|
Thomas Codrington (priest)
Thomas Codrington (died 1691?) was an English Roman Catholic theologian. He is chiefly known for his attempt to introduce into England the "Institute of Secular Priests Living in Community", founded in Bavaria by Bartholomaus Holzhauser. Life Codrington was educated and ordained at Douai, where he taught humanities for a time. Later on he lived with Cardinal Howard at Rome, acting as his chaplain and secretary. He returned to England in July, 1684, and on the accession of James II of England in the following year, he was appointed one of the royal chaplains and preachers in ordinary. While he was in Rome he had joined the institute above mentioned, in which Cardinal Howard took a great personal interest, and his return to England seemed to the superior, Stephen Hofer, a favourable opportunity for extending the institute. Accordingly Codrington and his companion, John Morgan, were appointed procurators to introduce the institute into England. The object of the society, the constit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of ancient Rome *''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter in the New Testament of the Christian Bible Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music *Romans (band), a Japanese pop group * ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 * ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *"Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television *Film Roman, an American animation studio * ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film * ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film * ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film * ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People * Roman (given name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters * Roman (surname), including a list of people named Roman or Romans *Ῥωμα� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany. With over 13 million inhabitants, it is second in population only to North Rhine-Westphalia, but due to its large size its population density is below the German average. Bavaria's main cities are Munich (its capital and largest city and also the third largest city in Germany), Nuremberg, and Augsburg. The history of Bavaria includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Raetia and Noricum. It became the Duchy of Bavaria (a stem duchy) in the 6th century AD following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. It was later incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartholomaus Holzhauser
Venerable Bartholomew Holzhauser (August 24, 1613 – May 20, 1658) was a German priest, a founder of a religious community, and a visionary and writer of prophecies. Early life Bartholomew Holzhauser was born in Laugna, into the family of Leonard and Catherine Holzhauser, who were poor, pious, and honest people. Leonard and Catherine had eleven children, including Bartholomew. Leonard Holzhauser practiced as a shoemaker. Young Bartholomew developed a great love for books and an earnest desire to enter the sacred ministry. At Augsburg, he was admitted to a free school for poor boys, earning his living by going from door to door singing and begging. He fell sick of an epidemic raging at that time. After his recovery, Bartholomew went home and for a time helped his father at work. Education He then continued his studies at Neuburg an der Donau and Ingolstadt, with the aid of kind friends and the Jesuits in particular. His teachers were unanimous in praising his tal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douai
Douai (, , ,; pcd, Doï; nl, Dowaai; formerly spelled Douay or Doway in English) is a city in the Nord département in northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department. Located on the river Scarpe some from Lille and from Arras, Douai is home to one of the region's most impressive belfries. History Its site probably corresponds to that of a 4th-century Roman fortress known as Duacum. From the 10th century, the town was a romance fiefdom of the counts of Flanders. The town became a flourishing textile market centre during the Middle Ages, historically known as Douay or Doway in English. In 1384, the county of Flanders passed into the domains of the Dukes of Burgundy and thence in 1477 into Habsburg possessions. In 1667, Douai was taken by the troops of Louis XIV of France, and by the 1668 Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle, the town was ceded to France. During successive sieges from 1710 to 1712, Douai was almost completely destroyed by the British Army. By 1713, the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James II Of England
James VII and II (14 October 1633 16 September 1701) was King of England and King of Ireland as James II, and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II, on 6 February 1685. He was deposed in the Glorious Revolution of 1688. He was the last Catholic monarch of England, Scotland, and Ireland. His reign is now remembered primarily for conflicts over religious tolerance, but it also involved struggles over the principles of absolutism and the divine right of kings. His deposition ended a century of political and civil strife in England by confirming the primacy of the English Parliament over the Crown. James succeeded to the thrones of England, Ireland, and Scotland following the death of his brother with widespread support in all three countries, largely because the principles of eligibility based on divine right and birth were widely accepted. Tolerance of his personal Catholicism did not extend to tolerance of Catholicism in general, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Innocent XI
Pope Innocent XI ( la, Innocentius XI; it, Innocenzo XI; 16 May 1611 – 12 August 1689), born Benedetto Odescalchi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 21 September 1676 to his death on August 12, 1689. Political and religious tensions with Louis XIV of France were a constant preoccupation for Innocent XI. Within the Papal States, he lowered taxes, produced a surplus in the papal budget and repudiated nepotism within the Church. Innocent XI was frugal in his governance of the Papal States, his methods evident in matters ranging from his manner of dress to a wide range of standards of personal behavior consistent with his conception of Christian values. Once he was elected to the papacy, he applied himself to moral and administrative reform of the Roman Curia. He abolished sinecures and pushed for greater simplicity in preaching as well as greater reverence in worship, requesting this of both the clergy and faithful. In consideration of his d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and VII of England and Scotland in November 1688, and his replacement by his daughter Mary II and her husband and James's nephew William III of Orange, de facto ruler of the Dutch Republic. A term first used by John Hampden in late 1689, it has been notable in the years since for having been described as the last successful invasion of England as well as an internal coup, with differing interpretations from the Dutch and English perspectives respectively. Despite his personal Catholicism, a religion opposed by the Protestant majority in England and Scotland, James became king in February 1685 with widespread support in both countries, since many feared that his exclusion would lead to a repetition of the 16391651 Wars of the Three Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
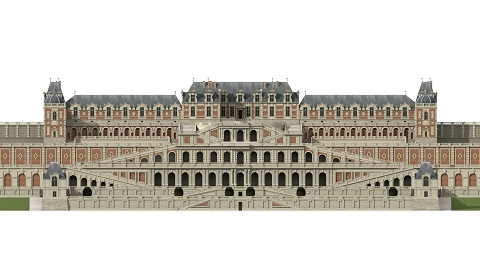
Château De Saint-Germain-en-Laye
The Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye () is a former royal palace in the commune of Saint-Germain-en-Laye, in the ''département'' of Yvelines, about 19 km west of Paris, France. Today, it houses the ''musée d'Archéologie nationale'' (National Museum of Archaeology). History 12th–13th centuries The first castle, named the ''Grand Châtelet'', was built on the site by Louis VI in 1124. The castle was expanded by Louis IX in the 1230s. Louis IX's chapelle Saint Louis at the castle belongs to the Rayonnant phase of French Gothic architecture. A 1238 charter of Louis IX instituting a regular religious service at the chapel is the first mention of a chapel having been built at the royal castle. This was a ''Sainte Chapelle'', to house a relic of the Crown of Thorns or the True Cross. Its plan and architecture prefigure the major Sainte-Chapelle which Saint Louis built within the Palais de la Cité at Paris between 1240 and 1248. Both buildings were built by Lou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Chapter
The Old Chapter was the body in effective control of the Roman Catholic Church in England from 1623 until an episcopal hierarchy was restored in 1850. Origin The origin of the body known as the Old Chapter, dates from 1623, when after a period of more than half a century during which there was no episcopal government in England, Dr. William Bishop was at length created vicar apostolic. He survived less than a year, but during this period he organized a form of Catholic ecclesiastical government, by means of archdeacons and rural deans, throughout the country. It continued in force with little change down to the re-establishment of the hierarchy.Ward, Bernard. "The Old Chapter." The Catholic Encyclopedia Vol. 11. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1911. 18 January 2019 An integral part of his sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonaventure Giffard
Bonaventure Giffard (1642–1734) was a Roman Catholic bishop who served as the Vicar Apostolic of the Midland District of England from 1687 to 1703 and Vicar Apostolic of the London District of England from 1703 to 1734. Life He was the second son of Andrew Giffard of Chillington, in the parish of Brewood, Staffordshire, by Catherine, daughter of Sir Walter Leveson, born at Wolverhampton in 1642. His father was slain in a skirmish near Wolverhampton early in the Civil War. The family still exists, and traces a pedigree without failure of heirs male from before the Conquest. Bonaventure was educated in the English College, Douai, and thence proceeded on 23 October 1667 to complete his ecclesiastical studies in Paris. He received the degree of D.D. in 1677 from the Sorbonne, having previously been ordained as a secular priest for the English mission. King James II soon after his accession made Giffard one of his chaplains and preachers. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1691 Deaths
Events January–March * January 6 – King William III of England, who rules Scotland and Ireland as well as being the Stadtholder of the Dutch Republic, departs from Margate to tend to the affairs of the Netherlands. * January 14 – A fleet of ships carrying 827 Spanish Navy sailors and marines arrives at Manzanillo Bay on the island of Hispaniola in what is now the Dominican Republic and joins 700 Spanish cavalry, then proceeds westward to invade the French side of the island in what is now Haiti. * January 15 – King Louis XIV of France issues an order specifically prohibiting play of games of chance, specifically naming basset and similar games, on penalty of 1,000 livres for the first offence. * January 23 – Spanish colonial administrator Domingo Terán de los Ríos, most recently the governor of Sonora y Sinaloa on the east side of the Gulf of California, is assigned by the Viceroy of New Spain to administer a new province that governs lands on both sides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |