|
Thomasin Von Zirclaere
Thomasin von Zirclaere, also called Thomasîn von Zerclaere or Tommasino Di Cerclaria (c. 1186 – c. 1235) was an Italian Middle High German lyric poet. The epic poem ''Der Wälsche Gast'' (original: ''Der welhische gast'', "The Romance stranger") is the only preserved work by him. Life Thomasin's ancestry remains obscure. The noble ''Cerclaria'' dynasty from Cividale was among the '' ministeriales'' in the Patria del Friuli (Patriarchate of Aquileia), an ecclesiastical Imperial State in Italy. From about 1206 he was a canon of the cathedral chapter under Patriarch Wolfger von Erla, the former Bishop of Passau, who had already been a patron of Walther von der Vogelweide and Albrecht von Johansdorf. The title ''wälsch/welsch'' (''walhaz'') refers to himself, as his mother tongue was Italian (or Friulian) and he apologizes in advance for any linguistic inadequacies. The poem has about 14,750 lines and is written in the Middle High German language with distinct Bavarian element ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Der Wälsche Gast - CPG389 F116r
Der or DER may refer to: Places * Darkənd, Azerbaijan * Dearborn (Amtrak station) (station code), in Michigan, US * Der (Sumer), an ancient city located in modern-day Iraq * d'Entrecasteaux Ridge, an oceanic ridge in the south-west Pacific Ocean Science and technology * Derivative chromosome, a structurally rearranged chromosome * Distinguished Encoding Rules, a method for encoding a data object, including public key infrastructure certificates and keys * Distributed Energy Resources * ∂, the partial derivative symbol * Derivation (differential algebra) on an algebra ''A'' over a field ''K'', the space (module) of which is denoted Der''K''(A) * Deep energy retrofit, an energy conservation measure Organizations * Digital Education Revolution, former Australian Government-funded educational reform program * DER rental (Domestic Electric Rentals Ltd), a UK television rentals company * Documentary Educational Resources, a non-profit film producer and distributor Other uses * De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friulian Language
Friulian ( ) or Friulan (natively or ; ; ; ) is a Romance languages, Romance language belonging to the Rhaeto-Romance languages, Rhaeto-Romance family. Friulian is spoken in the Friuli region of northeastern Italy and has around 600,000 speakers, the vast majority of whom also speak Italian language, Italian. It is sometimes called Eastern Ladin since it shares the same roots as Ladin language, Ladin, but over the centuries, it has diverged under the influence of surrounding languages, including German language, German, Italian language, Italian, Venetian language, Venetian, and Slovene language, Slovene. Documents in Friulian are attested from the 11th century and poetry and literature date as far back as 1300. By the 20th century, there was a revival of interest in the language. History A question that causes many debates is the influence of the Latin spoken in Aquileia and surrounding areas. Some claim that it had peculiar features that later passed into Friulian. Epigrap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th-century Italian Poets
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 (represented by the Roman numerals MCCI) through December 31, 1300 (MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched from Eastern Asia to Eastern Europe. The conquests of Hulagu Khan and other Mongol invasions changed the course of the Muslim world, most notably the Siege of Baghdad (1258) and the destruction of the House of Wisdom. Other Muslim powers such as the Mali Empire and Delhi Sultanate conquered large parts of West Africa and the Indian subcontinent, while Buddhism witnessed a decline through the conquest led by Bakhtiyar Khilji. The earliest Islamic states in Southeast Asia formed during this century, most notably Samudera Pasai. The Kingdoms of Sukhothai and Hanthawaddy would emerge and go on to dominate their surrounding territories. Europe entered the apex of the High Middle Ages, characterized by rapid legal, cultural, and religious evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1230s Deaths
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1180s Births , synthetic chemical element with atomic number 118
{{Numberdis ...
118 may refer to: *118 (number) *AD 118 *118 BC *118 (TV series) *118 (film) *118 (Tees) Corps Engineer Regiment *118 (Tees) Field Squadron, Royal Engineers *118 Peitho, a main-belt asteroid See also *11/8 (other) *Oganesson Oganesson is a synthetic element, synthetic chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Og and atomic number 118. It was first synthesized in 2002 at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) in Dubna, near Moscow, Russia, by a joint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberal Arts Education
Liberal arts education () is a traditional academic course in Western higher education. ''Liberal arts'' takes the term '' art'' in the sense of a learned skill rather than specifically the fine arts. ''Liberal arts education'' can refer to studies in a liberal arts degree course or to a university education more generally. Such a course of study contrasts with those that are principally vocational, professional, or technical, as well as religiously based courses. The term ''liberal arts'' for an educational curriculum dates back to classical antiquity in the West, but has changed its meaning considerably, mostly expanding it. The seven subjects in the ancient and medieval meaning came to be divided into the trivium of rhetoric, grammar, and logic, and the quadrivium of astronomy, arithmetic, geometry, and music. Since the late 1990s, major universities have gradually dropped the term ''liberal arts'' from their curriculum or created schools for liberal art disciplines to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scholasticism
Scholasticism was a medieval European philosophical movement or methodology that was the predominant education in Europe from about 1100 to 1700. It is known for employing logically precise analyses and reconciling classical philosophy and Catholic Christianity. The Scholastics, also known as Schoolmen, utilized dialectical reasoning predicated upon Aristotelianism and the categories (Aristotle), Ten Categories. Scholasticism emerged within the monastic schools that translated medieval Judeo-Islamic philosophies (800–1400), Judeo-Islamic philosophies, and "rediscovered" the Corpus Aristotelicum, collected works of Aristotle. Endeavoring to harmonize Aristotle's metaphysics (Aristotle), metaphysics and Latin Catholic theology, these monastic schools became the basis of the earliest European medieval university, medieval universities, and thus became the bedrock for the development of History of science, modern science and Western philosophy, philosophy in the Western world. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chivalry
Chivalry, or the chivalric language, is an informal and varying code of conduct that developed in Europe between 1170 and 1220. It is associated with the medieval Christianity, Christian institution of knighthood, with knights being members of various chivalric orders, and with knights' and gentlemen's behaviours which were governed by chivalrous social codes. The ideals of chivalry were popularized in medieval literature, particularly the literary cycles known as the Matter of France, relating to the legendary companions of Charlemagne and his men-at-arms, the paladins, and the Matter of Britain, informed by Geoffrey of Monmouth's , written in the 1130s, which popularized the legend of King Arthur and his knights of the Round Table. The code of chivalry that developed in medieval Europe had its roots in earlier centuries. It arose in the Carolingian Empire from the idealisation of the cavalryman—involving military bravery, individual training, and service to others—especia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minnesang
(; "love song") was a tradition of German lyric- and song-writing that flourished in the Middle High German period (12th to 14th centuries). The name derives from '' minne'', the Middle High German word for love, as that was ''Minnesang'''s main subject. People who wrote and performed ''Minnesang'' were known as ''Minnesänger'' (), and a single song was called a ''Minnelied'' (). The ''Minnesänger'' are comparable to the Occitan troubadours and northern French ''trouvères,'' but they are "an original German contribution to courtly lyric." Social status In the absence of reliable biographical information, there has been debate about the social status of the ''Minnesänger''. Some clearly belonged to the higher nobility – the 14th-century Codex Manesse includes songs by dukes, counts, kings, and the Emperor Henry VI. Some ''Minnesänger'', as indicated by the title ''Meister'' (master), were clearly educated commoners, such as Meister Konrad von Würzburg. It is thought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
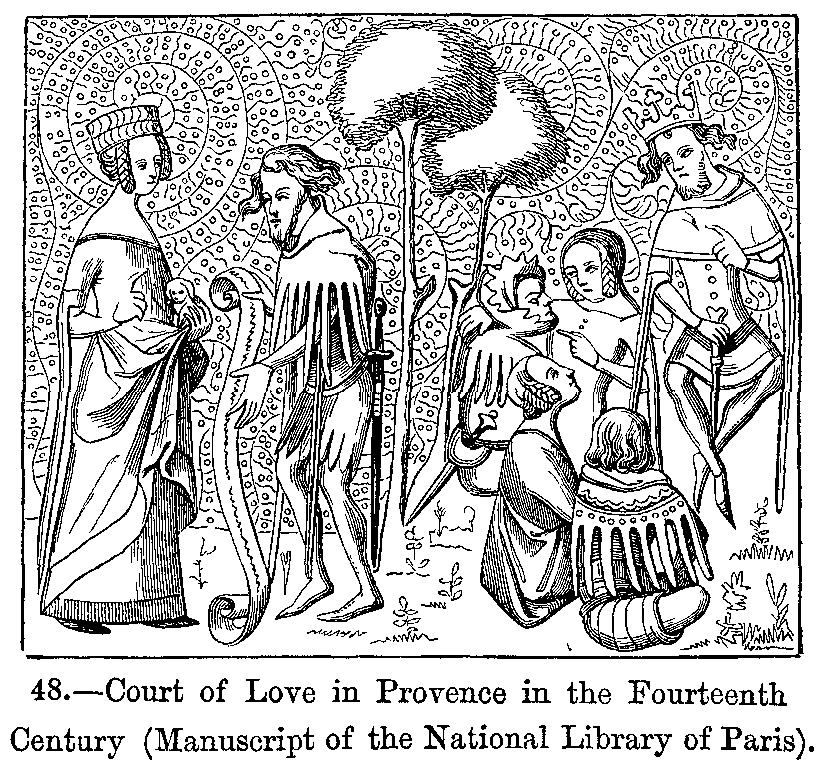
Courtly Love
Courtly love ( ; ) was a medieval European literary conception of love that emphasized nobility and chivalry. Medieval literature is filled with examples of knights setting out on adventures and performing various deeds or services for ladies because of their "courtly love". This kind of love was originally a literary fiction created for the entertainment of the nobility, but as time passed, these ideas about love spread to popular culture and attracted a larger literate audience. In the High Middle Ages, a "game of love" developed around these ideas as a set of social practices. "Loving nobly" was considered to be an enriching and improving practice. Courtly love began in the ducal and princely courts of Aquitaine, Provence, Champagne, ducal Burgundy and the Norman Kingdom of Sicily at the end of the eleventh century. In essence, courtly love was an experience between erotic desire and spiritual attainment, "a love at once illicit and morally elevating, passionate and disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courtesy
Courtesy (from the word , from the 12th century) is gentle politeness and courtly manners. In the Middle Ages in Europe, the behaviour expected of the nobility was compiled in courtesy books. History The apex of European courtly culture was reached in the Late Middle Ages and the Baroque period (i.e. roughly the four centuries spanning 1300–1700). The oldest courtesy books date to the 13th century, but they become an influential genre in the 16th, with the most influential of them being '' Il Cortegiano'' (1508), which not only covered basic etiquette and decorum but also provided models of sophisticated conversation and intellectual skill. The royal courts of Europe persisted well into the 18th century (and to some limited extent to the present day), but in the 18th century, the notion of ''courtesy'' was replaced by that of '' gallantry'', referring to an ideal emphasizing the display of affected sensitivity in direct contrast with the ideals of self-denial and dignif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miniature (illuminated Manuscript)
A miniature (from the Latin verb 'to colour with minium', a red lead) is a small illustration used to decorate an ancient or medieval illuminated manuscript; the simple illustrations of the early codices having been miniated or delineated with that pigment. The generally small scale of such medieval pictures has led to etymological confusion with minuteness and to its application to small paintings, especially portrait miniatures, which did however grow from the same tradition and at least initially used similar techniques. Apart from the Western, Byzantine and Armenian traditions, there is another group of Asian traditions, which is generally more illustrative in nature, and from origins in manuscript book decoration also developed into single-sheet small paintings to be kept in albums, which are also called miniatures, as the Western equivalents in watercolor and other media are not. These include Arabic miniatures, and their Persian, Mughal, Ottoman and other Indian of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |