|
Thomas Bendyshe
Thomas Bendyshe (1827–1886) was an English barrister and academic, known as a magazine proprietor and translator. Life He was the fourth son of John Bendyshe R.N. and his wife Catherine Matcham, a niece of Lord Nelson. He was educated at Eton College, and matriculated at King's College, Cambridge in 1845, graduating B.A. in 1849 and M.A. in 1852. Bendyshe was admitted to the Inner Temple in 1848, and was called to the bar in 1857. He became in 1846 a Fellow of King's College, a position he kept for the rest of his life. In college matters, Bendyshe as a Senior Fellow objected to financial reforms. Considered "eccentric", he obstructed them for nearly 20 years, and was the only Fellow to claim money in a compromise solution proposed by the Visitor. A settlement, the Eirenicon, emerged in 1872. The memoirs of Augustus Austen Leigh record Bendyshe's 1870 effort to retain the right to dine separately in the college hall. According to Montague Rhodes James, Richard Okes, Provost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Nelson
Vice-Admiral Horatio Nelson, 1st Viscount Nelson, 1st Duke of Bronte (29 September 1758 – 21 October 1805) was a British flag officer in the Royal Navy. His inspirational leadership, grasp of strategy, and unconventional tactics brought about a number of decisive British naval victories during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest naval commanders in history. Nelson was born into a moderately prosperous Norfolk family and joined the navy through the influence of his uncle, Maurice Suckling, a high-ranking naval officer. Nelson rose rapidly through the ranks and served with leading naval commanders of the period before obtaining his own command at the age of 20, in 1778. He developed a reputation for personal valour and firm grasp of tactics, but suffered periods of illness and unemployment after the end of the American War of Independence. The outbreak of the French Revolutionary Wars allowed Nelson to return to servic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X Club
The X Club was a dining club of nine men who supported the theories of natural selection and academic liberalism in late 19th-century England. Thomas Henry Huxley was the initiator; he called the first meeting for 3 November 1864. The club met in London once a month—except in July, August and September—from November 1864 until March 1893, and its members are believed to have wielded much influence over scientific thought. The members of the club were George Busk, Edward Frankland, Thomas Archer Hirst, Joseph Dalton Hooker, Thomas Henry Huxley, John Lubbock, Herbert Spencer, William Spottiswoode, and John Tyndall, united by a "devotion to science, pure and free, untrammelled by religious dogmas." The nine men who would compose the X Club already knew each other well. By the 1860s, friendships had turned the group into a social network, and the men often dined and went on holidays together. After Charles Darwin's ''On the Origin of Species'' was published in 1859, the men b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Pierre Flourens
Marie Jean Pierre Flourens (13 April 1794 – 6 December 1867), father of Gustave Flourens, was a French physiologist, the founder of experimental brain science, and a pioneer in anesthesia. Biography Flourens was born at Maureilhan, near Béziers, in the ''département'' of Hérault. At fifteen he began studying medicine at Montpellier, where he received the degree of doctor in 1813. In the following year he went to Paris, carrying an introduction from A. P. de Candolle, the botanist, to Georges Cuvier, who received him kindly, and took an interest in him. In Paris, Flourens engaged in physiological research, occasionally contributing to publications; and, in 1821, at the Athénée, he gave a course of lectures on the physiological theory of the sensations, which attracted much attention amongst men of science. In 1815, Flourens pioneered the experimental method of carrying out localized lesions of the brain in living rabbits and pigeons and carefully observing their effects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Friedrich Heinrich Marx
Karl Friedrich Heinrich Marx (10 March 1796 – 2 October 1877) was a German physician and college lecturer. He was not related to Karl Marx, the founder of Marxism. Life and works Marx was born on 10 March 1796 in Karlsruhe, the son of a Jewish antiquarian, and attended the Karlsruhe Lyceum, where he was taught by Johann Peter Hebel and Karl Christian Gmelin. In 1813 he began studies in philosophy and medicine in Heidelberg, where, in 1817, he participated in the Old Heidelberg ''Burschenschaft'' as a friend of Heinrich Carl Alexander Pagenstecher. He had contacts with Jean Paul and attended ''inter alia'' lectures by Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, becoming a follower of his. In 1817 he completed his studies and, in 1818, passed his exams with distinction. For his work on the subject, ''Die Struktur und das Leben der Venen'' he was awarded a prize by the university. In 1818, he probably participated in the founding of the first Freiburg ''Burschenschaft'', having been in Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Friedrich Blumenbach
Johann Friedrich Blumenbach (11 May 1752 – 22 January 1840) was a German physician, naturalist, physiologist, and anthropologist. He is considered to be a main founder of zoology and anthropology as comparative, scientific disciplines. He was also important as a race theorist. He was one of the first to explore the study of the human being as an aspect of natural history. His teachings in comparative anatomy were applied to his classification of human races, of which he claimed there were five, Caucasian, Mongolian, Malayan, Ethiopian, and American. He was a member of what modern historians call the Göttingen School of History. Blumenbach's peers considered him one of the great theorists of his day, and he was a mentor or influence on many of the next generation of German biologists, including Alexander von Humboldt. Early life and education Blumenbach was born at his family house in Gotha. His father was Heinrich Blumenbach, a local school headmaster; his mother wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippolyte Fauche
In Classical Greek mythology, Hippolyta, or Hippolyte (; grc-gre, Ἱππολύτη ''Hippolytē'') was a daughter of Ares and Otrera, queen of the Amazons, and a sister of Antiope and Melanippe. She wore her father Ares' ''zoster'', the Greek word found in the Iliad and elsewhere meaning "war belt." Some traditional English translations have preferred the more feminine-sounding "girdle." Hippolyta figures prominently in the myths of both Heracles and Theseus. The myths about her are varied enough that they may therefore be about several different women. The name ''Hippolyta'' comes from Greek roots meaning "horse" and "let loose." Legends Ninth Labor of Heracles In the myth of Heracles, Hippolyta's belt (ζωστὴρ Ἱππολύτης) was the object of his ninth labour. He was sent to retrieve it for Admete, the daughter of King Eurystheus.Hyginus, ''Fabulae'', 30 Most versions of the myth indicate that Hippolyta was so impressed with Heracles that she gave him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the '' Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the Kurukshetra War and the fates of the Kaurava and the Pāṇḍava princes and their successors. It also contains philosophical and devotional material, such as a discussion of the four "goals of life" or ''puruṣārtha'' (12.161). Among the principal works and stories in the ''Mahābhārata'' are the ''Bhagavad Gita'', the story of Damayanti, the story of Shakuntala, the story of Pururava and Urvashi, the story of Savitri and Satyavan, the story of Kacha and Devayani, the story of Rishyasringa and an abbreviated version of the '' Rāmāyaṇa'', often considered as works in their own right. Traditionally, the authorship of the ''Mahābhārata'' is attributed to Vyāsa. There have been many attempts to unravel its historical growth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Cannibal Club
The Cannibal Club was a Victorian dining club associated with the Anthropological Society of London, likely founded at the same time in 1863 by Sir Richard Francis Burton and Dr James Hunt. The club met in Bartolini's dining rooms near Fleet Street, London. Its official symbol was a mace carved to look like an African head gnawing on a human thighbone. The club's name is thought to derive from Burton's interest in cannibalism which he regretted that he never witnessed on his travels.Lovell, p. 413 Club members included: Richard Monkton Milnes, Charles Bradlaugh, Thomas Bendyshe, Algernon Swinburne, Sir James Plaisted Wilde, General Studholme John Hodgson and Charles Duncan Cameron. In his biography of Burton, Dane Kennedy suggests that "the very name of the new club signaled the determination of its organizers to create an atmosphere where subjects deemed deviant by society could receive an open airing" and to liberate its participants from "the sober, 'scientific' etiquette tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Burton
Richard Burton (; born Richard Walter Jenkins Jr.; 10 November 1925 – 5 August 1984) was a Welsh actor. Noted for his baritone voice, Burton established himself as a formidable Shakespearean actor in the 1950s, and he gave a memorable performance of Hamlet in 1964. He was called "the natural successor to Olivier" by critic Kenneth Tynan. A heavy drinker, Burton's perceived failure to live up to those expectations disappointed some critics and colleagues and added to his image as a great performer who had wasted his talent. Nevertheless, he is widely regarded as one of the most acclaimed actors of his generation. Burton was nominated for an Academy Award seven times, but never won an Oscar. He was a recipient of BAFTAs, Golden Globes, and Tony Awards for Best Actor. In the mid-1960s, Burton ascended into the ranks of the top box office stars. By the late 1960s, Burton was one of the highest-paid actors in the world, receiving fees of $1 million or more plus a share of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmund Gosse
Sir Edmund William Gosse (; 21 September 184916 May 1928) was an English poet, author and critic. He was strictly brought up in a small Protestant sect, the Plymouth Brethren, but broke away sharply from that faith. His account of his childhood in the book ''Father and Son'' has been described as the first psychological biography. His friendship with the sculptor Hamo Thornycroft inspired a successful career as a historian of late-Victorian sculpture. His translations of Henrik Ibsen helped to promote that playwright in England, and he encouraged the careers of W. B. Yeats and James Joyce. He also lectured in English literature at Cambridge University. Early life Gosse was the son of Philip Henry Gosse and Emily Bowes. His father was a naturalist and his mother an illustrator who published a number of books of poetry. Both were deeply committed to a small Protestant sect, the Plymouth Brethren. His childhood was initially happy as they spent their summers in Devon where hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Gordon Latham
Robert Gordon Latham FRS (24 March 1812 – 9 March 1888) was an English ethnologist and philologist. Early life The eldest son of Thomas Latham, vicar of Billingborough, Lincolnshire, he was born there on 24 March 1812. He entered Eton College in 1819, and in 1829 went on to King's College, Cambridge, where he graduated B.A. in 1832, and was soon afterwards elected a Fellow. Philologist Latham studied philology for a year on the continent, near Hamburg, then in Copenhagen with Rasmus Christian Rask, and finally in Christiania (now Oslo). In Norway he knew Ludvig Kristensen Daa and Henrik Wergeland; he wrote about the country in ''Norway and the Norwegians'' (1840). In 1839 he was elected professor of English language and literature in University College, London. Here he associated with Thomas Hewitt Key and Henry Malden, linguists working in the tradition of Friedrich August Rosen. Together they developed the Philological Society, expanding it from a student group to a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservative Club
The Association of Conservative Clubs is an organisation associated with the Conservative Party in the United Kingdom. It represents and provides support to the largest association of political clubs in the country estimated at 1,100. The Association of Conservative Clubs was formed in 1894. Its objects are to assist and encourage the formation of clubs and to support the principles of Conservatism and aims of the Conservative Party. From 1895 to 1941, the association published ''The Clubman''. It was succeeded by ''Conservative Clubs' Gazette'' and ''Conservative Clubs' Magazine''. Such clubs can vary from Conservative working men's clubs to more prestigious clubs known as ''constitutional clubs''. Significantly, constitutional clubs are under no obligation to contribute to Conservative Party funds. Reflecting the dual origins of the modern Conservative and Unionist Party, some affiliates are called ''unionist clubs''. They may also be known as Beaconsfield clubs (after Benjam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




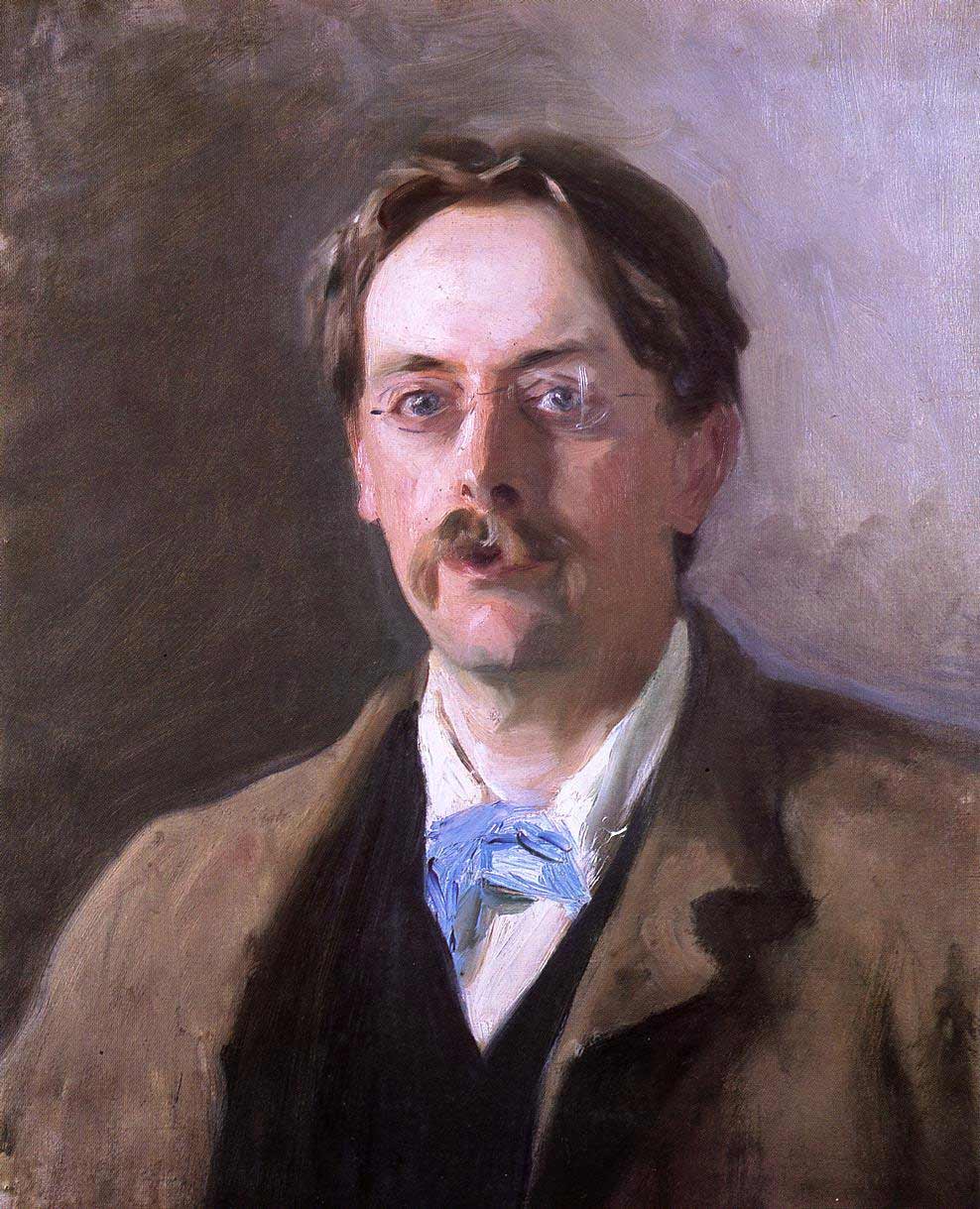

_002.jpg)