|
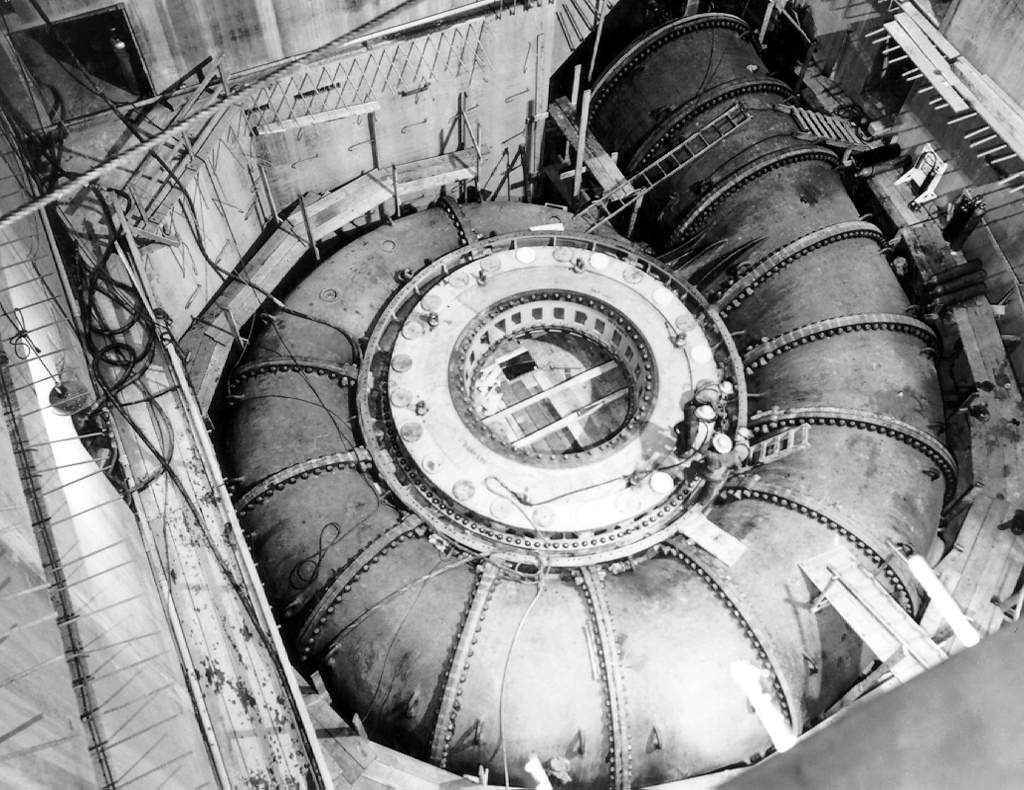
Tinau Hydropower Plant
Tinau Hydropower Plant (Nepali: तिनाउ जलविद्युत आयोजना, Tinau Jalbidyut Ayojana) is a run-of-river hydro-electric plant located in Rupandehi District of Nepal. The flow from Tinau River is used to generate 1.024 MW electricity. The plant was constructed in the leadership of Odd Hoftun. It was commissioned in 1978 with two 250-kW turbine-generators with total capacity of 500-kW. The project was later upgraded to 1.024 MW in assistance from ADB. The project has 2.462 km long tunnel, underground desilting chamber, and semi-underground powerhouse. The weir is 10 m high and 63 m long. The design flow is 2.5 m3/s. The power plant was initially owned by Butwal Power Company, a private company that constructed the plant. After the expiry of licence, the ownership was transferred to Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA). The plant had suffered damage due to flood in 1983. Significance The plant is considered instrumental to train Nepali Technic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinau
The Tinau is a river originating from the Mahabharat Mountains and flowing through the Siwalik Hills and Terai Plain at Butwal, Nepal before joining the Ganges. River morphology The length of the Tinau is 95 km starting from Palpa to Indo-Nepal Border at Marchawar. The catchment area of the river is about 1081 sq. km up to the border. River flow The minimum flow of the river is about 2.2 m3/s in April while the calculated 100 years return period flow in 2500m3/s. The maximum recorded flow at DHM station no 390 is as follows: Floods 1981 In 1981, there was a huge flood that destroyed two suspension bridges and the powerhouse shaft of Himal Hydro. 2007 In the flood of 2007 at least 500 households of Butwal municipality were displaced. 2008 In 2008, due to outburst of embankment, about 250 households were displace in Butwal municipality due to the flood. Water Use Hydropower Tinau Hydropower Plant Tinau Hydropower Plant (Nepali: तिनाउ जलवि� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepal Electricity Authority
Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA), founded on 16 August 1985, is the parent generator, transmittor and retail distributor of electric power under the supervision of the government of Nepal. NEA has its own power plants. In addition it also buys power from Independent Power Producers (IPP). Most of the power is generated from hydro electricity. It operates two fuel operated plants generating 53 Megawatts. Power production Plants owned by NEA NEA owns and operates following power plants. It has a dedicated department for operation and maintenance for those plants. Independent power producers NEA being a de facto purchaser of any electricity generated inside Nepal, it buys electricity from all the IPPs of Nepal. Solar Power Stations Diesel power stations Transmission and distribution lines All transmission and distributions lines in Nepal is owned and operated by NEA. As of 2024, Nepal's total transmission line length is 6,507 kilometers. This includes 4,136 km ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis-type
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The process of arriving at the modern Francis runner design took from 1848 to approximately 1920. It became known as the Francis turbine around 1920, being named after British-American engineer James B. Francis who in 1848 created a new turbine design. Francis turbines are primarily used for producing electricity. The power output of the electric generators generally ranges from just a few kilowatts up to 1000 MW, though mini-hydro installations may be lower. The best performance is seen when the head height is between . Penstock diameters are between . The speeds of different turbine units range from 70 to 1000 rpm. A wicket gate around the outside of the turbine's rotating runner controls the rate of water flow through the turbine f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rupandehi District
Rupandehi District (; ), a part of Lumbini Province, is one of the seventy-seven districts of Nepal and covers an area of . The district headquarter is Bhairahawa. As per the national census 2011, the population of Rupandehi was 880,196. Etymology Rupandehi is named after Rupandevi temple which is situated in garden of Lumbini, where, the queen of King Suddhodana visited and give birth to Siddhartha Gautama Buddha. History Lumbini, birthplace of Buddha, lies in Rupandehi district. Devdaha, the birthplace of Mayadevi (mother of Buddha), also lies in Rupandehi district. Demographics At the time of the 2011 Nepal census, Rupandehi District had a population of 880,196 (432,193 male, 448,003 female) in 163,916 households. Ethnicity/caste: 15.9% were Hill Brahmin, 10.7% Magar, 9.7% Tharu, 8.3% Musalman, 7.4% Yadav, 6.8% Chhetri, 3.7% Chamar/Harijan/Ram, 3.1% Kami, 2.9% Lodh, 2.5% Kewat, 2.3% Kahar, 2.1% Newar, 2.0% Dhobi, 2.0% Gurung, 2.0% Kurmi, 2.0% Mallaha, 1.6% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China China–Nepal border, to the north, and India India–Nepal border, to the south, east, and west, while it is narrowly separated from Bangladesh by the Siliguri Corridor, and from Bhutan by the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Sikkim. Nepal has a Geography of Nepal, diverse geography, including Terai, fertile plains, subalpine forested hills, and eight of the world's ten List of highest mountains#List, tallest mountains, including Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth. Kathmandu is the nation's capital and List of cities in Nepal, its largest city. Nepal is a multi-ethnic, multi-lingual, multi-religious, and multi-cultural state, with Nepali language, Nepali as the official language. The name "Nepal" is first record ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odd Hoftun
Odd Hoftun (27 December 1927 – 15 March 2023) was a Norwegian engineer and missionary. Biography Hoftun was born in Ål to power station operator Erik Hoftun and schoolteacher Martha Indergaard. He was educated as electrical engineer from the Norwegian Institute of Technology, and subsequently worked at and ''Drammen’s elektrisitetsverk'' (electric power plant). From 1958 to 1995 he worked in Nepal, sent by HimalPartner. Hoftun's first assignment was to lead the construction of a Mission hospital in Tansen, for United Mission to Nepal (UMN). During the construction of the hospital Hoftun found that there was a lack of skilled workers in Nepal and he became the driving force establishing a vocational training centre in Butwal called Butwal Technical Institute (BTI), that opened in 1963. Hoftun was further a pioneer and key person in the early development of hydropower in Nepal, through ''Butwal Power Company Ltd.'', ''Himal Hydro Ltd.'', and ''Nepal Hydro and Electric ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butwal Power Company
Butwal (), officially Butwal Sub-Metropolitan City (), previously known as Khasyauli (Nepali: खस्यौली), is a sub-metropolitan city and economic hub in Lumbini Province in West Nepal. Butwal has a city population of 195,054 as per the 2021 AD Nepal census. The city is one of the tetra-cities of rapidly growing Butwal-Tilottama-Bhairahawa-Devdaha urban agglomeration primarily based on the Siddhartha Highway in West Nepal with a total urban agglomerated population of 4,74,541. It is one of the fastest-growing cities in Nepal for health, education, construction, communication, trade, and banking sectors. It has highway connections to the Indian border at Sunauli and to the hilly towns in Tansen and Pokhara valley, and holds the title of being "The Best City in Nepal" five times in a row. Geographically, Butwal is at the intersection of Nepal's two different National Highways, Mahendra Highway and Siddhartha Highway. It connects western Nepal with the capital Kathmandu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Power Stations In Nepal
As of 4 March 2025, Nepal's total installed electricity capacity is 3421.956 megawatts (MW). This includes 3255.806 MW from hydropower, 106.74 MW from solar, 53.41 MW from thermal, and 6 MW from Co-generation.https://myrepublica.nagariknetwork.com/news/nepal-s-electricity-production-capacity-tripled-to-3-157-mw-in-past-eight-years The following is a list of the power stations in Nepal. Hydroelectric stations Note: Dates before say 2040 are presumably Anno Domini and those after 2040 are Bikram Sambat. It would be useful for comparison purposes, and to enable sorting, for all the dates to be shown on the same calendar. Solar power stations Diesel power stations Co-generation plants Hydropower stations under construction Upcomming hydroelectricity projects Special projects Other power stations * Solar power stations ** Simikot 50 kW ** Gamgadhi 50 kW ** Dhobighat Oxidaizing Pond 680.4 kW, Owner:KUKL, Dedicated 11 kV feeder connecting to Tek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectric Power Stations In Nepal
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energy, renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of Low-carbon power, low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity Dams
A gravity dam is a dam constructed from concrete or stone masonry and designed to hold back water by using only the weight of the material and its resistance against the foundation. Gravity dams are designed so that each section of the dam is stable and independent of any other dam section. Characteristics Gravity dams generally require stiff rock foundations of high bearing strength (slightly weathered to fresh), although in rare cases, they have been built on soil. Stability of the dam primarily arises from the range of normal force angles viably generated by the foundation. Also, the stiff nature of a gravity dam structure endures differential foundation settlement poorly, as it can crack the dam structure. The main advantage to gravity dams over embankments is the scour-resistance of concrete, which protects against damage from minor over-topping flows. Unexpected large over-topping flows are still a problem, as they can scour dam foundations. A disadvantage of gravi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Run-of-the-river Power Stations
Run-of-river hydroelectricity (ROR) or run-of-the-river hydroelectricity is a type of hydroelectricity, hydroelectric generation plant whereby little or no water storage is provided. Run-of-the-river power plants may have no water storage at all or a limited amount of storage, in which case the storage reservoir is referred to as pondage. A plant without pondage is subject to seasonal river flows, so the plant will operate as an intermittent energy source. Conventional hydro uses reservoirs, which regulate water for flood control, dispatchable generation, dispatchable electrical power, and the provision of fresh water for agriculture. Concept Run-of-the-river, or ROR, hydroelectricity is considered ideal for streams or rivers that can sustain a minimum flow or those regulated by a lake or reservoir upstream. A small dam is usually built to create a headpond ensuring that there is enough water entering the penstock pipes that lead to the turbines, which are at a lower elevatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dams In Nepal
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aquaculture, and navigability. Hydropower is often used in conjunction with dams to generate electricity. A dam can also be used to collect or store water which can be evenly distributed between locations. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees (also known as Dike (construction), dikes) are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions. The word ''dam'' can be traced back to Middle English, and before that, from Middle Dutch, as seen in the names of many old cities, such as Amsterdam and Rotterdam. Ancient dams were built in Mesopotamia and the Middle East for water control. The earliest known dam is the Jawa Dam (Jordan), Jawa Dam in Jordan, dating t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |