|
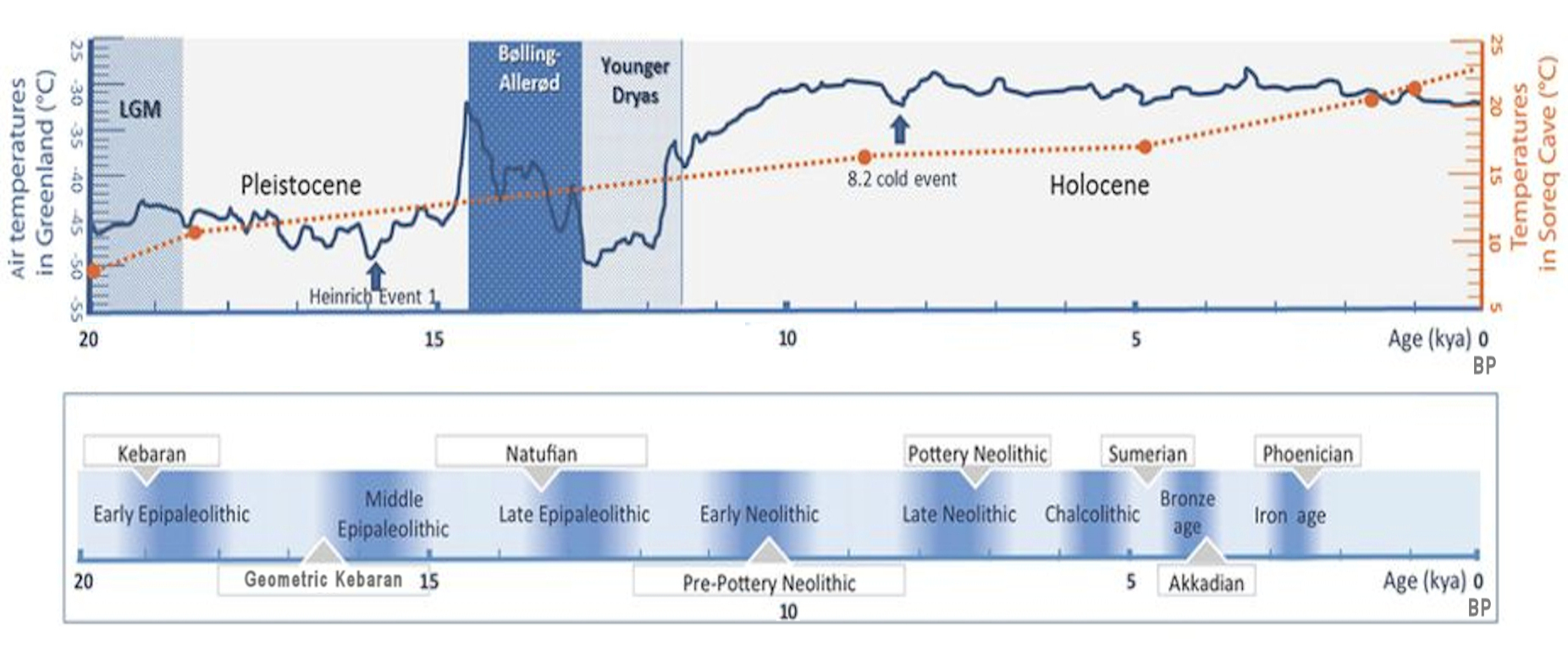
Timeline Of Middle Eastern History
This timeline tries to show dates of important historical events that happened in or that led to the rise of the Middle East/ South West Asia .The Middle East is the territory that comprises today's Egypt, the Persian Gulf states, Iran, Iraq, Israel and Palestine, Cyprus, Jordan, Lebanon, Oman, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. The Middle East, with its particular characteristics, was not to emerge until the late second millennium AD. To refer to a concept similar to that of today's Middle East but earlier in time, the term ancient Near East is used. This list is intended as a timeline of the history of the Middle East. For more detailed information, see articles on the histories of individual countries. See ancient Near East for ancient history of the Middle East. Paleolithic period * 16000 BC – Kebaran period * 13050 to 7050 BC – Natufian culture * 14400 BC – The world's oldest evidence of bread-making has been found at Shubayqa 1, in Jord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq. The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western European nations in the early 20th century as a replacement of the term Near East (both were in contrast to the Far East). The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions. Since the late 20th century, it has been criticized as being too Eurocentrism, Eurocentric. The region includes the vast majority of the territories included in the closely associated definition of West Asia, but without the South Caucasus. It also includes all of Egypt (not just the Sinai Peninsula, Sinai) and all of Turkey (including East Thrace). Most Middle Eastern countries (13 out of 18) are part of the Arab world. The list of Middle Eastern countries by population, most populous countries in the region are Egypt, Turkey, and Iran, whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was home to many cradles of civilization, spanning Mesopotamia, Egypt, Iran (or Persia), Anatolia and the Armenian highlands, the Levant, and the Arabian Peninsula. As such, the fields of ancient Near East studies and Near Eastern archaeology are one of the most prominent with regard to research in the realm of ancient history. Historically, the Near East denoted an area roughly encompassing the centre of West Asia, having been focused on the lands between Greece and Egypt in the west and Iran in the east. It therefore largely corresponds with the modern-day geopolitical concept of the Middle East. The history of the ancient Near East begins with the rise of Sumer in the 4th millennium BC, though the date that it ends is a subject of debate among scholars; the term covers the region's developments in the Bronze Age and the Iron Age, and is variously considered to end with either the establishment of the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC, the establi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shepherd Neolithic
Shepherd Neolithic is a name given by archaeologists to a style (or industry) of small flint tools from the Hermel plains in the north Beqaa Valley, Lebanon.Fleisch, Henri., Les industries lithiques récentes de la Békaa, République Libanaise, Acts of the 6th C.I.S.E.A., vol. XI, no. 1. Paris, 1960. The Shepherd Neolithic industry has been insufficiently studied and was provisionally named based on a limited typology collected by Jesuit archaeologist "Père" Henri Fleisch. Lorraine Copeland and Peter J. Wescombe suggested it was possibly ''"of quite late date"''. Characteristics Shepherd Neolithic material can be found dispersed over a wide area of the north Beqaa Valley in low concentrations. M. Billaux and Henri Fleisch suggested that the flints were of a higher quality than the brittle flint in the nearby conglomerates indicating origin from elsewhere. Three groups of flint could be determined; light brown, red-brown and that varied but was usually grey-chocolat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunter Gatherers
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, especially wild edible plants but also insects, fungi, honey, bird eggs, or anything safe to eat, or by hunting game (pursuing or trapping and killing wild animals, including catching fish). This is a common practice among most vertebrates that are omnivores. Hunter-gatherer societies stand in contrast to the more sedentary agricultural societies, which rely mainly on cultivating crops and raising domesticated animals for food production, although the boundaries between the two ways of living are not completely distinct. Hunting and gathering was humanity's original and most enduring successful competitive adaptation in the natural world, occupying at least 90 percent of human history. Following the invention of agriculture, hunter-gatherers who d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netiv HaGdud
Netiv HaGdud () is an Israeli settlement organized as a moshav in the West Bank.Netiv HaGdud Bik'at HaYarden Regional Council Located in the Jordan Valley around twenty kilometres north of , it falls under the jurisdiction of Bik'at HaYarden Regional Council. In it had a population of . The international community considers Israeli settlements in the West Bank [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emmer Wheat
Emmer is a hybrid species of wheat, producing edible seeds that have been used as food since ancient times. The domesticated types are ''Triticum turgidum'' subsp. ''dicoccum'' and ''T. t. ''conv.'' durum''. The wild plant is called ''T. t.'' subsp. ''dicoccoides''. The seeds have an awned covering, the sharp spikes helping the seeds to become buried in the ground. The principal difference between the wild and the domestic forms is that the ripened seed head of the wild plant shatters and scatters the seed onto the ground, while in the domesticated emmer, the seed head remains intact, thus making it easier for people to harvest the grain. Along with einkorn, emmer was one of the first crops domesticated in the Near East. It was widely cultivated in the ancient world, but is now a relict crop in mountainous regions of Europe and Asia. Emmer is one of the three grains called farro in Italy. Etymology Emmer is first attested in 1908 in English as a loanword from German , v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean Sea to the west, the Turkish Straits to the northwest, and the Black Sea to the north. The eastern and southeastern limits have been expanded either to the entirety of Asiatic Turkey or to an imprecise line from the Black Sea to the Gulf of Alexandretta. Topographically, the Sea of Marmara connects the Black Sea with the Aegean Sea through the Bosporus and the Dardanelles, and separates Anatolia from Thrace in Southeast Europe. During the Neolithic, Anatolia was an early centre for the development of farming after it originated in the adjacent Fertile Crescent. Beginning around 9,000 years ago, there was a major migration of Anatolian Neolithic Farmers into Neolithic Europe, Europe, with their descendants coming to dominate the continent a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Göbekli Tepe
Göbekli Tepe (, ; Kurdish: or , 'Wish Hill') is a Neolithic archaeological site in Upper Mesopotamia (''al-Jazira'') in modern-day Turkey. The settlement was inhabited from around to at least , during the Pre-Pottery Neolithic. It is famous for its large circular structures that contain massive stone pillarsamong the world's oldest known megaliths. Many of these pillars are decorated with anthropomorphic details, clothing, and sculptural reliefs of wild animals, providing archaeologists rare insights into prehistoric religion and the particular iconography of the period. The high, tell is densely covered with ancient domestic structures and other small buildings, quarries, and stone-cut cisterns from the Neolithic, as well as some traces of activity from later periods. The site was first used at the dawn of the southwest Asian Neolithic period, which marked the appearance of the oldest permanent human settlements anywhere in the world. Prehistorians link this Neolith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Pottery Neolithic A
Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (PPNA) denotes the first stage of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, in early Levantine and Anatolian Neolithic culture, dating to years ago, that is, 10,000–8800 BCE. Archaeological remains are located in the Levantine and Upper Mesopotamian region of the Fertile Crescent. The time period is characterized by tiny circular mud-brick dwellings, the cultivation of crops, the hunting of wild game, and unique burial customs in which bodies were buried below the floors of dwellings. The Pre-Pottery Neolithic A and the following Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (PPNB) were originally defined by Kathleen Kenyon in the type site of Jericho, State of Palestine. During this time, pottery was not yet in use. They precede the ceramic Neolithic Yarmukian culture. PPNA succeeds the Natufian culture of the Epipalaeolithic Near East. Settlements PPNA archaeological sites are much larger than those of the preceding Natufian hunter-gatherer culture, and contain traces of commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Carmel
Mount Carmel (; ), also known in Arabic as Mount Mar Elias (; ), is a coastal mountain range in northern Israel stretching from the Mediterranean Sea towards the southeast. The range is a UNESCO biosphere reserve. A number of towns are situated there, most notably Haifa, Israel's third largest city, located on the northern and western slopes. Etymology The word ''karmel'' ("garden-land") has been explained as a compound of ''kerem'' and ''el'' meaning "vineyard of El (deity), God" or a clipping of ''kar male,'' meaning "full kernel." Martin Jan Mulder suggested a third etymology, that of ''kerem + l'' with a lamed wiktionary:sufformative, sufformative, meaning only "vineyard", but this is considered unlikely as evidence for the existence of a lamed sufformative is weak. In Song of Songs 7:6, ''karmel'' is generally interpreted as a color, perhaps "crimson" or "yellow". suggests connecting it to the yellow "''karmel'' lily" mentioned by the Jerusalem Talmudy. Sukkah 3:6) in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natufian
The Natufian culture ( ) is an archaeological culture of the late Epipalaeolithic Near East in West Asia from 15–11,500 Before Present. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentism, sedentary or semi-sedentary population even before the Origins of agriculture in West Asia, introduction of agriculture. Natufian communities may be the ancestors of the builders of the region's first List of Neolithic settlements, Neolithic settlements, which may have been the earliest in the world. Some evidence suggests deliberate cultivation of cereals, specifically rye, by the Natufian culture at Tell Abu Hureyra, the site of the earliest evidence of agriculture in the world. The world's oldest known evidence of the production of bread-like foodstuff has been found at Shubayqa 1, a 14,400-year-old site in Jordan, Jordan's northeastern desert, 4,000 years before the Origins of agriculture in West Asia, emergence of agriculture in Southwest Asia. In addition, the oldest known evidence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kebaran
The Kebaran culture, also known as the 'Early Near East Epipalaeolithic', is an archaeological culture of the Eastern Mediterranean dating to c. 23,000 to 15,000 Before Present (BP). Its type site is Kebara Cave, south of Haifa. The Kebaran was produced by a highly mobile nomadic population, composed of hunters and gatherers in the Levant and Sinai areas who used microlithic tools. Overview The Kebaran is the first phase of the Epipalaeolithic in the Levant. Kebaran stone tool assemblages are characterized by small, geometric microliths, and are thought to have lacked the specialized grinders and pounders found in later Near Eastern cultures. Small stone tools called microliths and retouched bladelets can be found for the first time. The microliths of this culture period differ greatly from the Aurignacian artifacts. The Kebaran is preceded by the final phase of the Upper Paleolithic Levantine Aurignacian (also known as the Athlitian or Antelian) and followed by the pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |