|
Thomas Haliburton
Thomas Chandler Haliburton (17 December 1796 – 27 August 1865) was a Nova Scotian politician, judge, and author who was the first international best-selling fiction author from what is now Canada, and who served as a Conservative Member of Parliament in England. He was the father of the British civil servant Lord Haliburton and of the anthropologist Robert Grant Haliburton. Life Thomas Chandler Haliburton was born on 17 December 1796, in Windsor, Nova Scotia, to William Hersey Otis Haliburton, a judge and politician, and Lucy Chandler Grant. His mother died when he was a small child. When Thomas was seven, his father married Susanna Davis, the daughter of Michael Francklin, who had been Nova Scotia's Lieutenant Governor. He attended University of King's College in Windsor, from which he graduated in 1815 to become a lawyer who practiced at Annapolis Royal. Between 1826 and 1829, Haliburton represented Annapolis County in the Nova Scotia House of Assembly. Haliburton's fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
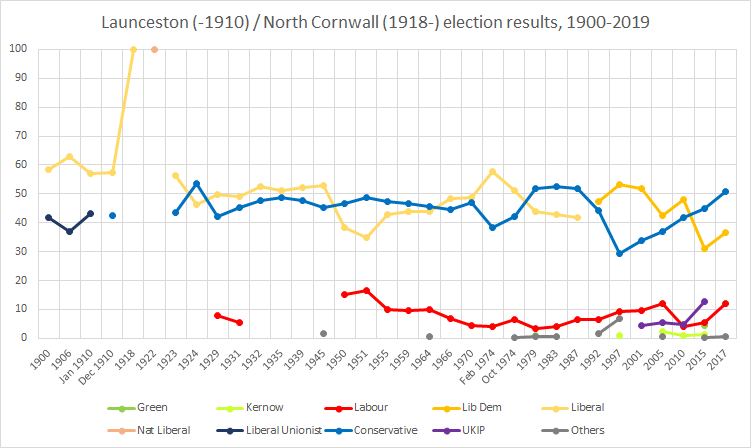
Launceston (UK Parliament Constituency)
Launceston, also known at some periods as Dunheved, was a parliamentary constituency in Cornwall which returned two Members of Parliament to the British House of Commons from 1295 until 1832, and one member from 1832 until 1918. It was a parliamentary borough until 1885, and a county constituency thereafter. Boundaries 1832–1885: The old Borough of Launceston and the Parish of St Stephen, and all such parts of the several Parishes of Lawhitton, St Thomas the Apostle, and South Petherwin as are without the old Borough of Launceston. 1885–1918: The Sessional Division of East Middle, East North, Lesnewth, and Stratton, and part of the Sessional Division of Trigg. History Launceston was one of 21 parliamentary boroughs in Cornwall between the 16th and 19th centuries; unlike many of these, which had been little more than villages even when established and were rotten boroughs from the start, Launceston, Cornwall, Launceston had been a town of reasonable size and importance th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Author
In legal discourse, an author is the creator of an original work that has been published, whether that work exists in written, graphic, visual, or recorded form. The act of creating such a work is referred to as authorship. Therefore, a sculptor, painter, or composer is considered the author of their respective sculptures, paintings, or musical compositions. Although in common usage, the term "author" is often associated specifically with the writer of a book, Article (publishing), article, Play (theatre), play, or other written work. In cases involving a work for hire, the employer or commissioning party is legally considered the author of the work, even if it was created by someone else. Typically, the first owner of a copyright is the creator of the copyrighted work, i.e., the author. If more than one person created the work, then joint authorship has taken place. Copyright laws differ around the world. The United States Copyright Office, for example, defines copyright as "a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornwall
Cornwall (; or ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is also one of the Celtic nations and the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, Devon to the east, and the English Channel to the south. The largest urban area is the Redruth and Camborne conurbation. The county is predominantly rural, with an area of and population of 568,210. After the Redruth-Camborne conurbation, the largest settlements are Falmouth, Cornwall, Falmouth, Penzance, Newquay, St Austell, and Truro. For Local government in England, local government purposes most of Cornwall is a Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area, with the Isles of Scilly governed by a Council of the Isles of Scilly, unique local authority. The Cornish nationalism, Cornish nationalist movement disputes the constitutional status of Cornwall and seeks greater autonomy within the United Kingdom. Cornwall is the weste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sam Slick
Sam Slick is a character created in 1835 by Thomas Chandler Haliburton, a Nova Scotian judge and author. With his wry wit and Yankee voice, Sam Slick of Slicksville put forward his views on "human nature" in a regular column in the '' Novascotian''. The twenty-one sketches were published in a collection entitled ''The Clockmaker or, also known as, the Sayings and Doings of Samuel Slick of Slicksville First Series'' in 1836 and supplemented by an additional 12 unpublished or new sketches. The book was Canada's first international bestseller and was hugely popular not only in Nova Scotia, but also in Britain and the United States. Slick’s wise-cracking commentary on the colonial life of Nova Scotia and relations with the U.S. and Britain struck a note with readers, which led to a second series in 1838 and a third in 1840. The satirical sketches, mocking both Canadians and Americans, made Haliburton one of the most popular writers of comic fiction in English of that era. '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the English overseas possessions, overseas possessions and trading posts established by Kingdom of England, England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries, and colonisation attempts by Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland during the 17th century. At its height in the 19th and early 20th centuries, it became the List of largest empires, largest empire in history and, for a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, Westminster system, its constitutional, Common law, legal, English language, linguistic, and Culture of the United Kingdom, cultural legacy is widespread. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novascotian
