|
Tianwen-3
''Tianwen-3'' is a planned interplanetary mission by China to send two spacecrafts (an orbiter/Earth-returner and a lander/ascent-vehicle) via two separate launches to Mars. Together, the two spacecrafts will seek to obtain samples of Martian rocks and soil and then return the cached samples to Earth. Overview In summer 2022 during a deep space exploration technology forum held at Nanjing University, Sun Zezhou, chief designer of the Tianwen-1 mission, detailed plans for a Mars sample-return mission based on a two-launch architecture. The mission, which appears to have the backing of senior government and space-industry authorities, is known as "Tianwen-3" and constitutes part of the Tianwen series of space missions. The current mission architecture envisions two launches during 2028 by the Long March 5 carrier rocket. One launch occurring in November 2028 will send an orbiter/return-vehicle on a " Trans Mars Injection" trajectory; this spacecraft is anticipated to enter Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2028 In Spaceflight
This article documents expected notable spaceflight events during the 2020s. Overview The trend towards cost reduction in access to orbit is expected to continue. In 2022, SpaceX plans to launch its new fully reusable Starship to orbit and Vulcan is planned to replace its more expensive predecessors. Ariane 6 is expected to replace the more expensive Ariane 5 in 2023, and Blue Origin plans to launch the maiden flight of New Glenn with a reusable first stage in early 2023. Mars stays a focus for missions to other planets, with three missions launched in 2020 (by China, the United Arab Emirates and the United States) and at least two missions planned for 2024 (India and Japan). In 2028, as part of the NASA-ESA Mars Sample Return mission, NASA plans to launch a Sample Retrieval Lander. In 2027, ESA plans to launch the Earth Return Orbiter, which will transport the retrieved samples from Mars to Earth by 2033. China is also planning to retrieve samples from Mars by 2031. N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
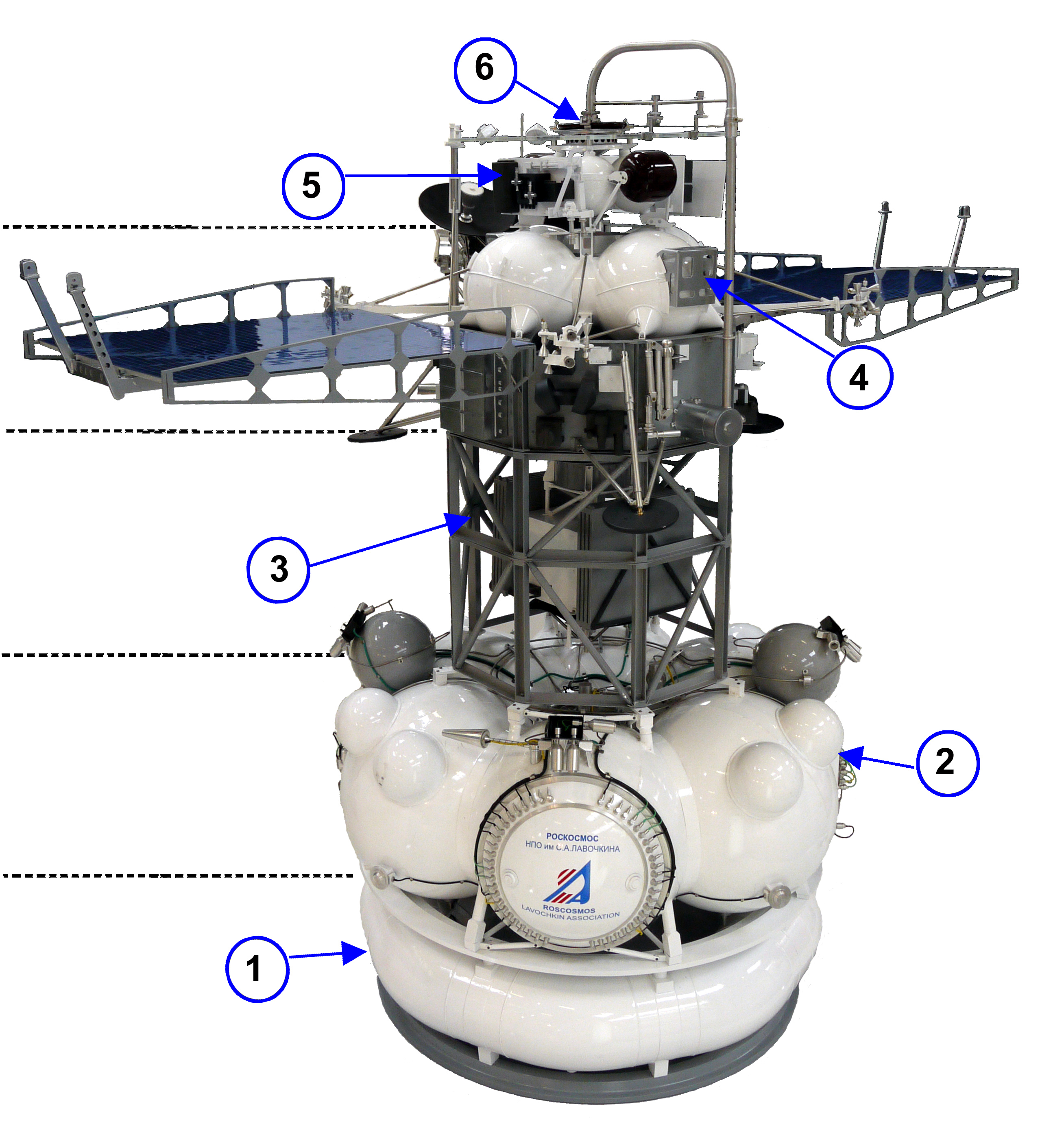
Mars Sample-return Mission
A Mars sample-return (MSR) mission is a proposed mission to collect rock and dust samples on Mars and return them to Earth. Such a mission would allow more extensive analysis than that allowed by onboard sensors. The three most recent concepts are a NASA–ESA proposal, a CNSA proposal, Tianwen-3, and a Roscosmos proposal, Mars-Grunt. Although NASA and ESA's plans to return the samples to Earth are still in the design stage as of 2022, samples have been gathered on Mars by the '' Perseverance'' rover. Risks of cross-contamination of the Earth biosphere from returned Martian samples have been raised, though the risk of this occurring is considered to be extremely low. Scientific value Once returned to Earth, stored samples can be studied with the most sophisticated science instruments available. Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for science at NASA Headquarters in Washington, expect such studies to allow several new discoveries at many fields. Samples may be rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tianwen-4
''Tianwen-4'' is a planned interplanetary mission by China to study the Jovian system and its environs, sharing a launch with a spacecraft which will make a flyby of Uranus. Prior to its naming as ''Tianwen-4'', the mission was known as ''Gan De''. Overview The goals of the planned ''Tianwen-4'' Jupiter mission were detailed in an article published in a Chinese academic journal, they include the following: study of the interaction between magnetic fields and plasma present in the Jovian system, examination of the compositional variations in the Jovian atmosphere, exploration of the internal structures and surface characteristics of either Ganymede or Callisto, as well as investigation of the space environment surrounding the aforementioned Galilean satellites. According to reports in the Western media, there are two competing mission profiles as of January 2021: the 'Jupiter Callisto Orbiter' (JCO) and the 'Jupiter System Observer' (JSO). 'JCO' would involve a spacecraft con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sample-return Mission
A sample-return mission is a spacecraft mission to collect and return samples from an extraterrestrial location to Earth for analysis. Sample-return missions may bring back merely atoms and molecules or a deposit of complex compounds such as loose material and rocks. These samples may be obtained in a number of ways, such as soil and rock excavation or a collector array used for capturing particles of solar wind or cometary debris. Nonetheless, concerns have been raised that the return of such samples to planet Earth may endanger Earth itself. To date, samples of Moon rock from Earth's Moon have been collected by robotic and crewed missions, the comet Wild 2 and the asteroids 25143 Itokawa and 162173 Ryugu have been visited by robotic spacecraft which returned samples to Earth, and samples of the solar wind have been returned by the robotic ''Genesis'' mission. Samples from the asteroid 101955 Bennu are en route back to Earth and are expected to arrive in September 2023. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary Exploration Of China
The Planetary Exploration of China (PEC; ), also known as Tianwen (), is the Robotic spacecraft, robotic interplanetary spaceflight program conducted by the China National Space Administration (CNSA). The program aims to explore planets of the Solar System, starting from Mars, and will be expanded to Jupiter and more in the future. The program was initially known as the Mars mission of China at the early stage. It was later announced as Planetary Exploration of China in April 2020. The series of missions was named ''Tianwen''. The first mission of the program, Tianwen-1 Mars exploration mission, began on July 23, 2020. A spacecraft, which consisted of an orbiter, a lander, and a rover, was launched by a Long March 5 rocket from Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site, Wenchang. The Tianwen-1 was inserted into orbit of Mars, Mars orbit in February 2021 after a seven-month journey, followed by a successful soft landing (aeronautics), soft landing of the lander and Zhurong (rover), ''Zhuron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tianwen-2
''Tianwen-2'', formerly known as ''ZhengHe'', is a planned Chinese asteroid sample-return and comet exploration mission that is currently under development. Overview ''Tianwen-2'' is planned to be launched by a Long March 3B rocket around 2025. It will use solar electric propulsion to explore the co-orbital near-Earth asteroid 469219 Kamoʻoalewa and the main-belt comet 311P/PANSTARRS. The spacecraft will rendezvous with Kamoʻoalewa and conduct remote sensing observations in orbit, before landing on the asteroid to collect a sample of of regolith. A nano-orbiter and nano-lander will be deployed to conduct remote sensing and sampling observations, and explosives will be used to expose potential subsurface volatiles for detection. The spacecraft will use both anchor-and-attach and touch-and-go methods to attempt collection of a sample from the asteroid. It would be the first time an anchor-and-attach method has been used on an asteroid, as both OSIRIS-REx and ''Hayabusa2'' u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missions To Mars
This is a list of the 50 spacecraft missions (including unsuccessful ones) relating to the planet Mars, such as orbiters and rovers. Missions ;Mission Type Legend: Mars landing locations There are a number of derelict orbiters around Mars whose location is not known precisely; there is a proposal to search for small moons, dust rings, and old orbiters with the Optical Navigation Camera on the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter''. There should be 8 derelict Mars orbiters barring unforeseen events if they have not decayed as of 2016. One example is Mariner 9, which entered Mars orbit in 1971 and is expected to remain in orbit until approximately 2022, when the spacecraft is projected to enter the Martian atmosphere and either burn up or crash into the planet's surface. The Viking 1 orbiter is predicted not to decay until at least 2019. One orbiter that is confirmed to have undergone Mars atmospheric entry is Mars Climate Orbiter. Timeline Future missions In development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere (less than 1% that of Earth's), and has a crust primarily composed of elements similar to Earth's crust, as well as a core made of iron and nickel. Mars has surface features such as impact craters, valleys, dunes and polar ice caps. It has two small and irregularly shaped moons, Phobos and Deimos. Some of the most notable surface features on Mars include Olympus Mons, the largest volcano and highest known mountain in the Solar System and Valles Marineris, one of the largest canyons in the Solar System. The Borealis basin in the Northern Hemisphere covers approximately 40% of the planet and may be a large impact feature. Days and seasons on Mars are comparable to those of Earth, as the planets have a similar rotation period a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wenchang Space Launch Site
The Wenchang Space Launch Site ( zh, 文昌航天发射场, links=no), located in Wenchang, Hainan, China, is a rocket launch site — one of the two spacecraft launch sites of Xichang Satellite Launch Center (the other site is in Xichang, Sichuan). It is a former suborbital test center. It is China's fourth and southernmost space vehicle launch facility ( spaceport). It has been specially selected for its low latitude, which is only 19° north of the equator, allowing for the increase in payload necessary for launching China's future space station. It is capable of launching the Long March 5, currently the most powerful Chinese rocket. Unlike the space centers on the mainland, whose rail tracks are too narrow to transport the new five meter core boosters, Wenchang uses its sea port for deliveries. Initial launches of the CZ-5 booster from Wenchang were expected to start in 2014, one year after the intended commissioning of the Wenchang Launch Site. However, the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China National Space Administration
China National Space Administration (CNSA; ) is the government agency of the People's Republic of China that is responsible for civil space administration and international space cooperation, including organizing or leading foreign exchanges and cooperation in the aerospace field. An administrative agency under the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, its headquarters are located in Haidian, Beijing. Founded in 1993, CNSA has pioneered a number of achievements in space for China despite its relatively short history, including becoming the first space agency to land on the far side of the Moon with Chang'e 4, bringing material back from the Moon with Chang'e 5, and being the second agency who successfully landed a rover on Mars with Tianwen-1. As the governing body of civil space activities, China National Space Administration does not execute any space program. The China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation executes China's state space programs instead. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tianwen-1
-1 (TW-1; zh, t=, s=, l=' Heavenly Questions') is an interplanetary mission by the China National Space Administration (CNSA) which sent a robotic spacecraft to Mars, consisting of 6 spacecraft: an orbiter, two deployable cameras, lander, remote camera, and the ' rover. The spacecraft, with a total mass of nearly five tons, is one of the heaviest probes launched to Mars and carries 14 scientific instruments. It is the first in a series of planned missions undertaken by CNSA as part of its Planetary Exploration of China program. The mission's scientific objectives include: investigation of Martian surface geology and internal structure, search for indications of current and past presence of water, and characterization of the space environment and the atmosphere of Mars. The mission was launched from the Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site on 23 July 2020 on a Long March 5 heavy-lift launch vehicle. After seven months of transit through the inner Solar System, the spacecraft e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)