|
Thomas Jech
Thomas J. Jech (, ; born 29 January 1944 in Prague) is a mathematician specializing in set theory who was at Penn State for more than 25 years. Life He was educated at Charles University (his advisor was Petr Vopěnka) and from 2000 is at thInstitute of Mathematicsof the Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic. Work Jech's research also includes mathematical logic, algebra, analysis, topology, and measure theory. Jech gave the first published proof of the consistency of the existence of a Suslin line. With Karel Prikry, he introduced the notion of precipitous ideal. He gave several models where the axiom of choice failed, for example one with ω1 measurable. The concept of a Jech–Kunen tree is named after him and Kenneth Kunen Herbert Kenneth Kunen (August 2, 1943August 14, 2020) was a professor of mathematics at the University of Wisconsin–Madison who worked in set theory and its applications to various areas of mathematics, such as set-theoretic topology a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its Prague metropolitan area, metropolitan area is home to approximately 2.3 million people. Prague is a historical city with Romanesque architecture, Romanesque, Czech Gothic architecture, Gothic, Czech Renaissance architecture, Renaissance and Czech Baroque architecture, Baroque architecture. It was the capital of the Kingdom of Bohemia and residence of several Holy Roman Emperors, most notably Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles IV (r. 1346–1378) and Rudolf II, Holy Roman Emperor, Rudolf II (r. 1575–1611). It was an important city to the Habsburg monarchy and Austria-Hungary. The city played major roles in the Bohemian Reformation, Bohemian and the Protestant Reformations, the Thirty Years' War and in 20th-century history a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
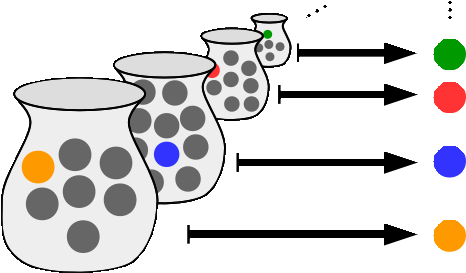
Precipitous Ideal
{{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Set Theorists
Set, The Set, SET or SETS may refer to: Science, technology, and mathematics Mathematics *Set (mathematics), a collection of elements *Category of sets, the category whose objects and morphisms are sets and total functions, respectively Electronics and computing *Set (abstract data type), a data type in computer science that is a collection of unique values ** Set (C++), a set implementation in the C++ Standard Library * Set (command), a command for setting values of environment variables in Unix and Microsoft operating-systems * Secure Electronic Transaction, a standard protocol for securing credit card transactions over insecure networks * Single-electron transistor, a device to amplify currents in nanoelectronics * Single-ended triode, a type of electronic amplifier * Set!, a programming syntax in the scheme programming language Biology and psychology * Set (psychology), a set of expectations which shapes perception or thought *Set or sett, a badger's den *Set, a small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
21st-century Czech Mathematicians
File:1st century collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Jesus is crucified by Roman authorities in Judaea (17th century painting). Four different men (Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian) claim the title of Emperor within the span of a year; The Great Fire of Rome (18th-century painting) sees the destruction of two-thirds of the city, precipitating the empire's first persecution against Christians, who are blamed for the disaster; The Roman Colosseum is built and holds its inaugural games; Roman forces besiege Jerusalem during the First Jewish–Roman War (19th-century painting); The Trưng sisters lead a rebellion against the Chinese Han dynasty (anachronistic depiction); Boudica, queen of the British Iceni leads a rebellion against Rome (19th-century statue); Knife-shaped coin of the Xin dynasty., 335px rect 30 30 737 1077 Crucifixion of Jesus rect 767 30 1815 1077 Year of the Four Emperors rect 1846 30 3223 1077 Great Fire of Rome rect 30 1108 1106 2155 Boudican revolt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Purpose: Because living persons may suffer personal harm from inappropriate information, we should watch their articles carefully. By adding an article to this category, it marks them with a notice about sources whenever someone tries to edit them, to remind them of WP:BLP (biographies of living persons) policy that these articles must maintain a neutral point of view, maintain factual accuracy, and be properly sourced. Recent changes to these articles are listed on Special:RecentChangesLinked/Living people. Organization: This category should not be sub-categorized. Entries are generally sorted by family name In many societies, a surname, family name, or last name is the mostly hereditary portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family. It is typically combined with a given name to form the full name of a person, although several give .... Maintenance: Individuals of advanced age (over 90), for whom there has been no new documentation in the last ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1944 Births
Events Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix. January * January 2 – WWII: ** Free France, Free French General Jean de Lattre de Tassigny is appointed to command First Army (France), French Army B, part of the Sixth United States Army Group in North Africa. ** Landing at Saidor: 13,000 US and Australian troops land on Papua New Guinea in an attempt to cut off a Japanese retreat. * January 8 – WWII: Philippine Commonwealth troops enter the province of Ilocos Sur in northern Luzon and attack Japanese forces. * January 11 ** United States President Franklin D. Roosevelt proposes a Second Bill of Rights for social and economic security, in his State of the Union address. ** The Nazi German administration expands Kraków-Płaszów concentration camp into the larger standalone ''Konzentrationslager Plaszow bei Krakau'' in occupied Poland. * January 12 – WWII: Winston Churchill and Charles de Gaulle begin a 2-day conference in Marrakech. * Janua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karel Hrbáček
Karel Hrbáček (born 1944) is professor emeritus of mathematics at City College of New York. He specializes in mathematical logic, set theory, and non-standard analysis. Early life and education Karel studied at Charles University with Petr Vopěnka, looking at large cardinal numbers. He was awarded the degree RNDr. Before his appointment at CCNY he was an exchange fellow at University of California, Berkeley and a research associate at Rockefeller University. In 1980 he received an award from the Mathematical Association of America for his article on Non-standard Set Theory. Selected publications * 1999: (with Thomas Jech) ''Introduction to Set Theory'', Third edition. Monographs and Textbooks in Pure and Applied Mathematics, 220. Marcel Dekker J. M. Henle (1985), Review of ''Introduction to set theory'', 2nd ed., . * 1992: (with David Ballard) "Standard foundations for nonstandard analysis", Journal of Symbolic Logic 57(2): 741–748 * 1979: "Nonstandard set theory", Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenneth Kunen
Herbert Kenneth Kunen (August 2, 1943August 14, 2020) was a professor of mathematics at the University of Wisconsin–Madison who worked in set theory and its applications to various areas of mathematics, such as set-theoretic topology and measure theory. He also worked on non-associative algebraic systems, such as loops, and used computer software, such as the Otter theorem prover, to derive theorems in these areas. Personal life Kunen was born in New York City New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ... in 1943 and died in 2020. He lived in Madison, Wisconsin, with his wife Anne, with whom he had two sons, Isaac and Adam. Education Kunen completed his undergraduate degree at the California Institute of Technology and received his Ph.D. in 1968 from Stanford ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jech–Kunen Tree
A Jech–Kunen tree is a set-theoretic tree with properties that are incompatible with the generalized continuum hypothesis. It is named after Thomas Jech and Kenneth Kunen, both of whom studied the possibility and consequences of its existence. Definition In set theory, a tree is a partially ordered set in which the predecessors of any element form a well-ordering. The height of any element is the order type of this well-ordering, and the height of the tree is the least ordinal number that exceeds the height of all elements. A ''branch'' of a tree is a maximal well-ordered subset. A ''ω''1-tree is a tree with cardinality \aleph_1 and height ''ω''1, where ''ω''1 is the first uncountable ordinal and \aleph_1 is the associated cardinal number. A Jech–Kunen tree is a ''ω''1-tree in which the number of branches is greater than \aleph_1 and less than 2^. Existence The generalized continuum hypothesis implies that there is no cardinal number between \aleph_1 and 2^; when this is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measurable Cardinal
In mathematics, a measurable cardinal is a certain kind of large cardinal number. In order to define the concept, one introduces a two-valued measure (mathematics), measure on a cardinal ''κ'', or more generally on any set. For a cardinal ''κ'', it can be described as a subdivision of all of its subsets into large and small sets such that ''κ'' itself is large, ∅ and all singleton (mathematics), singletons (with ''α'' ∈ ''κ'') are small, set complement, complements of small sets are large and vice versa. The intersection of fewer than ''κ'' large sets is again large. It turns out that uncountable cardinals endowed with a two-valued measure are large cardinals whose existence cannot be proved from ZFC. The concept of a measurable cardinal was introduced by Stanisław Ulam in 1930. Definition Formally, a measurable cardinal is an uncountable cardinal number ''κ'' such that there exists a ''κ''-additive, non-trivial, 0-1-valued measure (mathematics), measure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axiom Of Choice
In mathematics, the axiom of choice, abbreviated AC or AoC, is an axiom of set theory. Informally put, the axiom of choice says that given any collection of non-empty sets, it is possible to construct a new set by choosing one element from each set, even if the collection is infinite. Formally, it states that for every indexed family (S_i)_ of nonempty sets (S_i as a nonempty set indexed with i), there exists an indexed set (x_i)_ such that x_i \in S_i for every i \in I. The axiom of choice was formulated in 1904 by Ernst Zermelo in order to formalize his proof of the well-ordering theorem. The axiom of choice is equivalent to the statement that every partition has a transversal. In many cases, a set created by choosing elements can be made without invoking the axiom of choice, particularly if the number of sets from which to choose the elements is finite, or if a canonical rule on how to choose the elements is available — some distinguishing property that happens to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |