|
Thomas Gray (1788–1848)
Thomas Gray (1788–1848) was a British railway advocate. Thomas Gray spent most of his adult life promoting the idea of a passenger railway system for the UK and Europe. He wrote "Observations on a General Iron Railway" which was first published in 1820, followed by further, and expanded, editions up to 1825. Copies of the book are in the British Library and many more in UK and US libraries in differing editions. There was at least one US library that still offered it on loan to the general public in 2005. He was a contemporary of William James, the Stephensons and Isambard Kingdom Brunel, all considered by many to be "Fathers of the Railways". It is very likely, as indicated by the sequence of events after his first edition, that Gray's first published proposals directly and significantly influenced the writings and actions of William James and the Stephensons, among many others, when they began to design and build the earliest passenger railway system in Britain. Much as to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in railway track, tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel railway track, rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of land transport, next to road transport. It is used for about 8% of passenger and rail freight transport, freight transport globally, thanks to its Energy efficiency in transport, energy efficiency and potentially high-speed rail, high speed.Rolling stock on rails generally encounters lower friction, frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, allowing rail cars to be coupled into longer trains. Power is usually provided by Diesel locomotive, diesel or Electric locomotive, electric locomotives. While railway transport is capital intensity, capital-intensive and less flexible than road transport, it can carry heavy loads of passengers and cargo with greater energy efficiency and safety. Precursors of railways driven by human or an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William James (railway Promoter)
William James (13 June 1771 – 10 March 1837) was an English lawyer, surveyor, land agent and pioneer promoter of rail transport. According to his obituary "He was the original projector of the Liverpool & Manchester and other railways, and may with truth be considered as the father of the railway system, as he surveyed numerous lines at his own expense at a time when such an innovation was generally ridiculed." Life and career Early life William James was born in Henley-in-Arden in Warwickshire in 1771, the second of the seven children of William James, a solicitor from Moseley near Birmingham, and his wife Mary, who came from a wealthy and well-connected family in Kings Norton. The young James was educated at Warwick School, The King's School, Warwick (Now Warwick School); at another school in Winson Green, Birmingham and at Lincoln's Inn in London. After training and qualifying as a solicitor in Birmingham, he returned to Henley-in-Arden around 1797 to work in his father's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
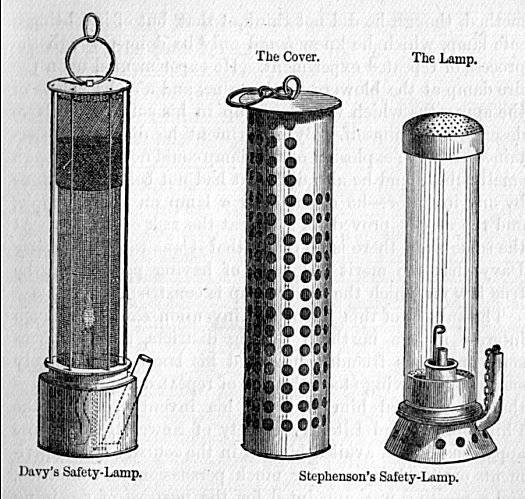
George Stephenson
George Stephenson (9 June 1781 – 12 August 1848) was an English civil engineer and Mechanical engineering, mechanical engineer during the Industrial Revolution. Renowned as the "Father of Railways", Stephenson was considered by the Victorian era, Victorians as a great example of diligent application and thirst for improvement. His chosen Track gauge#The Stockton and Darlington Railway, rail gauge, sometimes called "Stephenson gauge", was the basis for the standard gauge used by most of the world's railways. Pioneered by Stephenson, rail transport was one of the most important technological inventions of the 19th century and a key component of the Industrial Revolution. Built by George and his son Robert Stephenson, Robert's company Robert Stephenson and Company, the Locomotion No. 1, ''Locomotion'' No. 1 was the first steam locomotive to carry passengers on a public rail line, the Stockton and Darlington Railway in 1825. George also built the first public inter-city railway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isambard Kingdom Brunel
Isambard Kingdom Brunel ( ; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was an English civil engineer and mechanical engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history", "one of the 19th-century engineering giants", and "one of the greatest figures of the Industrial Revolution, hochanged the face of the English landscape with his groundbreaking designs and ingenious constructions". Brunel built dockyards, the Great Western Railway (GWR), a series of steamships including the first purpose-built transatlantic steamship, and numerous important bridges and tunnels. His designs revolutionised public transport and modern engineering. Though Brunel's projects were not always successful, they often contained innovative solutions to long-standing engineering problems. During his career, Brunel achieved many engineering firsts, including assisting his father in the building of the first tunnel under a navigable river (the River Thames) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brussels
Brussels, officially the Brussels-Capital Region, (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) is a Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium#Regions, region of Belgium comprising #Municipalities, 19 municipalities, including the City of Brussels, which is the capital of Belgium. The Brussels-Capital Region is located in the central portion of the country. It is a part of both the French Community of Belgium and the Flemish Community, and is separate from the Flemish Region (Flanders), within which it forms an enclave, and the Walloon Region (Wallonia), located less than to the south. Brussels grew from a small rural settlement on the river Senne (river), Senne to become an important city-region in Europe. Since the end of the Second World War, it has been a major centre for international politics and home to numerous international organisations, politicians, Diplomacy, diplomats and civil servants. Brussels is the ''de facto' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1788 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – The first edition of ''The Times'', previously ''The Daily Universal Register'', is published in London. * January 2 – Georgia ratifies the United States Constitution, and becomes the fourth U.S. state under the new government. * January 9 – Connecticut ratifies the United States Constitution, and becomes the fifth U.S. state. * January 18 – The leading ship (armed tender HMS ''Supply'') in Captain Arthur Phillip's First Fleet arrives at Botany Bay, to colonise Australia. * January 22 – The Congress of the Confederation, effectively a caretaker government until the United States Constitution can be ratified by at least nine of the 13 states, elects Cyrus Griffin as its last president.''Harper's Encyclopaedia of United States History from 458 A. D. to 1909'', ed. by Benson John Lossing and, Woodrow Wilson (Harper & Brothers, 1910) p167 * January 24 – The La Perouse expedition in the ''Astrolabe'' and '' Boussole'' arrives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1848 Deaths
1848 is historically famous for the wave of revolutions, a series of widespread struggles for more liberal governments, which broke out from Brazil to Hungary; although most failed in their immediate aims, they significantly altered the political and philosophical landscape and had major ramifications throughout the rest of the century. Ereignisblatt aus den revolutionären Märztagen 18.-19. März 1848 mit einer Barrikadenszene aus der Breiten Strasse, Berlin 01.jpg, Cheering revolutionaries in Berlin, on March 19, 1848, with the new flag of Germany Lar9 philippo 001z.jpg, French Revolution of 1848: Republican riots force King Louis-Philippe to abdicate Zeitgenössige Lithografie der Nationalversammlung in der Paulskirche.jpg, German National Assembly's meeting in St. Paul's Church Pákozdi csata.jpg, Battle of Pákozd in the Hungarian Revolution of 1848 Events January–March * January 3 – Joseph Jenkins Roberts is sworn in as the first president of the inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Railway Pioneers
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. * British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** British Isles, an island group ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** British Empire, a historical global colonial empire ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) * British Raj, colonial India under the British Empire * British Hong Kong, colonial H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |