|
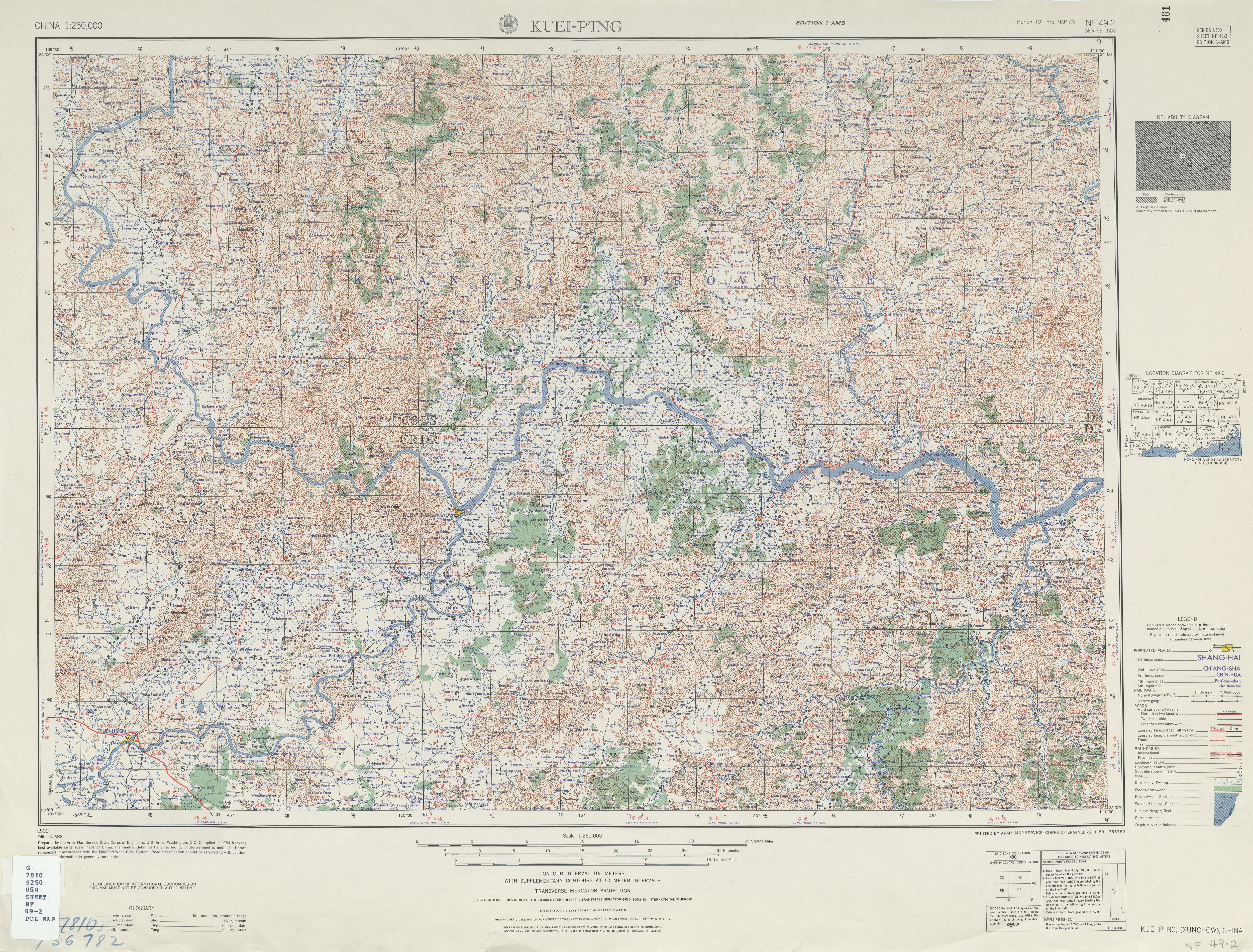
Thistle Mountain
The Thistle Mountains () are a mountain range in Guangxi, China that is part of the Dayao Mountains ( :zh:大瑤山). They are mostly concentrated in Guiping County. In the 1840s the area was the primary base of the God Worshipping Society, which eventually launched the Taiping Rebellion against the Qing dynasty The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak .... References Landforms of Guangxi Mountain ranges of China {{Guangxi-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Redbud
''Cercis chinensis'', the Chinese redbud, () is a plant in the legume the family Fabaceae. It is endemic to China, where it grows in southern and north-central China and Manchuria. Description As a tree, the Chinese redbud may grow up to tall with a trunk diameter of up to , however, the species is normally found growing in shrub form. The flowers are pink or milky white in color whilst the leaf body is almost circular in shape, in length and tapers to a point at the end. Flowering in April, the Chinese redbud produces fruit in October. The Chinese cercis (Cercis chinensis) Bunge is a native of China and a member of the Fabaceae family, which is extensively dispersed there. Its many parts can be utilized for traditional Chinese medicine, which dates back a long way, in addition to its high beauty value. Cultivation Although hardy, in cultivation this plant requires a sheltered spot in a southerly or westerly aspect, with damp well-drained soil. The following cultivars hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangxi
Guangxi (; ; alternately romanized as Kwanghsi; ; za, Gvangjsih, italics=yes), officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (GZAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China, located in South China and bordering Vietnam ( Hà Giang, Cao Bằng, Lạng Sơn, and Quảng Ninh Provinces) and the Gulf of Tonkin. Formerly a province, Guangxi became an autonomous region in 1958. Its current capital is Nanning. Guangxi's location, in mountainous terrain in the far south of China, has placed it on the frontier of Chinese civilization throughout much of Chinese history. The current name "Guang" means "expanse" and has been associated with the region since the creation of Guang Prefecture in 226 AD. It was given provincial level status during the Yuan dynasty, but even into the 20th century, it was considered an open, wild territory. The abbreviation of the region is "" (Hanyu pinyin: ; Zhuang: ), which comes from the name of the city of Guilin, the provin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land, the List of countries and territories by land borders, most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces of China, provinces, five autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, four direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and two special administrative regions of China, Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the List of cities in China by population, most populous cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dayao Mountains
Dayao County (; Chuxiong Yi script: , IPA:) is a county of north-central Yunnan province, People's Republic of China, under the administration of Chuxiong Yi Autonomous Prefecture. Administrative divisions Dayao County has 8 towns, 3 townships and 1 ethnic township. ;8 towns ;3 townships * Tanhua () * Tiesuo () * Santai Santai County ( zh, t=三台縣, s=三台县, w=San1-t῾ai2 Hsien4, p=Sāntái Xiàn; formerly known as Tungchwanfu) is a county under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Mianyang, in the northeast of Sichuan Province of China. ... () ;1 ethnic township * Wanbi Dai and Lisu () Ethnic groups The ''Dayao County Gazetteer'' (1999:780) lists the following Yi subgroups. *''Luoluopu'' 罗罗濮 dialect (spoken in the northwest hill districts) **Luoluopu 罗罗濮 **Laluobo 腊罗拨 **Popei 婆胚 *''Lipu'' 俚濮 dialect: (spoken in the Qingling River 蜻蛉河 and Yipao River 一泡江 watersheds) **Lipu 俚濮 **Machipu 骂池濮 **Ges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guiping County
Guiping () is a county-level city in eastern Guangxi, China. It is under the administration of Guigang City, located at the confluence of the Qian and Yu rivers, which are the Xi River's primary north and south tributaries, respectively. Names Guiping was formerly known as Xunzhou. From 1855 to 1861 it was the capital of the rebel state of Da Cheng and was called ''Xiujing''. Geography and climate Guiping has a monsoon-influenced humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cfa''), with short, mild winters, and long, hot, humid summers. Winter begins dry but becomes progressively wetter and cloudier. Spring is generally overcast and often rainy, while summer continues to be rainy though it is the sunniest time of year. Autumn is sunny and dry. The monthly 24-hour average temperature ranges from in January to in July, and the annual mean is . The annual rainfall is around , and is delivered in bulk (~46%) from May to July, when the plum rains occur and often create the risk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
God Worshipping Society
The God Worshipping Society, in its literal translation Emperor Worshipping Society (), was a religious movement founded and led by Hong Xiuquan which drew on his own unique interpretation of Protestant Christianity and combined it with Chinese folk religion, based on the faith in Shangdi (the Emperor), and other religious traditions. According to historical evidence, his first contact with Christian pamphlets occurred in 1836 when he directly received American Congregationalist missionary Edwin Stevens' personal copy of the ''Good Words to Admonish the Age'' (by Liang Fa, 1832). He only briefly looked over and did not carefully examine it. Subsequently, Hong claimed to have experienced mystical visions in the wake of his third failure of the imperial examinations in 1837 and after failing for a fourth time in 1843, he sat down to carefully examine the tracts with his distant cousin Feng Yunshan, believing that they were "the key to interpreting his visions" coming to the conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiping Rebellion
The Taiping Rebellion, also known as the Taiping Civil War or the Taiping Revolution, was a massive rebellion and civil war that was waged in China between the Manchu-led Qing dynasty and the Han, Hakka-led Taiping Heavenly Kingdom. It lasted from 1850 to 1864, although following the fall of Tianjing (now Nanjing) the last rebel army was not wiped out until August 1871. After fighting the bloodiest civil war in world history, with over 20 million dead, the established Qing government won decisively, although at a great price to its fiscal and political structure. The uprising was commanded by Hong Xiuquan, an ethnic Hakka (a Han subgroup) and the self-proclaimed brother of Jesus Christ. Its goals were religious, nationalist, and political in nature; Hong sought the conversion of the Han people to the Taiping's syncretic version of Christianity, to overthrow the Qing dynasty, and a state transformation. Rather than supplanting the ruling class, the Taipings sought to upen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria (modern-day Northeast China and Outer Manchuria). It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Guangxi
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)