The ''Novascotian'' was a newspaper published in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada. It became one of the most influential voices in the British North American colonies in its nearly one century of existence. The paper was founded as the ''Nova Scotian'' or ''Colonial Herald'' by George R. Young, in 1824. Joseph Howe took control of it in 1827, establishing the paper's motto: "The free constitution which guards the British press." Published as a weekly, the paper played a key role in the intellectual and political life of Nova Scotia. A letter published in the ''Novascotian'' in 1835 led to charges of libel against Howe. When acquitted, he proclaimed: "the Press of Nova Scotia is free." With a circulation of 3000 subscribers, the ''Novascotian'' became the leading provincial newspaper in the 1840s. A well-known contributor was Thomas Chandler Haliburton, creator of the immensely popular character Sam Slick. Howe's entry into politics necessitated selling the paper. Nevertheles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova Scotia House Of Assembly
The Nova Scotia House of Assembly (; ), or Legislative Assembly, is the deliberative assembly of the General Assembly of Nova Scotia, and together with the lieutenant governor of Nova Scotia makes up the Nova Scotia Legislature. The assembly is the oldest in Canada, having first sat in 1758; in 1848, it was the site of the first responsible government in the British Empire. Bills passed by the House of Assembly are given royal assent by the lieutenant governor in the name of the King of Canada. Originally (in 1758), the Legislature consisted of the Crown represented by a governor (later a lieutenant governor), the appointed Nova Scotia Council holding both executive and legislative duties and an elected House of Assembly (lower chamber). In 1838, the council was replaced by an executive council with the executive function and a legislative council with the legislative functions based on the House of Lords. In 1928, the Legislative Council was abolished and the members pensio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annapolis County
Annapolis County is a county in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia located in the western part of the province located on the Bay of Fundy. The county seat is Annapolis Royal. History Established August 17, 1759, by Order in Council, Annapolis County took its name from the town of Annapolis Royal which had been named in honour of Anne, Queen of Great Britain. The town was the successor to the French settlement of Port Royal, the chief Acadian settlement in the area. The Acadians had been forcibly removed by British government officials in the 1755 Grand Dérangement. In 1817 the population of the county was 9,817, and that had grown to 14,661 by 1827. At that time, the county was divided into six townships: Annapolis, Granville, Wilmot, Clements, Digby and Clare. By 1833, a number of reasons had been advanced for making two counties out of Annapolis County. Two petitions were presented to the House of Assembly in that year requesting that the county be divided. However, it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annapolis Royal, Nova Scotia
Annapolis Royal is a town in and the county seat of Annapolis County, Nova Scotia, Canada. The community, known as Port Royal before 1710, is recognised as having one of the longest histories in North America, preceding the settlements at Plymouth, Jamestown and Quebec. For nearly 150 years, it served as the capital of Acadia and subsequently Nova Scotia until the establishment of Halifax in 1749. In 1605, France established a settlement on the Annapolis Basin, centred on the habitation at Port Royal. By 1629, British colonization of the Americas renewed the settlement, this time centred around Charles Fort, which is the site of the modern town. The settlement of Port Royal passed several times between France, England and Great Britain until it was finally ceded to Great Britain in 1713. Due to its location on the boundary between the colonial powers of France and Great Britain, it encountered a grand total of thirteen assaults, surpassing all other locations in North Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of King's College
The University of King's College is a public university, public Liberal arts college, liberal arts university in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Halifax, Nova Scotia.Roper, Henry. "Aspects of the History of a Loyalist College: King's College, Windsor, and Nova Scotian Higher Education in the Nineteenth Century." Anglican and Episcopal History 61 (1991). Established in 1789, it is the oldest chartered university in Canada, and the oldest English-speaking university in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth outside the United Kingdom. The university is regarded for its Foundation Year Program (FYP), an undergraduate curriculum designed to comprehensively study a variety of intellectual developments—past and present—through great books, great books and ideas. It is also known for its upper-year interdisciplinary programs, particularly in contemporary philosophy, contemporary studies, Early modern philosophy, early modern studies, and the history of science and technology. In addition, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant Governor
A lieutenant governor, lieutenant-governor, or vice governor is a high officer of state, whose precise role and rank vary by jurisdiction. Often a lieutenant governor is the deputy, or lieutenant, to or ranked under a governor — a "second-in-command", rather like deputy governor. In Canadian provinces and in the Dutch Caribbean, the lieutenant governor is the representative of the Monarchy in Canada, Canadian monarch or Monarchy of the Netherlands, Dutch monarch in that jurisdiction, and thus outranks the head of government, but for practical purposes has virtually no power. In India, lieutenant governors are in charge of union territories in that country. Lieutenant governor (United States), In the United States, lieutenant governors are usually second-in-command to a governor (United States), state governor, and the actual power held by the lieutenant governor varies greatly from state to state. The lieutenant governor is often first in line of succession to the governorship, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |