|
Thiosulfate Complex
A transition metal thiosulfate complex is a coordination complex containing one or more thiosulfate ligands. Thiosulfate occurs in nature and is used industrially, so its interactions with metal ions are of some practical interest. Examples Thiosulfate is a potent ligand for HSAB theory, soft metal ions. A typical complex is , which features a pair of S-bonded thiosulfate ligands. Simple aquo and ammine complexes are also known. Three binding modes are common: monodentate (κ1-), ''O'',''S''-bidentate (κ2-), and bridging ligand, bridging (μ-). Linkage isomerism (O vs S) has been observed in . Preparation Typically, thiosulfate complexes are prepared from thiosulfate salts by displacement of aquo or chloro ligands. In some cases, they arise by oxidation of polysulfido complexes, or by binding of sulfur trioxide to sulfido ligands. Applications Photography Silver-thiosulfate complexes are produced by common photographic fixers. By dissolving silver halides, the fixer stabilises ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Complex
A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of chemical bond, bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing chemical compound, compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the periodic table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A Ligand#Polydentate and polyhapto ligand motifs and nomenclature, polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal, a group 11 element, and one of the noble metals. It is one of the least reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemical elements, being the second-lowest in the reactivity series. It is solid under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental (native state (metallurgy), native state), as gold nugget, nuggets or grains, in rock (geology), rocks, vein (geology), veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as in electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Complexes
A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the periodic table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Chemistry
A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of chemical bond, bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing chemical compound, compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the periodic table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A Ligand#Polydentate and polyhapto ligand motifs and nomenclature, polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUPAC Red Book
Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry, IUPAC Recommendations 2005 is the 2005 version of ''Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry'' (which is informally called the Red Book). It is a collection of rules for naming inorganic compounds, as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). Summary The 2005 edition replaces their previous recommendations ''Nomenclature The Red Book of Inorganic Chemistry, IUPAC Recommendations 1990 (Red Book I)'', and "where appropriate" (sic) ''Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry II, IUPAC Recommendations 2000 (Red Book II)''. The recommendations take up over 300 pages''Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry IUPAC Recommendations'' 2005 ed. N. G. Connelly et al. RSC Publishing https://iupac.org/what-we-do/books/redbook/ and the full text can be downloaded from IUPAC. Corrections have been issued. Apart from a reorganisation of the content, there is a new section on organometallics and a formal element list to be used in place o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activated Carbon
Activated carbon, also called activated charcoal, is a form of carbon commonly used to filter contaminants from water and air, among many other uses. It is processed (activated) to have small, low-volume pores that greatly increase the surface area available for ''adsorption '' or chemical reactions. (Adsorption, not to be confused with Absorption (chemistry), absorption, is a process where atoms or molecules adhere to a surface). The pores can be thought of as a microscopic "sponge" structure. Activation is analogous to making popcorn from dried corn kernels: popcorn is light, fluffy, and its kernels have a high surface-area-to-volume ratio. ''Activated'' is sometimes replaced by ''active''. Because it is so porous on a microscopic scale, one gram of activated carbon has a surface area of over , as determined by gas absorption and its porosity can run 10ML/day in terms of treated water per gram. Researchers at Cornell University synthesized an ultrahigh surface area activated ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adsorb
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. This process creates a film of the ''adsorbate'' on the surface of the ''adsorbent''. This process differs from absorption, in which a fluid (the ''absorbate'') is dissolved by or permeates a liquid or solid (the ''absorbent''). While adsorption does often precede absorption, which involves the transfer of the absorbate into the volume of the absorbent material, alternatively, adsorption is distinctly a surface phenomenon, wherein the adsorbate does not penetrate through the material surface and into the bulk of the adsorbent. The term '' sorption'' encompasses both adsorption and absorption, and ''desorption'' is the reverse of sorption. Like surface tension, adsorption is a consequence of surface energy. In a bulk material, all the bonding requirements (be they ionic, covalent or metallic) of the constituent atoms of the material are fulfilled by other atoms i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
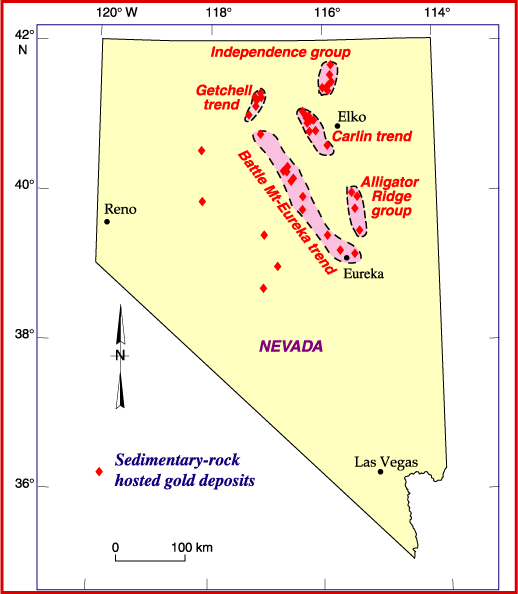
Carlin–type Gold Deposit
Carlin–type gold deposits are sediment-hosted disseminated gold deposits. These deposits are characterized by invisible (typically microscopic and/or dissolved) gold in pyrite, arsenic rich pyrite and arsenopyrite. This dissolved kind of gold is called "invisible gold", as it can only be found through chemical analysis. The deposit is named after the Carlin mine, the first large deposit of this type discovered in the Carlin Trend, Nevada. Geology The Carlin type deposits show enrichment in the elements gold, arsenic, antimony, mercury (element), mercury, thallium and barium. This enrichment is created by hydrothermal circulation with a temperature of up to 300 °C. The underlying rocks out of which the minerals are dissolved are normally silty Carbonate rock, carbonates, although Silicate mineral, silicates and other sediments are possible. The source of the heating for the water in the hydrothermal circulation is still under discussion. The material in the deposit is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 electrons. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three Isotopes of carbon, isotopes occur naturally, carbon-12, C and carbon-13, C being stable, while carbon-14, C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of 5,700 years. Carbon is one of the timeline of chemical element discoveries#Pre-modern and early modern discoveries, few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th abundance of elements in Earth's crust, most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the abundance of the chemical elements, fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon's abundance, its unique diversity of organic compounds, and its unusual abi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold Cyanidation
Gold cyanidation (also known as the cyanide process or the MacArthur–Forrest process) is a hydrometallurgical technique for extracting gold from low-grade ore through conversion to a water-soluble coordination complex. It is the most commonly used leaching process for gold extraction. Cyanidation is also widely used in silver extraction, usually after froth flotation. Production of reagents for mineral processing to recover gold represents 70% of cyanide consumption globally. While other metals, such as copper, zinc, and silver, are also recovered using cyanide, gold remains the primary driver of this technology. The highly toxic nature of cyanide has led to controversy regarding its use in gold mining, with it being banned in some parts of the world. However, when used with appropriate safety measures, cyanide can be safely employed in gold extraction processes. One critical factor in its safe use is maintaining an alkaline pH level above 10.5, which is typically controlle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractory
In materials science, a refractory (or refractory material) is a material that is resistant to decomposition by heat or chemical attack and that retains its strength and rigidity at high temperatures. They are inorganic, non-metallic compounds that may be porous or non-porous, and their crystallinity varies widely: they may be crystalline, polycrystalline, amorphous, or composite. They are typically composed of oxides, carbides or nitrides of the following elements: silicon, aluminium, magnesium, calcium, boron, chromium and zirconium. Many refractories are ceramics, but some such as graphite are not, and some ceramics such as clay pottery are not considered refractory. Refractories are distinguished from the '' refractory metals'', which are elemental metals and their alloys that have high melting temperatures. Refractories are defined by ASTM C71 as "non-metallic materials having those chemical and physical properties that make them applicable for structures, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Aurothiosulfate
Sodium aurothiosulfate, or sanocrysin, is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is the trisodium salt of the coordination complex of gold(I), . The dihydrate, which is colorless, crystallizes with two waters of crystallization. The compound has some medicinal properties as well as potential for hydrometallurgy. Structure left, X-ray crystallographic structure of . Color code: red = O, orange = Au, yellow = S, violet = Na. Hydrogen atoms are omitted. The anionic complex features a linear AuS2 core and is overall centrosymmetric. Like most other thiosulfate complexes, only the planetary sulfur of thiosulfate is coordinated to the metal. History The salt is typically prepared by reduction of gold(III) chloride with thiosulfate: : The compound was first synthesized in 1845 by Mathurin-Joseph Fordos and A. Gélis who were researching chemicals used in the Daguerrotype photographic process. It then came to be called Fordos and Gélis salt. It went out of interest u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |