|
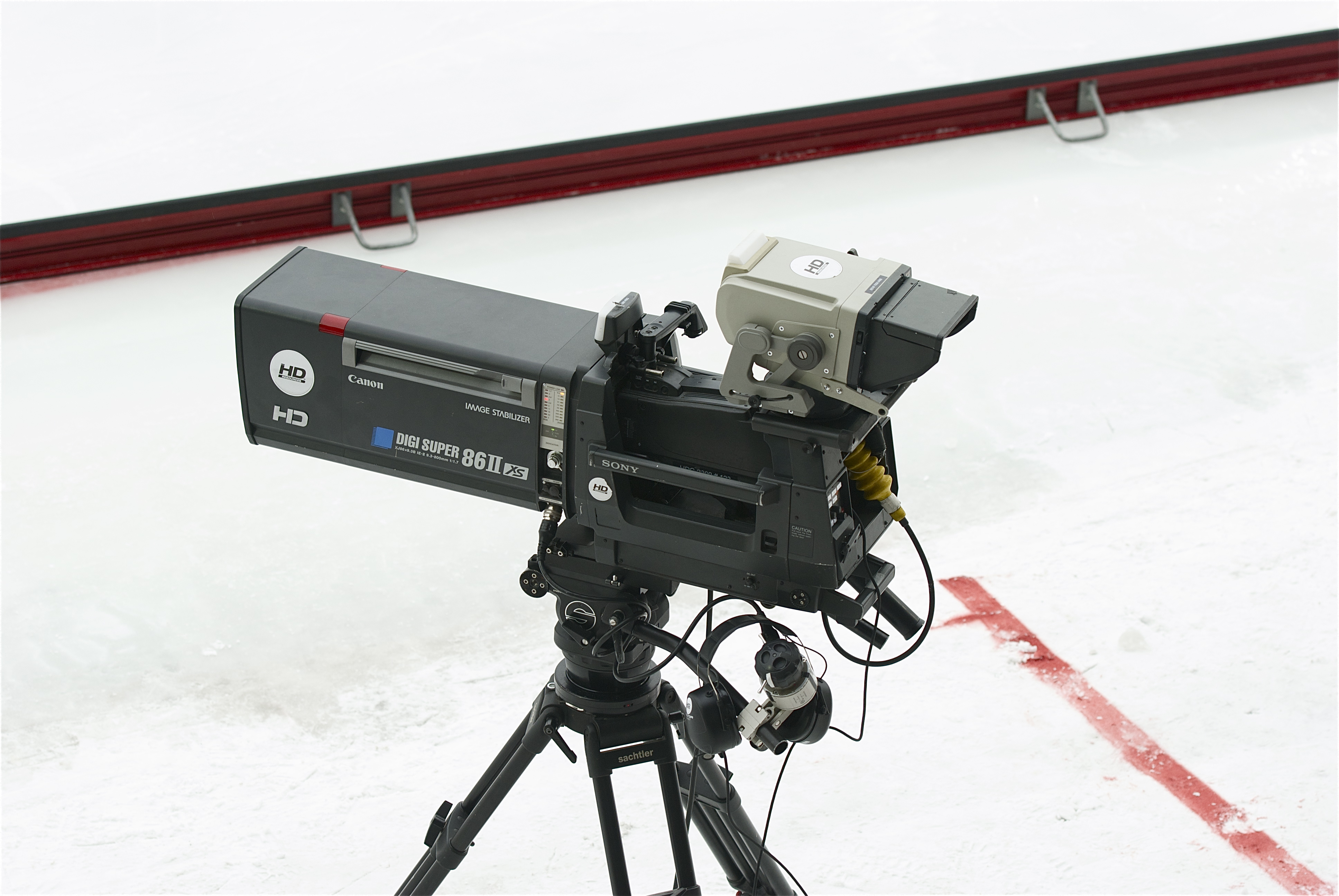
Three-CCD Camera
A three-CCD (3CCD) camera is a camera whose imaging system uses three separate charge-coupled devices (CCDs), each one receiving filtered red, green, or blue color ranges. Light coming in from the lens is split by a beam-splitter prism into three beams, which are then filtered to produce colored light in three color ranges or "bands". The system is employed by high quality still cameras, telecine systems, professional video cameras and some prosumer video cameras. Overview Compared to cameras with only one CCD, three-CCD cameras generally provide superior image quality by using full-frame dichroic filters to better separate the red, green and blue color bands, and better low-light performance. By separating red, green, and blue color ranges with a 1:1 pixel ratio (known as "4:4:4"), three-CCD cameras achieve much better precision than single-CCD cameras. In contrast, almost all single-CCD cameras use a Bayer filter A Bayer filter mosaic is a color filter array (CFA) f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Separation Prism
Color (or colour in Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is the visual perception based on the electromagnetic spectrum. Though color is not an inherent property of matter, color perception is related to an object's light absorption, emission, reflection and transmission. For most humans, colors are perceived in the visible light spectrum with three types of cone cells (trichromacy). Other animals may have a different number of cone cell types or have eyes sensitive to different wavelengths, such as bees that can distinguish ultraviolet, and thus have a different color sensitivity range. Animal perception of color originates from different light wavelength or spectral sensitivity in cone cell types, which is then processed by the brain. Colors have perceived properties such as hue, colorfulness (saturation), and luminance. Colors can also be additively mixed (commonly used for actual light) or subtractively mixed (commonly used for materials). If the colors a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Professional Video Camera
A professional video camera (often called a television camera even though its use has spread beyond television) is a high-end device for creating electronic moving images (as opposed to a movie camera, that earlier recorded the images on film). Originally developed for use in television studios or with outside broadcast trucks, they are now also used for music videos, direct-to-video movies (see digital movie camera), corporate and educational videos, wedding videos, among other uses. Since the 2000s, most professional video cameras are digital (instead of analog). The distinction between professional video cameras and movie cameras narrowed as HD digital video cameras with sensors the same size as 35mm movie cameras - plus dynamic range ( exposure latitude) and color rendition approaching film quality - were introduced in the late 2010s. Nowadays, HDTV cameras designed for broadcast television, news, sports, events and other works such as reality TV are termed as professional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thin-film Optics
Thin-film optics is the branch of optics that deals with very thin structured layers of different materials. In order to exhibit thin-film optics, the thickness of the layers of material must be similar to the coherence length; for visible light it is most often observed between 200 and 1000 nm of thickness. Layers at this scale can have remarkable reflective properties due to light wave interference and the difference in refractive index between the layers, the air, and the substrate. These effects alter the way the optic reflects and transmits light. This effect, known as thin-film interference, is observable in soap bubbles and oil slicks. More general periodic structures, not limited to planar layers, exhibit structural coloration with more complex dependence on angle, and are known as photonic crystals. In manufacturing, thin film layers can be achieved through the deposition of one or more thin layers of material onto a substrate (usually glass). This is most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayer Filter
A Bayer filter mosaic is a color filter array (CFA) for arranging RGB color model, RGB color filters on a square grid of photosensors. Its particular arrangement of color filters is used in most single-chip digital image sensors used in digital cameras, and camcorders to create a color image. The filter pattern is half green, one quarter red and one quarter blue, hence is also called BGGR, RGBG, GRBG, or RGGB. It is named after its inventor, Bryce Bayer of Eastman Kodak. Bayer is also known for his recursively defined matrix used in ordered dithering. color image sensor, Alternatives to the Bayer filter include both #Modifications, various modifications of colors and arrangement and completely different technologies, such as color co-site sampling, the Foveon X3 sensor, the dichroic filter, dichroic mirrors or a transparent diffractive-filter array. Explanation Bryce Bayer's patent (U.S. Patent No. 3,971,065) in 1976 called the green photosensors ''luminance-sensitive eleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichroic Filter
In optics, a dichroic material is either one which causes visible light to be split up into distinct beams of different wavelengths (colours) (not to be confused with dispersion), or one in which light rays having different polarizations are absorbed by different amounts. In beam splitters The original meaning of ''dichroic'', from the Greek ''dikhroos'', two-coloured, refers to any optical device which can split a beam of light into two beams with differing wavelengths. Such devices include mirrors and filters, usually treated with optical coatings, which are designed to reflect light over a certain range of wavelengths and transmit light which is outside that range. An example is the dichroic prism, used in some camcorders, which uses several coatings to split light into red, green and blue components for recording on separate CCD arrays, however it is now more common to have a Bayer filter to filter individual pixels on a single CCD array. This kind of dichroic device doe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Quality
Image quality can refer to the level of accuracy with which different imaging systems capture, process, store, compress, transmit and display the signals that form an image. Another definition refers to image quality as "the weighted combination of all of the visually significant attributes of an image". The difference between the two definitions is that one focuses on the characteristics of signal processing in different imaging systems and the latter on the perceptual assessments that make an image pleasant for human viewers. Image quality should not be mistaken with image fidelity. Image fidelity refers to the ability of a process to render a given copy in a perceptually similar way to the original (without distortion or information loss), i.e., through a digitization or conversion process from analog media to digital image. The process of determining the level of accuracy is called Image Quality Assessment (IQA). Image quality assessment is part of the quality of experience ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Camera
A video camera is an optical instrument that captures videos, as opposed to a movie camera, which records images on film. Video cameras were initially developed for the television industry but have since become widely used for a variety of other purposes. Video cameras are used primarily in two modes. The first, characteristic of much early broadcasting, is live television, where the camera feeds real time images directly to a screen for immediate observation. A few cameras still serve live television production, but most live connections are for security, military/tactical, and industrial operations where surreptitious or remote viewing is required. In the second mode the images are recorded to a storage device for archiving or further processing; for many years, videotape was the primary format used for this purpose, but was gradually supplanted by optical disc, hard disk, and then flash memory. Recorded video is used in television production, and more often surveillance and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosumer
A prosumer is an individual who both consumes and produces. The term is a portmanteau of the words '' producer'' and ''consumer''. Research has identified six types of prosumers: DIY prosumers, self-service prosumers, customizing prosumers, collaborative prosumers, monetised prosumers, and economic prosumers. The terms ''prosumer'' and ''prosumption'' were coined in 1980 by Alvin Toffler, an American futurist, and were widely used by many technology writers of the time. Technological breakthroughs and a rise in user participation blurs the line between production and consumption activities, with the consumer becoming a prosumer. Definitions and contexts Prosumers have been defined as "individuals who consume and produce value, either for self-consumption or consumption by others, and can receive implicit or explicit incentives from organizations involved in the exchange." The term has since come to refer to a person using commons-based peer production. In the digital and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecine
Telecine ( or ), or TK, is the process of transferring film into video and is performed in a color suite. The term is also used to refer to the equipment used in this post-production process. Telecine enables a motion picture, captured originally on film stock, to be viewed with standard video equipment, such as television sets, video cassette recorders (VCR), DVD-Video, DVD, Blu-ray or computers. Initially, this allowed television broadcasters to produce programs using film, usually 16 mm film, 16-mm stock, but transmit them in the same format, and quality, as other forms of television production. Furthermore, telecine allows film producers, television producers and film distributors working in the film industry to release their productions on video and allows producers to use video production equipment to complete their filmmaking projects. Within the film industry, it is also referred to as a ''TK'', ''TC'' having already been used to designate timecode. Motion picture fil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Still Camera
A camera is an instrument used to capture and store images and videos, either digitally via an electronic image sensor, or chemically via a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. As a pivotal technology in the fields of photography and videography, cameras have played a significant role in the progression of visual arts, media, entertainment, surveillance, and scientific research. The invention of the camera dates back to the 19th century and has since evolved with advancements in technology, leading to a vast array of types and models in the 21st century. Cameras function through a combination of multiple mechanical components and principles. These include exposure control, which regulates the amount of light reaching the sensor or film; the lens, which focuses the light; the viewfinder, which allows the user to preview the scene; and the film or sensor, which captures the image. Several types of camera exist, each suited to specific uses and offering unique cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichroic Prism
A dichroic prism is a prism (optics), prism that splits light into two beams of differing wavelength, wavelengths (colour). A trichroic prism assembly combines two dichroic prisms to split an image into 3 colours, typically as red, green and blue of the RGB colour model. They are usually constructed of one or more glass prisms with dichroism, dichroic optical coatings that selectively reflect or transmit light depending on the light's wavelength. That is, certain surfaces within the prism act as dichroic filters. These are used as beam splitters in many optical instruments. (See: Dichroism, for the etymology of the term.) Applications in camcorders or digital cameras One common application of dichroic prisms is in some camcorders and high-quality digital cameras. A ''trichroic prism assembly'' is a combination of two dichroic prisms which are used to split an image into red, green, and blue components, which can be separately detected on three charge-coupled device, CCD arrays. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |