Kwantl Hekwa, Bagolal, Kwanadi, Bagulaltsy, Kvanadin, and Kvanadintsy) are an Avar–Andi–Dido people of Dagestan, speaking the Bagvalal language. Since the 1930s they have been largely classed as and assimilated by the Avars. However there were still some people reported separately in the 2002 census. The Bagvalals are Sunni Muslims. Geography The Bagvalal live in mountain villages in the Tsumadinsky District of Dagestan Dagestan ( ; rus, Дагеста́н, , dəɡʲɪˈstan, links=yes), officially the Republic of Dagestan (russian: Респу́блика Дагеста́н, Respúblika Dagestán, links=no), is a republic of Russia situated in the North .... The names of the Bagvalal villages are: Kvanada, Gimerso, Tlisi, Tlibisho, Khushtada, and Tlondada. Demographics In 1926 there were 3,054 Bagvalals. References Sources *Wixman, Ronald. ''The Peoples of the USSR: An Ethnographic Handbook''. (Armonk, New York: M. E. Shar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akhvakh People
The Akhvakhs (also known as Akhwakh, Akhvakhtsy or G'akhevalal; ''ГІахьвалал'' in Avar) are one of the Andi–Dido peoples of Dagestan and have their own language. They call themselves Atluatii or Ashvado. Prior to 1930 Soviet ethnologists considered them to be a distinct ethnic group. Since that time they have often been classified as Avars. Demographics The Akvakh live in the Akhvakhsky District of Dagestan between the Avar and Andi Rivers. In 1926 they numbered 3,683. The Akhvakhs are mainly Sunni Muslims Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word ''Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagr .... They face continued assimilation by the Avars. By the early 1990s it was estimated that about 8,000 people were Akhvakh, although this number includes those who have been fully assimilated as Avars but still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |